Cable fault localization techniques
The long distance underground cables are the nerves of a Railway Signaling or Telecom system. If the cables connected with the system are healthy and free from any defect, it will run smoothly and efficiently. Any fault in the cable may affect the connected circuit or equipment and paralyze the train operation.
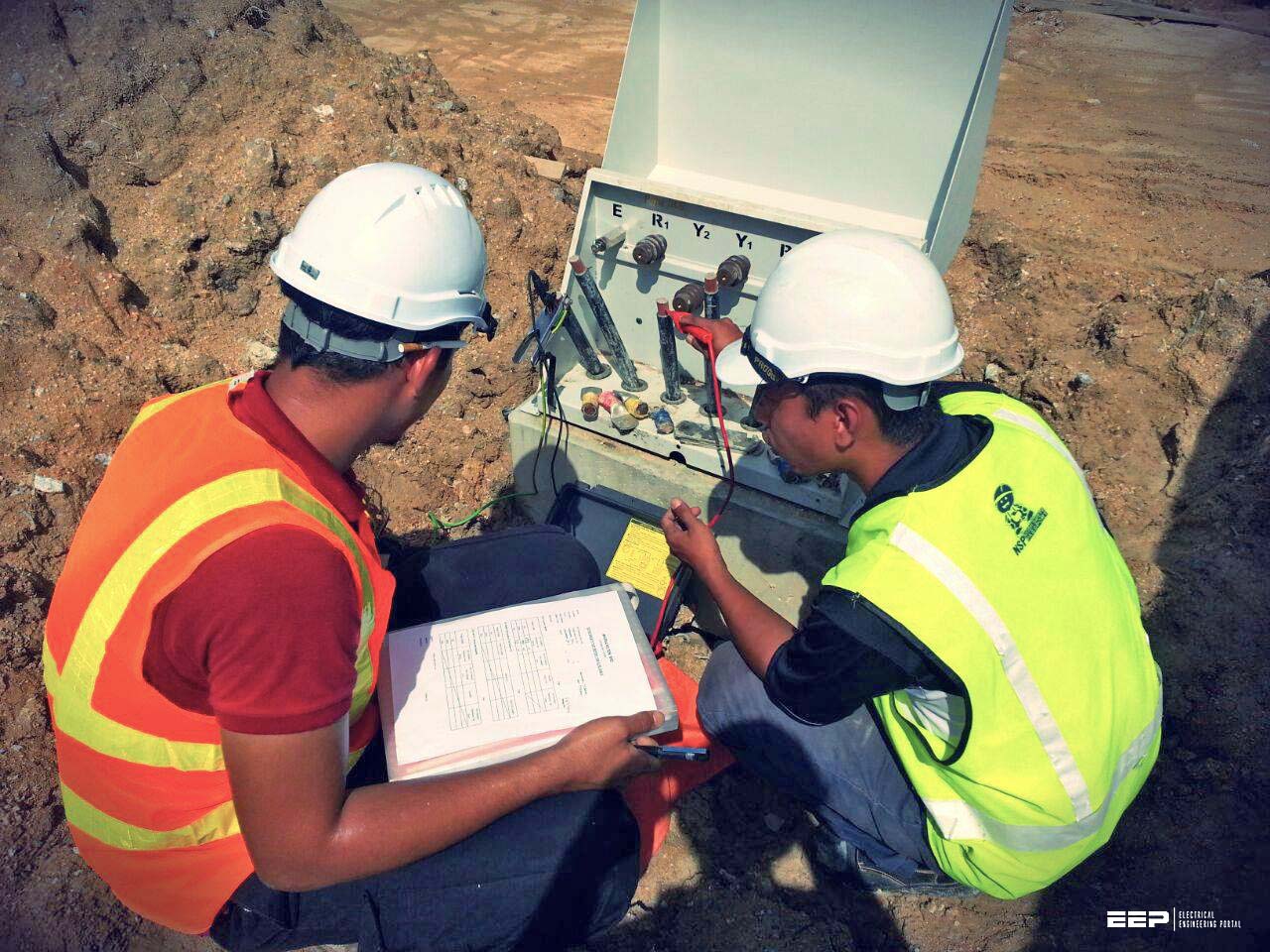

Locating the cable fault by conventional methods and repairing thereafter are time consuming and require substantial manpower. The repercussions for these failures may be in the form of punctuality losses and high maintenance cost to the Railways. To save time, manpower and at the same time reduce cost and downtime, Railways need to adopt innovative techniques in cable fault localization.
With the advent of advanced Electronics and Communication technology, equipment have been developed over the years which can accurately locate faults in underground cables.
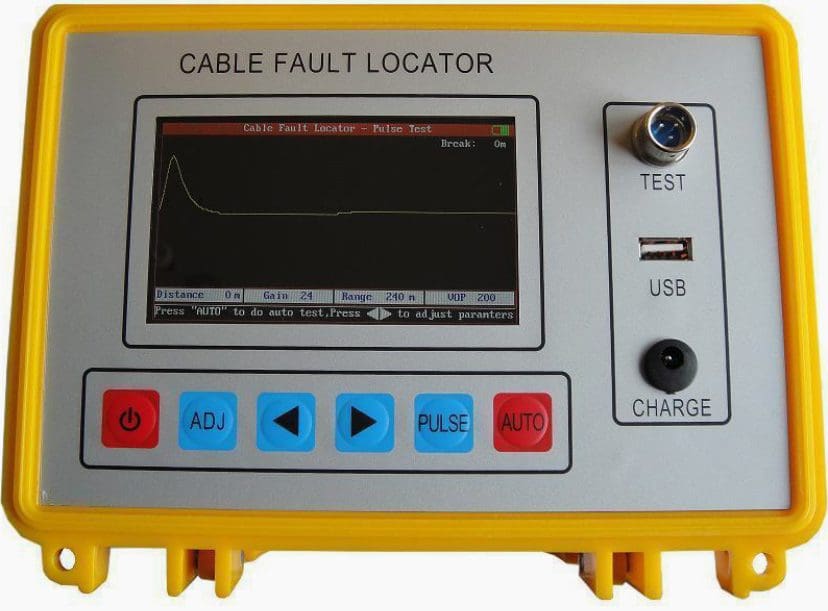
The type of fault for example earth, open, short or low insulation fault in underground cables can be detected easily with the help of a megger. But finding the exact location of the cable fault needs special techniques.
Figure 1 – Cable fault locator

Cable Fault Localization
Introduction
There are hundreds of trains which run daily on Indian Railways and the various systems which are involved in the operation of trains are Track, Rolling stock, Loco, Electrical Traction, Signaling and Telecom and traffic control systems.
Railway Signaling and Telecom circuits run on hundreds of kilometers of underground cables. Although adequate precautions are taken in lying of cables beneath the ground and underground cables are not affected by any adverse weather condition like pollution, heavy rainfall, snow and storm etc. there are other factors which may cause faults in the cables.
Type of Cables carrying S&T circuits
Signaling cables
PVC insulated PVC sheathed and armoured signalling cables. Generally, used copper conductor core sizes are 1.5 sq.mm. and 2.5sq.mm. Most commonly used cores are 2C, 4C, 6C, 8C, 9C, 12C, 19C, 20C, 24C & 30C.
Telecom cables
- Polyethylene Insulated Jelly Filled (PIJF) cables
- 4 or 6 Quad cables (Core size 0.9 mm)
- Co-Axial Cables
1.3 Major causes of cable fault
Some of the causes of cable faults are as given below:
- Ageing.
- Corrosion of sheath.
- Moisture in the insulation.
- Heating of cable.
- Fire and lightning surges.
- Electrical puncture
- Damage during laying.
- Damage while in use due to excavation works.
1.4 Types of cable faults
The common faults which develop in the conductors of multi-core cables are:
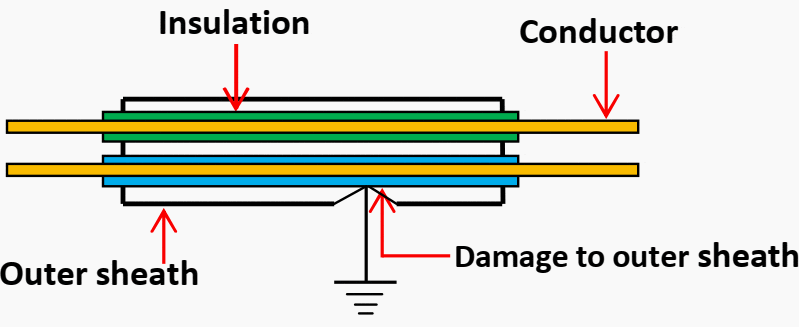
Earth fault
When any of the conductors of the cable comes in contact with the earth, it is called an earth fault. This type of fault allows the current, carried by the conductor to leak to the earth directly or indirectly instead of going to the apparatus to which the conductor is connected.
This usually occurs when the outer sheath is damaged due to chemical reactions with soil or due to vibrations and mechanical crystallization.
Figure 2 – Locating cable earth fault
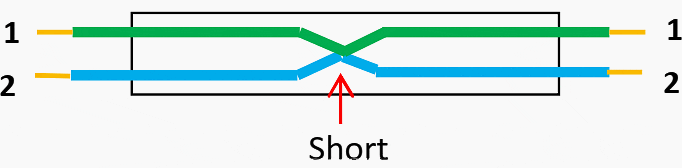
Short circuit fault
When two or more conductors of a multi-core cable come in contact with each other, then this is called a short circuit fault. A short-circuit fault occurs when the individual insulation of the conductor core is damaged.
Figure 3 – Locating cable short circuit fault
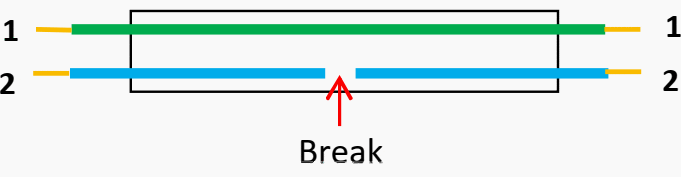
Open circuit fault
As the name suggests, this fault involves an open circuit in the conductors. When one or more cable conductors (cores) break, it leads to discontinuity. This discontinuity also occurs when the cable comes out of its joint due to mechanical stress.
This is known as Open circuit fault.
Figure 4 – Locating open circuit fault
Low insulation fault
Sometimes when the cable core insulation material is deteriorated by ageing, moisture, excessive heating or dirt the insulation resistance is dropped to very low value (several hundred to several kilo ohms) it is called as low insulation fault.
The need for cable fault localization
Whenever a fault occurs in one or more conductors of underground cable, be it an earth fault, open/short circuit fault or low insulation fault, the circuit completing through the conductor or conductors is interrupted which in turn affects the functioning of connected equipment.
In a railway signaling system the operation of signals or its associated equipment is badly affected due to cable fault.
Similarly if a cable fault occurs in a telecom cable, the circuits associated with Block working, Control or other communication systems may not work. Unless the fault is identified and rectified, the train movement is badly disrupted.
| Title: | Cable Fault Localization Guide – Government Of India Ministry Of Railways |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 3.70 MB |
| Pages: | 62 |
| Download: | Right here | Video Courses | Membership | Download Updates |


