Selection of rated circuit breaker
The general procedure for the selection of correctly rated circuit breaker follows the following scheme of seven major questions you should answer.

Let’s see the major questions:
- What is the task of the branch circuit or feeder?
- Which rated current / setting range?
- Breaking/making capacities / rated operational voltage?
- Any special requirements?
- Which type of co-ordination?
- What is the mode of mounting?
- Cross-section of the connecting wire/cable?
1. What is the task of the branch circuit or feeder?
Will it be used for the protection of connecting leads, protection of installation, group-protection or motor protection? Select the appropriate circuit breaker type, with or without the thermal overload protection. Decide which type of protective characteristic (cable or motor protection).
Go back to CB Selection Tips ↑
2. Which rated current / setting range?
Do the setting ranges of the thermal and the magnetic release cover the requirements of the particular application (protection of transformer or generator)?
The setting ranges of the various sizes of circuit breakers are overlapping. The same current settings may be partly covered by more than one size of circuit breakers (as for example 80 A setting can be covered by two or more CB sizes, 100A or 125A).
The following features depend on the size of the circuit breakers:
- Accessories (as for example types and numbers of auxiliary contacts),
- Mode of operation (toggle or rotating handle),
- Mode of mounting (snap-on or screw mounting) or
- The electrical characteristics (breaking capacity, selectivity etc.).
Go back to CB Selection Tips ↑
3. Breaking / making capacities / rated operational voltage?
- Where is the point of installation of the circuit breaker?
- What is the expected magnitude of the prospective short-circuit current at that location?
- Is a lower making/breaking capacity acceptable (appreciable reduction of the short-circuit current due to long connecting leads or due to other short circuit protective devices connected upstream)?
- Is the breaking capacity reduced due to higher rated operational voltage (as for example >400 V)?
- Does it indicate a selection on the basis of Icu (rated ultimate short-circuit breaking capacity, reduced functional capability after the interruption of a short-circuit) or on the basis of Ics (rated service short-circuit breaking capacity, full functional capability after the interruption of the short-circuit)?
- With the help of an efficient group-protection, can smaller and less expensive circuit breakers be utilised?
Go back to CB Selection Tips ↑
4. Any special requirements?
Must reduction factors for the rated current be taken into account due to: ambient air temperature (>40…60 °), altitude of the site of installation (>2000 m above m.s.l), higher supply frequency (>400 Hz)?
Go back to CB Selection Tips ↑
5. Which type of co-ordination?
Selection of the downstream contactor in accordance with the type of co-ordination type “1” or type “2”?
Go back to CB Selection Tips ↑
6. What is the mode of mounting?
Deciding factor for the supporting/adapter plates of the modular mounting system (suitability for the selected type of circuit breaker).


Go back to CB Selection Tips ↑
7. Cross-section of the connecting wire/cable?
The cross-section of the connecting leads to the motors are to be selected on the basis of the current setting of the thermal overload release of the circuit breaker. Eventually, the maximum permissible length of the connection is to be considered (shock hazard due to touch potential in the case of a short-circuit).
Go back to CB Selection Tips ↑
Circuit breaker rating plate //
Standardized characteristics indicated on the rating plate of Compact NSX circuit breaker:
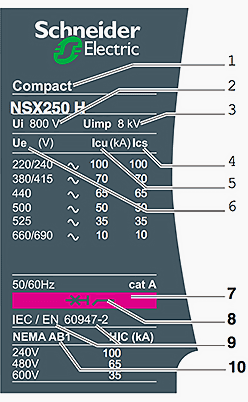

- Type of device – frame size and breaking capacity class
- Ui – rated insulation voltage.
- Uimp – rated impulse withstand voltage.
- Ics – service breaking capacity.
- Icu – ultimate breaking capacity for various values of the rated operational voltage Ue
- Ue – operational voltage.
- Colour label – indicating the breaking capacity class.
- Circuit breaker-disconnector symbol.
- Reference standard.
- Main standards with which the device complies.
When the circuit breaker is equipped with an extended rotary handle, the door must be opened to access the rating plate.
Go back to CB Selection Tips ↑
Reference // Basics of Circuit Breakers For Electrical Engineers (additional info for practical usage)- Rockwell











Icu=Ics, can we use this breaker after the first interruption?
While choosing CBs rated voltage, current and short circuit capacity of the system is must. This is very important while choose main incomer called upstream. Sometimes in smaller circuts short circuit capacity lesser in downstream circuit compared to upstream to reduce cost. Safer side short circuit capacity must be uniform all over circuit to avoid nuisance trip of main income.
Could I choose (or order) a Circuit breaker without knowing the value of the Short Circuit current? And after choosing, to receive a preselected Short Circuit current value information from the Breaker maker?
Sir,
Please help me for the Selection of Circuit Breaker for 45A Single Phase Genset AMF Panel.
i.e Ampere rating calculation and No. of Pole to be select.
If the amps calculated is 45A means you have to choose 63A SPN 10KA is enough
Respected sir please upload techique for fault finding in panel circuit at site of work and repairing and connection diagrame of 800 amp control panel with air circuit breaker.
thank for help . it is very clear lecture
Respected Edward highly regard for sharing very useful technical information my question is about fluctuating load which factors should we consider regarding MV/ LV breaker settings mainly installed for VFD
hi,good information there.
kindly assist me in programming an abb inverter starter for a drive system.the input is 240v ac output is three phases.415v.
Hi James, just follow the manual and setting accordingly follow the nameplate of motor specification.
Edvard,
When selecting a circuit breaker, I suggest that we sometimes need to consider mechanical as well as electrical ratings. For instance many breakers will hardly ever be switched (in the absence of a fault), but others may need to be routinely operated, say, twice a day, and not all devices are designed for that level of usage.
I suppose this might be included in section (4) ‘Special Requirements’.