 MiCOM P139 is a cost-effective one-box solution for integrated numerical time-overcurrent protection and control. The unit’s protection functions provide selective short-circuit protection, ground fault protection and overload protection in medium- and high voltage systems. The systems can be operated as solidlygrounded, low-impedance-grounded, resonantgrounded or isolated-neutral systems.
MiCOM P139 is a cost-effective one-box solution for integrated numerical time-overcurrent protection and control. The unit’s protection functions provide selective short-circuit protection, ground fault protection and overload protection in medium- and high voltage systems. The systems can be operated as solidlygrounded, low-impedance-grounded, resonantgrounded or isolated-neutral systems.
The multitude of protection functions incorporated into the unit enable the user to cover a wide range of applications in the protection of cable and line sections, transformers and motors. For easy adaptation to varying system operation conditions four independent parameter subsets are provided.
The control functions are designed for the control of up to six electrically operated switchgear units equipped with electrical check-back signaling located in the bay of a medium-voltage substation or a non-complex high-voltage station. For the selection of the bay type the P139 is provided with over 250 predefined bay types and allows download of customized bay type.
External auxiliary devices are largely obviated through the integration of binary inputs and power outputs that are independent of auxiliary voltages, by the direct connection option for current and voltage transformers and by the comprehensive interlocking capability.
During operation, the user-friendly interface facilitates setting of the unit and promotes safe operation of the substation by preventing nonpermissible switching operations. The P139 provides a extensive number of protection and control functions which can select individually for inclusion in the unit’s configuration or cancel them as desired. By means of a straightforward configuration procedure, the user can adapt the device flexibly to the scope of protection required in each particular application.
Due to the powerful, freely configurable logic of the device, special applications can be accommodated.
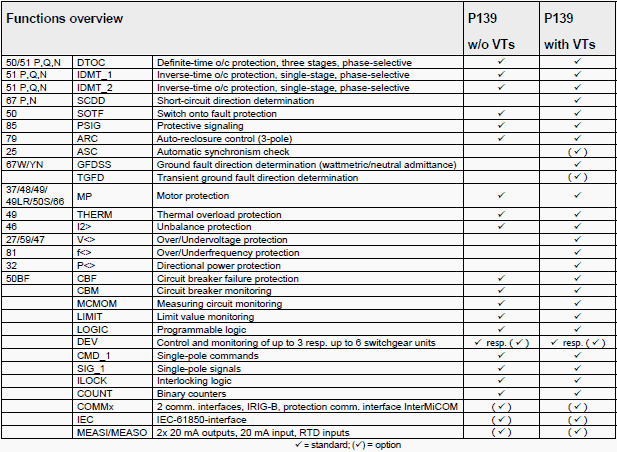
Functions Overview
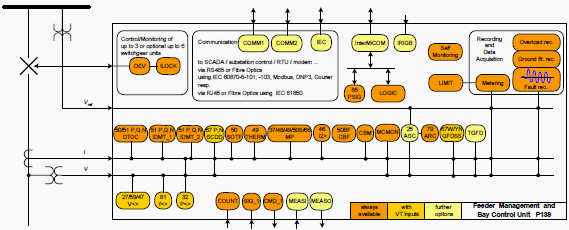
The P139 is of modular design. The pluggable modules are housed in a robust aluminum case and electrically connected via an analog and a digital bus printed circuit board.
The following global functions are available.
Global Functions
- Parameter subset selection
- Operating data recording
(time-tagged signal logging) - Overload data acquisition
- Overload recording
(time-tagged signal logging) - Ground fault data acquisition
- Ground fault recording
(time-tagged signal logging) - Measured fault data
- Fault recording
(time-tagged signal logging together with fault value recording of the three phase currents, the residual current, the three phase-to-ground voltages and the neutral displacement voltage).
The P139 has the following inputs and outputs:
I/O
- 4 current-measuring inputs
- 4 or 5 voltage-measuring inputs
- 6 (12) binary signal inputs (optical couplers) and 6 (12) output relays for the control of 3 (6) switchgear units (2-pole contacts).
- Up to 34 additional binary signal inputs (optical couplers) with freely configurable function assignment for individual control or protection signals
- Up to 14 additional output relays with freely configurable function assignment for individual control or protection applications
- Optional up to 16 high break output relays applicable for DC circuits with max. 2500 W inductive (L/R = 40 ms) or 10 A at 250 VDC
The maximum configuration of binary inputs and outputs provide the signaling of 10 switchgear units whereas 6 of them are controllable. The nominal currents or the nominal voltages, respectively, of the measuring inputs can be set with the help of function parameters.
Optional current and voltage measuring inputs for the connection to non-conventional instrument transformers (NCIT) can be used.
The nominal voltage range of the optical coupler inputs is 24 to 250 V DC without internal switching. Optional there are also other ranges with higher pick-up thresholds possible. The auxiliary voltage input for the power supply is a wide-range design as well. The nominal voltage ranges are 48 to 250 V DC and 100 to 230 V AC.
An additional version is available for the lower nominal voltage range of 24 V DC. All output relays are suitable for both signals and commands.
The optional resistance temperature detector (RTD) inputs are lead compensated and balanced. The optional 0 to 20 mA input provides open-circuit and overload monitoring, zero suppression defined by a setting, plus the option of linearizing the input variable via 20 adjustable interpolation points. Two freely selected measured signals (cyclically updated measured operating data and stored measured fault data) can be output as a loadindependent direct current via the two optional 0 to 20 mA outputs.
The characteristics are defined via 3 adjustable interpolation points allowing a minimum output current (4 mA, for example) for receiver-side open-circuit monitoring, knee-point definition for fine scaling and a limitation to lower nominal currents (10 mA, for example).
Information interface

Information exchange is done via the local control panel, the PC interface and 2 optional communication interfaces.
The first communication interface has settable protocols conforming to IEC 60870-5-103, IEC 60870-5-101, DNP 3.0, Modbus and Courier (COMM1) or provides alternatively protocol conforming to IEC 61850 (IEC). It’s intended for
integration with substation control systems.
The 2nd communication interface (COMM2) conforms to IEC 60870-5-103 and is intended for remote setting access only. Additionally, the optional InterMiCOM interface (COMM 3) allows a direct transfer of any digital status information between two devices.
Clock synchronization can be achieved using one of the protocols or using the IRIG-B signal input.











Thanks for newsletter
hi.i need help.
i have a micom p139 feeder manager for transformator ,when measured current is up to 150 ampers that shows: “not measured”.why?
Hi,
U must configured the seeting in Micom P139
BR
For those who don’t know, MiCOM is an ex AREVA protection and control relay, and now is Schneider Electric, since Schneider Electric bought AREVA MV switchgears, transformers and protection relays up to 52kV.
hello Eng. how are you can you help me the password for micom areva P 139?