Types of photovoltaic plants
Off-grid PV plants
Off-grid PV plants are plants that are not connected to the grid and consist of PV modules and of a storage system that guarantees electric energy supply also when lighting is poor or when it is dark. Since the current delivered by the PV generator is DC power, if the user plant needs AC current an inverter becomes necessary.

Such plants are advantageous from a technical and financial point of view since they can replace motor-generator sets whenever the electric network is not present or whenever it is not easy to reach.
Besides, in an off-grid configuration, the PV field is over-dimensioned so that, during the insolation hours, both the load supply as well as the recharge of the storing batteries can be guaranteed with a certain safety margin taking into account the days of poor insolation.
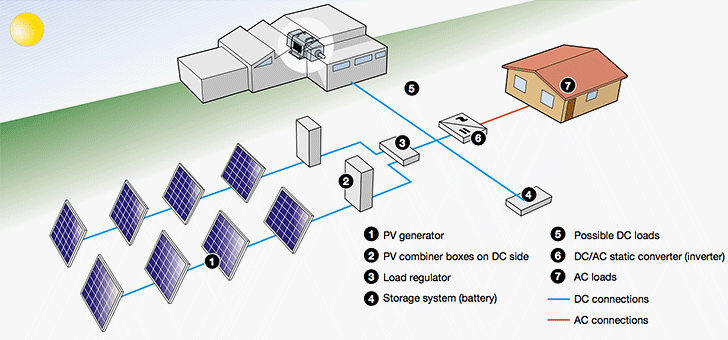
At present the most common applications are used to supply (Figure 1):
- Pumping water equipment;
- Radio repeaters, weather or seismic observation and data transmission stations;
- Lightning systems;
- Systems of signs for roads, harbors and airports;
- Service supply in campers;
- Advertising installations;
- Refuges at high altitudes.
Grid-connected PV plants
Permanently grid-connected PV plants draw power from the grid during the hours when the PV generator cannot produce the energy necessary to satisfy the needs of the consumer.
On the contrary, if the PV system produces excess electric power, the surplus is put into the grid, which therefore can operate as a big accumulator: as a consequence, grid-connected systems do not need accumulator banks.
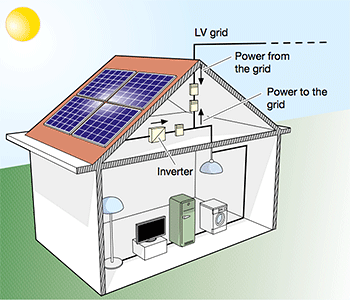
Such plants (Figure 2) offer the advantage of distributed – instead of centralized generation: in fact, the energy produced near the consumption area has a value higher than that produced in traditional large power plants, because the transmission losses are limited and the expenses of big transport and dispatch electric systems are reduced.
In addition, the energy production in the insolation hours allows the requirements for the grid to be reduced during the day, that is when the demand is higher.
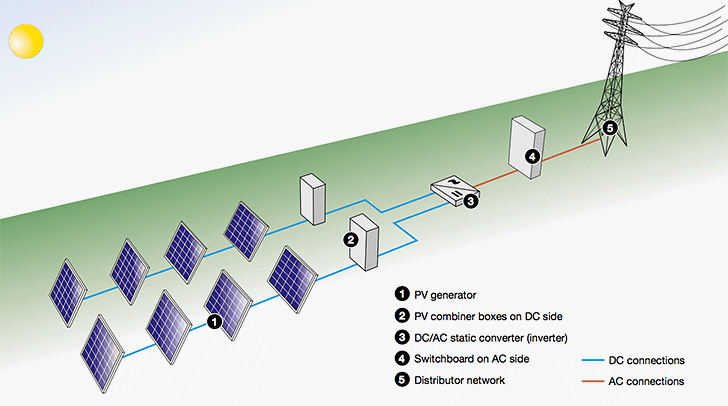
Figure 3 above shows the principle diagram of a grid-connected photovoltaic plant.
| Title: | Photovoltaic plants – Technical Application Papers No.10 – ABB |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 5.73 MB |
| Pages: | 124 |
| Download: | Here 🔗 (Get Premium Membership) | Video Courses | Download Updates |



Really Worth reading various informative article s.Clear many of our doubts.Waiting for article on Harmonics in the power supply utility systems.
Thanks a lot for all the great information you share here.
Thanks a lot for all the great information you share here.
Thanks a lot for all the great information you share here.
what is the impact of lattitude of location of installation
Findv more informaţion here : https://www.youtube.com/user/eugeniusro/videos
i have the same problem withdownload,already copy paste~Copy this link https://electrical-engineering-portal.com/download-center/books-and-guides/alternative-energy/photovoltaic-plants and open new tab in your browser. Paste it and it will work.~still don`t works?may your suggegest?
Not able to download the
Title: Photovoltaic plants – Technical Application Papers No.10 – ABB
After clicking the Download here , It wont start.
Copy this link https://electrical-engineering-portal.com/download-center/books-and-guides/alternative-energy/photovoltaic-plants and open new tab in your browser. Paste it and it will work.