SCADA overview
SCADA is an acronym for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition. SCADA systems are used to monitor and control a plant or equipment in industries such as telecommunications, water and waste control, energy, oil and gas refining and transportation.
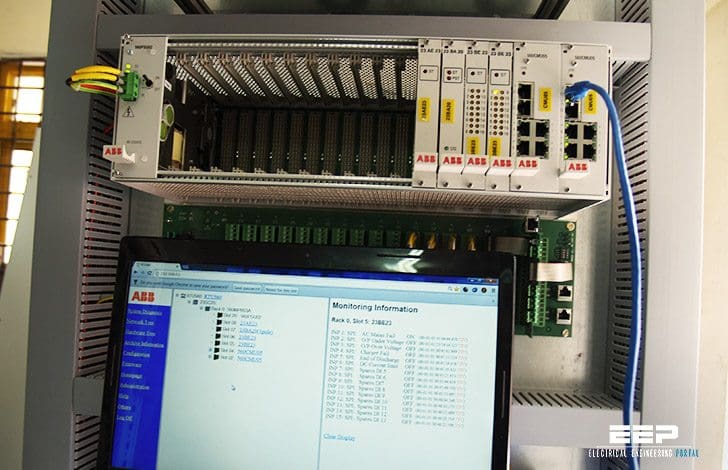

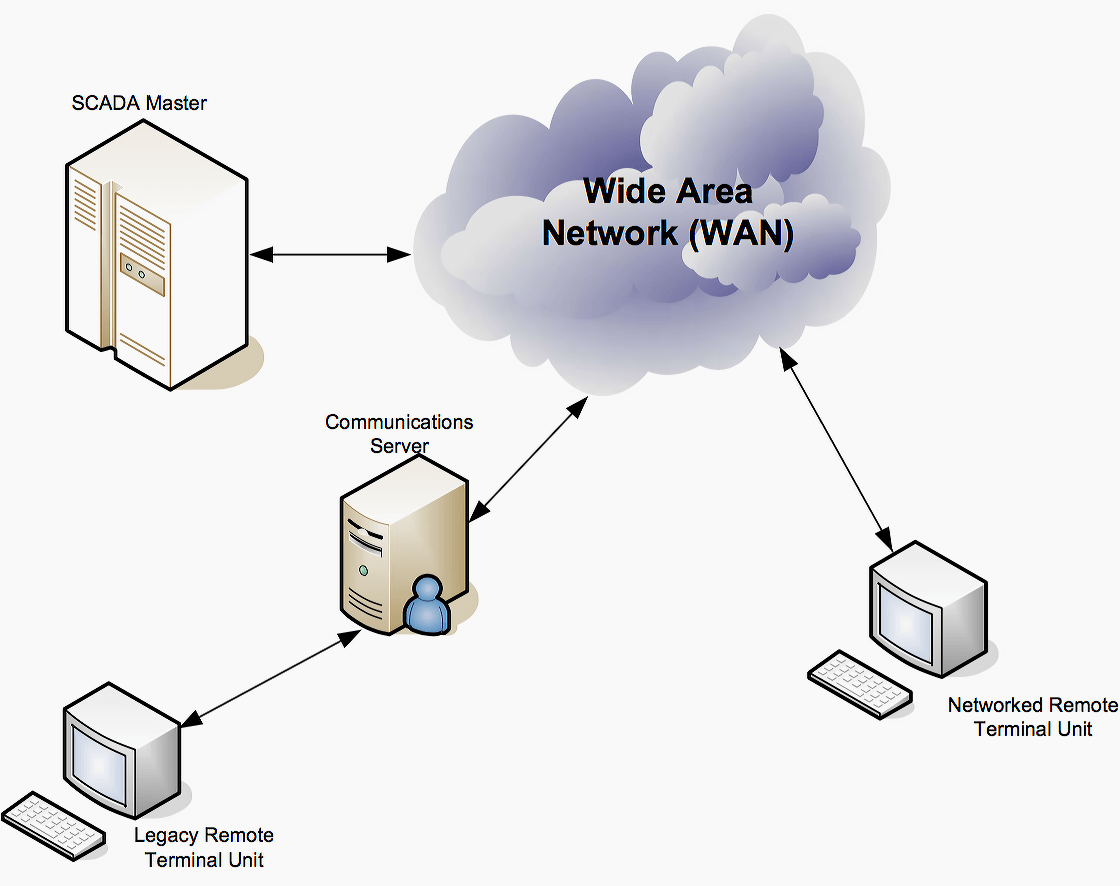
These systems encompass the transfer of data between a SCADA central host computer and a number of Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) and/or Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), and the central host and the operator terminals.
These systems can be relatively simple, such as one that monitors environmental conditions of a small office building, or very complex, such as a system that monitors all the activity in a nuclear power plant or the activity of a municipal water system. Traditionally, SCADA systems have made use of the Public Switched Network (PSN) for monitoring purposes.
Today many systems are monitored using the infrastructure of the corporate Local Area Network (LAN)/Wide Area Network (WAN). Wireless technologies are now being widely deployed for purposes of monitoring!

SCADA protocols
In a SCADA system, the RTU (remote terminal unit) accepts commands to operate control points, sets analog output levels, and responds to requests. It provides status, analog and accumulated data to the SCADA master station. The data representations sent are not identified in any fashion other than by unique addressing.
The addressing is designed to correlate with the SCADA master station database.
The RTU has no knowledge of which unique parameters since it is monitoring in the real world! It simply monitors certain points and stores the information in a local addressing scheme.
The SCADA master station is the part of the system that should “know” that the first status point of RTU number 27 is the status of a certain circuit breaker of a given substation. This represents the predominant SCADA systems and protocols in use in the utility industry today.
Each protocol consists of two message sets or pairs. One set forms the master protocol, containing the valid statements for master station initiation or response, and the other set is the RTU protocol, containing the valid statements an RTU can initiate and respond to. In most but not all cases, these pairs can be considered a poll or request for information or action and a confirming response.
Currently, in industry, there are several different protocols in use. The most popular are International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 60870-5 series, specifically IEC 60870-5-101 (commonly referred to as 101) and Distributed Network Protocol version 3 (DNP3).
| Title: | The basics of supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems – Communication Technologies, Inc. |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 1.3 MB |
| Pages: | 76 |
| Download: | Right here | Video Courses | Membership | Download Updates |


This for sharing this important
Advanced knowledge of SCADA 2
Im very happy to learn from you company
.. thanks for sharing all this knowledge! It is appreciated ??
Sir just me knowledge of scad operator from basic to end please