Power Semiconductor Device – Transistor
Power transistors are used in applications ranging from a few to several hundred kilowatts and switching frequencies up to about 10 kHz. Power transistors used in power conversion applications are generally npn type. The power transistor is turned on by… Read more
Oct 27, 2011 | By Edvard Csanyi

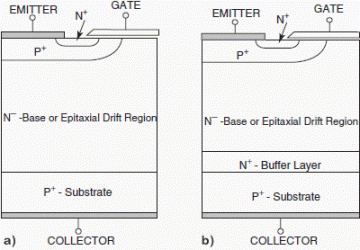
Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)
The IGBT has the high input impedance and high-speed characteristics of a MOSFET with the conductivity characteristic (low saturation voltage) of a bipolar transistor. The IGBT is turned on by applying a positive voltage between the gate and emitter and,… Read more
Oct 21, 2011 | By Edvard Csanyi
Use Hall Effect Measurements to Characterize Materials
Written by Robert Green Engineers have been using Hall effect measurements to characterize materials since Edwin Hall discovered the phenomenon in 1879. The Hall effect is the generation of a voltage, called the Hall voltage, across a sample of a… Read more
Oct 19, 2011 | By elaina

Power Semiconductor Devices – Thyristor and Triac
The thyristor, also called a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR), is basically a four-layer three-junction pnpn device. It has three terminals: anode, cathode, and gate. The device is turned on by applying a short pulse across the gate and cathode. Once the… Read more
Oct 15, 2011 | By Edvard Csanyi

State Machine Design
Written by Ray Salemi State machines are a foundation of digital design. Eventually we all reach the point where we need to control our digital algorithm, and we almost always turn to a state machine to do the job. Because… Read more
Sep 14, 2011 | By elaina

Resistors in detail
Resistors are one of the simplest varieties of electronic components. A resistor is a two-terminal device that has a fixed relationship between the current passing through the device and the voltage drop across the device. This relationship is described in… Read more
Aug 12, 2011 | By elaina

Designing Raw DC Power Supplies
Every type of electrical or electronic apparatus needs a source of electrical energy to function. The source of electrical energy is called the power supply. The two main classifications of power supplies are line-operated power supplies (operated from a standard… Read more
Jul 03, 2011 | By Sa'ad Eddin
ESD – Electro Static Discharge
An increasing problem today with the use of more and more electronic equipment in our systems is the Electro Static Discharge (ESD). The main source of the problem is the wrong handling of electronic components, printed circuit boards, etc. A… Read more
May 23, 2011 | By Edvard Csanyi
What Is Modulation?
Modulation is the use of one electrical signal to “control” a primary variable of another. For example, if an audio signal voltage is used to control the “amplitude” of a carrier signal, the result is amplitude modulation. It is important… Read more
Feb 20, 2011 | By Sa'ad Eddin
Ethernet History
Ethernet is the most popular and widely deployed network technology in the world. In 1973, while working on a way to link the Xerox “Alto” computer to a printer, Bob Metcalfe designed and tested the first Ethernet network. This first… Read more
Jan 25, 2011 | By Edvard Csanyi


