The strength of electric field or electrostatic force strength or intensity of field (all synonymous terms) is measured & expressed in terms of force experienced by unit positive charge placed in sphere of influence of another source charge, which has produced the electric field.
We often express the strength of electric field as electric lines of forces. When we say electric lines of forces it is nothing but a vectorial way of saying; which specifies the direction of electric field. The direction is actually the direction of line denoting the electric electrostatic force. So we can say electric field intensity is basically a force on unit positive charge hence direction of these force are the direction lines denoting electric lines of force.
Let us consider a closed path denoted by ABCD.
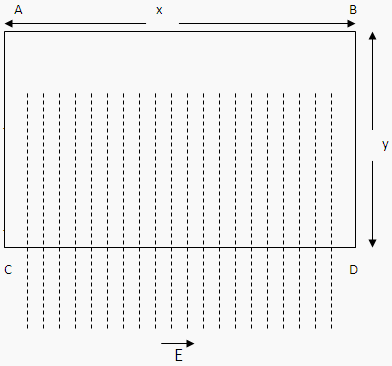
This closed path (Hollow or solid, immaterial at this stage of discussion) is placed in uniform electric field of strength E.
Electric field intensity = E
Now the force on unit positive charge is = E
This force will act on each & every point of surface ABCD. The total number of electric lines of forces will be total force acting inside the closed path ABCD.
Similarly we cannot count physically the total number of electric lines of force so alternatively we calculate the total force on the whole surface ABCD. Since for each point on ABCD there would be a line of force so this can be mathematically obtained by taking the surface integral of electric field over the surface ABCD.
The physical quantity thus obtained is electric flux and in case of magnetism it is magnetic flux.
![]()
The above integral has to be carried over surface ABCD so we can write:
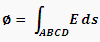
Now the above equation one is not fully correct as we not incorporated or taken into consideration the fact that the (free space or vacuum or anything else) be the medium has different ability or power to let through or establish an electric field.
It is very clear from below figure that the field intensity (or number of lines of forces) upon entering the closed surface ABCD is different from what it was before entering.
So for medium inside ABCD we can write equation 2.
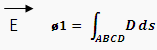
Now from equation 1 and 2:
Ø/ ø1 = E/D [Equation 3]
The ratio represented by equation 3 is called reciprocal of permittivity that is:
Ø1/ ø1 = D/E = 1/Є0
Hence we can finally write in case of electrostatics:
D = E Є0 [Equation 4]
Hence we can finally write in case of magnetism:
B = H µ0 [Equation 5]
So we can observe from equation 4 and 5 that the strength of electric filed or magnetic field is altered by a factor Є0 or µ0.
Hence for any point on closed surface ABCD, the strength of electric & magnetic field which was supposed to be E or B respectively has become E Є0 or H µ0 because of limitation to the establishment of electric field or magnetic field in any medium. Now the rectified equation 1 valid for any medium other than vacuum is:
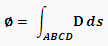
Now using 4 in above equation we can write:
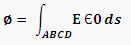
Now equation 7 is the final equation for total electric flux through the surface ABCD in any medium. If we want to calculate the density of that flux than it will be:
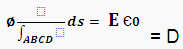
Because of equation 8:
- D in electricity and B in magnetism are called flux density.
- Є in electricity and µ in magnetism are called permittivity and permeability that power or ability to conduct the electric and magnetic field.










