Power Quality problems
To make the study of Power Quality problems useful, the various types of disturbances need to be classified by magnitude and duration.

This is especially important for manufacturers and users of equipment that may be at risk. Manufacturers need to know what is expected of their equipment, and users, through monitoring, can determine if an equipment malfunction is due to a disturbance or problems within the equipment itself.
Standards are essential for manufacturers and users alike, to define what is reasonable in terms of disturbances that might occur and what equipment should withstand.
Table 1 provides a broad classification of the disturbances that may occur on a power system, some typical causes of them and the potential impact on equipment. From this Table, it will be evident that the electricity supply waveform, often thought of as composed of pure sinusoidal quantities, can suffer a wide variety of disturbances.
Table 1 – Power Quality issues
| Category | Causes | Impacts |
| Voltage dips |
|
|
| Voltage surges |
|
|
| Overvoltage |
|
|
| Harmonics |
|
|
| Power frequency variation |
|
|
| Voltage fluctuation |
|
|
| Rapid voltage change |
|
|
| Voltage imbalance |
|
|
| Short and long voltage interruptions |
|
|
| Undervoltage |
|
|
| Transients |
|
|
Table 2 lists the limits given in Standard EN 50160 and notes where other standards have similar limits.
Table 2 – Power system disturbance classification to EN 50160
| Type of disturbance | Voltage level | Limits from EN50160 | Measurement period | Typical duration | Other applicable standards |
| Voltage Variation | 230V | +/- 10% | 95% of 1 week | – | |
| Voltage Dips | 230V | 10-1000/year | 10ms –1sec | IEEE 1159 | |
| Rapid voltage changes | 230V | 5% to 10% | Several per day | Short duration | |
| 1kV-35kV | <6% | Per day | Short duration | IEEE 1159 | |
| Short Interruptions | 230V | >99% | 20-200 per day | Up to 3 mins | EN61000-4-11 |
| Long Interruptions | 230V | >99% | 10-50 per day | >3 mins | IEEE 1159 |
| Transient Overvoltage | 230V | Generally <6kV | Not specified | <1ms | IEEE 1159 |
| Voltage unbalance | 230V | ||||
| Undervoltage | 230V | <-10% | Not specified | >1 min | IEEE 1159 |
| Voltage surge | 230V | <150% of nominal voltage | Not specified | >200ms | IEEE 1159 |
| Voltage fluctuations | 230V | 3% | 10 min | <200ms | IEC 60827 |
| Frequency variation | +/- 1% | 95% of 1 week | Not specified | Measured over 10s | |
| +4%, -6% | 100% of 1 week | Not specified | Measured over 10s | ||
| Harmonics | THD<8% up to 40th | 95% of 1 week | Not specified |
For computer equipment, a common standard that manufacturers use is the ITI (Information Technology Industry) curve, illustrated in Figure 1.
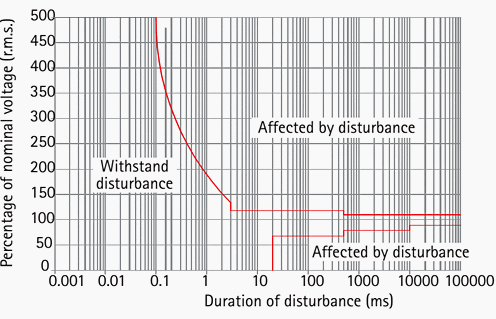
Voltage disturbances that lie in the area indicated as ‘safe’ should not cause a malfunction in any way. However, some disturbances at LV levels that lie within the boundaries defined by EN50160 might cause a malfunction because they do not lie in the safe area of the ITI curve.
What is Power Quality and Why It’s Important (Webinar)
Reference // Network Protection and automation Guide – Areva











Powerful update
Good article
Power quality ..need to create more awareness..in third world countries…
Need such power quality review and u tube for demonstrating to electrical engineering studentd
need more downloads