Direct-on-line (DOL) or Star-delta?
The primary challenge in starting induction motors of large or medium size is predominantly due to the necessity for a high starting current when employing direct-on-line (DOL) starting method. Consider that the distribution line comes from a substation, where the supply voltage remains stable. The line supplies multiple consumers, one of which includes an induction motor equipped with a direct-on-line starter, drawing a current that exceeds the design specifications of the line.

This will result in a voltage drop along the line, affecting both the consumers located between the substation and this particular consumer, as well as those downstream of this consumer. The observed voltage drop exceeds the allowable limit set by Internation Standard, as the current being drawn exceeds the design specifications of the line.
Only for the current that is below the design specification of the line, the voltage drop is minimized to the lower limit.
The supply authorities impose a restriction on the rating or size of the induction motor that can be started directly on line. Any motor that surpasses the specified rating cannot be started Direct-On-Line; therefore, a starter must be employed to limit the inrush current during startup.
Motor starting methods
Direct-on-line starting (DOL)
As the name suggests, direct-on-line starting means that the motor is started by connecting it directly to the supply at rated voltage. Direct-on-line starting, (DOL), is suitable for stable supplies and mechanically stiff and well-dimensioned shaft systems – and pumps qualify as examples of such systems.
Figure 1 – Line diagram for Direct-on-line motor starting
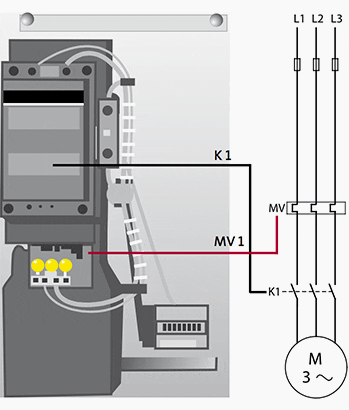

Where:
- K1 – Main contactor
- MV1 – Overload relay
Advantages of Direct-on-line (DOL) Motor Starting
DOL starting is the simplest, cheapest and most common starting method. Furthermore it actually gives the lowest temperature rise within the motor during start up of all the starting methods.
Power plants may have varying rules and regulations in different countries. For example: Three-phase motors with locked-rotor currents above 60 A must not use direct-on-line starting in Denmark. In such cases, it will obviously be necessary to select another starting method.
Motors that start and stop frequently often have some kind of control system, which consist of a contactor and overload protection such as a thermal relay.
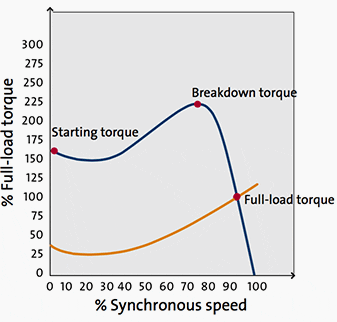
Figure 2 – DOL curve – Synchronous speed / Full-load torque

Drawbacks of Direct-on-line (DOL) Motor Starting
Small motors which do not start and stop frequently need only very simple starting equipment, often in the form of a hand-operated motor protection circuit breaker.
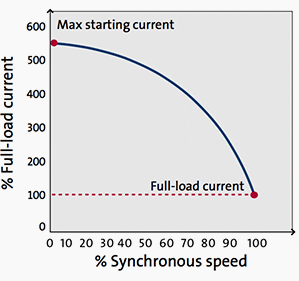
Full voltage is switched directly onto the motor terminals. For small motors, the starting torque will be 150% to 300% of the full-load value, while the starting current will be 300% to 800% of the full-load current or even higher.
Figure 3 – DOL curve – Synchronous speed / Full-load current

Star-delta starting
The objective of this starting method, which is used with three-phase induction motors, is to reduce the starting current. In starting position, current supply to the stator windings is connected in star (Y) for starting.
In the running position, current supply is reconnected to the windings in delta (∆) once the motor has gained speed.
Figure 4 – Line diagram for star-delta motor starter
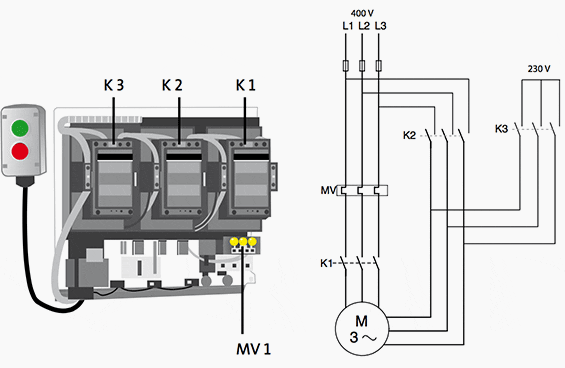

Advantages of Y-Δ (star-delta) starting)
Normally, low-voltage motors over 3 kW will be dimensioned to run at either 400 V in delta (∆) connection or at 690 V in star (Y) connection. The flexibility provided by this design can also be used to start the motor with a lower voltage. Star-delta connections give a low starting current of only about one third of that found with direct-on-line starting.
Star-delta starters are particularly suited for high inertias, where the load are initiated after full load speed.
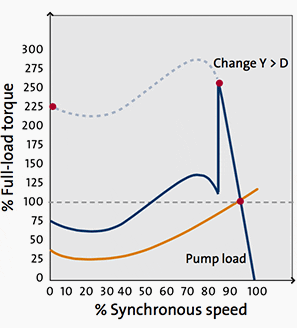
Figure 5 – Start-delta starter curve – Synchronous speed / Full-load torque

Drawbacks of of Y-Δ (star-delta) starting)
But they also reduce the starting torque to about 33%. The motor is started in Y-connection and accelerated and switched to the star-delta connection. This method can only be used with induction motors that are delta connected to the supply voltage.
The two illustrations to the right show two features which should be taken into consideration when using star-delta starting. The starter first connects the motor in star (contactor K1 and K3). After a time period – which depends on individual needs – it connects the motor in delta contactor K3 open and contactor K2 close.
Figure 6 – Star-delta starter curve – Synchronous speed / Full-load current
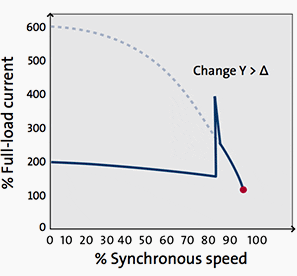

Starting torque and current are considerably lower at star-delta starting than at direct-on-line starting: one third of the equivalent DOL value. Mismatching of motor torque speed curve and load torque speed curve.
In the example shown here, the motor would slowly accelerate up to approximately 50 per cent rated speed.
Figure 7 – Mismatching of motor torque speed curve and load torque speed curve
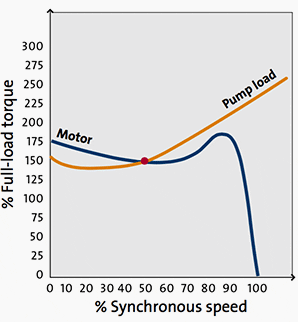

Comparision of DOL and Star-delta starting
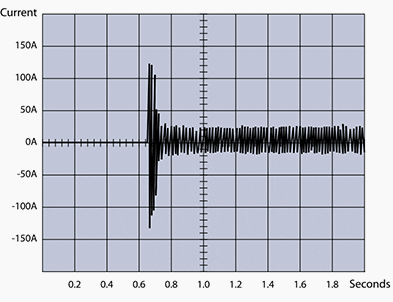
The following graphs illustrate currents for a Grundfos CR pump started with a Grundfos MG 7.5 kW motor by means of DOL and star-delta starting, respectively. As you will see, the DOL starting method features a very high locked-rotor current which eventually flattens and becomes constant.
Figure 8 – Direct-on-line starting of a Grundfos 7.5 kW motor installed on a Grundfos CR pump

The star-delta starting method features a lower locked-rotor current, but peaks during the starting process as the changeover from star to delta is made.
When starting in star (t = 0.3 s), the current is reduced.
Figure 9 – Star-delta starting of a 7.5 kW Grundfos motor installed on a Grundfos CR pump
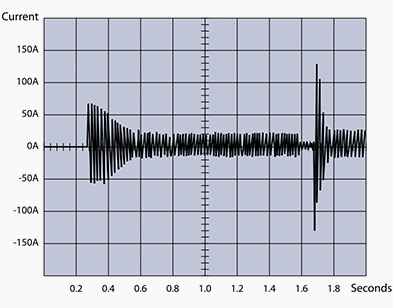

However, when switching over from star to delta (at t = 1 .7 s), the current pulse reaches the same level as the locked-rotor current seen with direct-on-line starting. The current pulse can even get higher, because the motor during the switching period is un-powered which means it reduce speed before the full voltage (delta voltage) are supplied.
Reference // The Motor Book – Grundfos (Download)











Hello ,
Sorry , just only forgot the
FLC ( AMPS ) = 308 A
Starting Method = Star – Delta
Good Morning Gents ,
I have Fire Fighting Electrical Pump , the Technical Data : PH = 3 , Insul Class = F , HP = 250 , AMPS = 387 , SF AMPS = 387 , RPM = 3565 , HZ = 60 ,NEMA NOM EFF = 95 , DES = B , Guaranteed Efficiency = 94.1 , DUTY : CONT , WT = 1200 LBS , PF = 89
And i have Diesel Generator : KVA = 513 , KW = 410 , COS = 0.8 , HZ =60
V = 380 , AMPS = 779 , RPM 1800 REV / MIN
Kindly requested to confirm us if could we start the Motor / Pump as per the above DATA .
Thanks .
Your explanation is great and having clear and easy concepts
But which i want is that:Dol,star/delta and rotor resistance starter
Thank you very such a very useful information for me with details & Good Examples
DOL is used in small rating/low cost motors only and only because of economic reasons.
Generally in Y delta Starting, it was proven that Y reduces starting current. But when I experimented on centrifugal pumps, I found the reverse reality. Meaning , I started the centrifugal pump in Y and recorded the Starting current. Then I used the same pump and used DOL, meaning I started it in Delta. My record shows that the Delta starting was even lesser. Can you please explain this. I’ve been trying to search explanations for this but till now I haven’t seen any. No one seems to have noticed this either. I wonder, probably its due to the nature of the impeller mechanism. Hoping to find get answer for this question at last.
Good article Edvard! Good work!
I need to convert Star/ Delta to DOL to operate with auto transformer , shall I connect R1 with T2 , S1 with S2 and T1 with R2
VERY HELPFUL
Hello Edvard
Can you send me your contact email adress or phone
Thanks
My requested question is, why should we have used to three contactor in star-delta
I have a confusion that How can we calculate motor current in delta and star.
Suppose we have a motor rating 11kw, 380 volt PF 0.90,
How can i calculate line current if motor is connected in delta? Also current in star?
Muy buena información me gustaría subcribirme a su blog
what is the advantage of using star delta starting as it causes the same high current of direct online during switching from star to delta?
Same question.
thank you very much… very useful information.
The decision to adopt DOL starting also depends on the capacity of the source, usually a transformer, and the distance from the source to the motor control centre. For example, if a 100 kW pump motor controller is located close to a power transformer of 1000 kVA, it can be started DOL. But if the same motor control centre is located 500 meter from the source transformer, it is better to adopt a star-delta starter because the starting current for this motor will cause sufficient voltage drop to affect starting of this motor.
But then, if the motor is driving a centrifugal blower, it will be wise to use a star-delta starter even if the MCC is close to the transformer. As has been pointed out, a high inertia load like a centrifugal blower will draw enormous starting current and cause instability.
your article is so much useful for me and also this article has been explained in a simple manner,so every electrical engineer can understand this type article…keep up
Very good and helpful article. Keep up.
Dear Edvard, in order to disseminate the knowledge to Electrical Engineering fraternity, can we publish these articles or present on other forums??. Pl let me know on my mail…thanks
Sure, no problem. Just put the reference URL at the bottom.
Hi, good artical again, your article is very helpful for practical analysis.
Thank you