The basics of digital multimeters
There are two common types of multimeters, analog and digital. Digital multimeter (DMM) is the most common nowdays. It uses a liquid crystal display (LCD) technology to give more accurate readings.
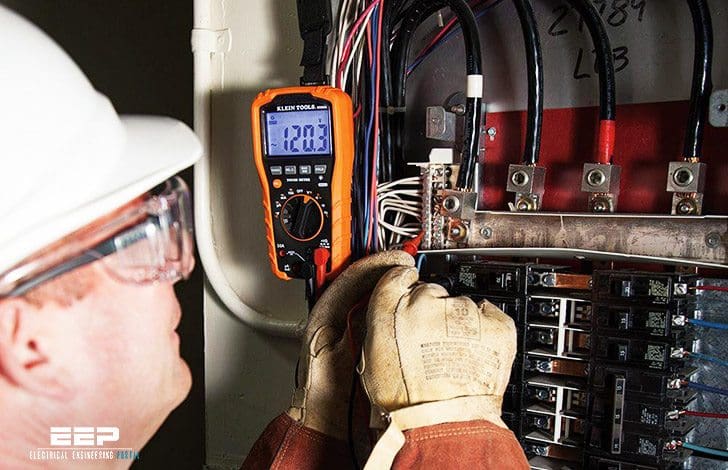

Other advantages include higher input impedances, which will not load down sensitive circuits, and input protection. This guide will help you to understand the basic features and functions of a digital multimeter.
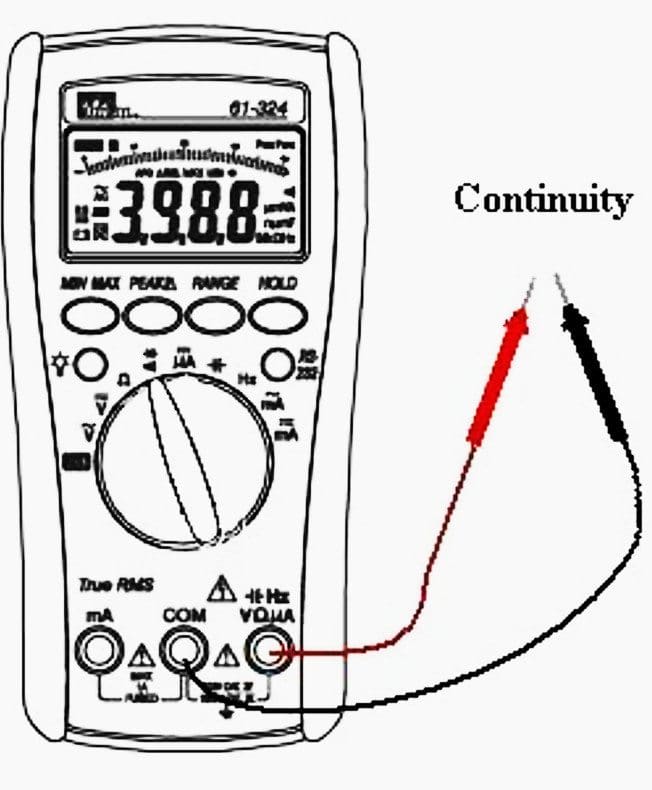
Continuity measurements
Continuity is a quick check to see if a circuit is complete. Good fuses and closed switches have continuity. During a continuity measurement, the multimeter sends a small current potential through the circuit to measures the resistance of the circuit.
The value for the maximum resistance can vary from meter to meter. Most will indicate continuity from 0 to 50 ohms. An audible alarm was added to aid in making fast go-no-go testing without taking your eyes of your work.
Resistance measurements
Resistance is easured in ohms (Ω). When you first place the meter in the (Ω) function the meter will give a display of “OL” or “1____” indicating an infinite reading. It is important when measuring Resistance that the circuit be de-energized or turned off, or the circuit may damage the meter.
Most meters have overload protection on all ranges to prevent this, but you should check the specifications of your digital multimeter to be sure.
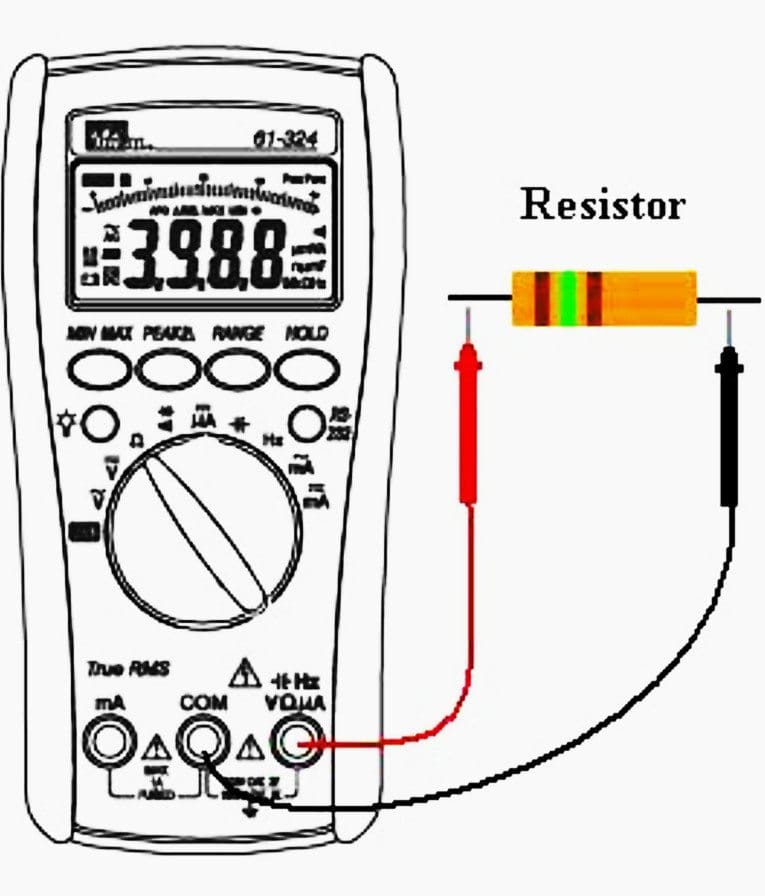
For resistance measurements, place the test leads on each side of the resistor. Other components in parallel with the resistor being measured will have an effect on the measurement.
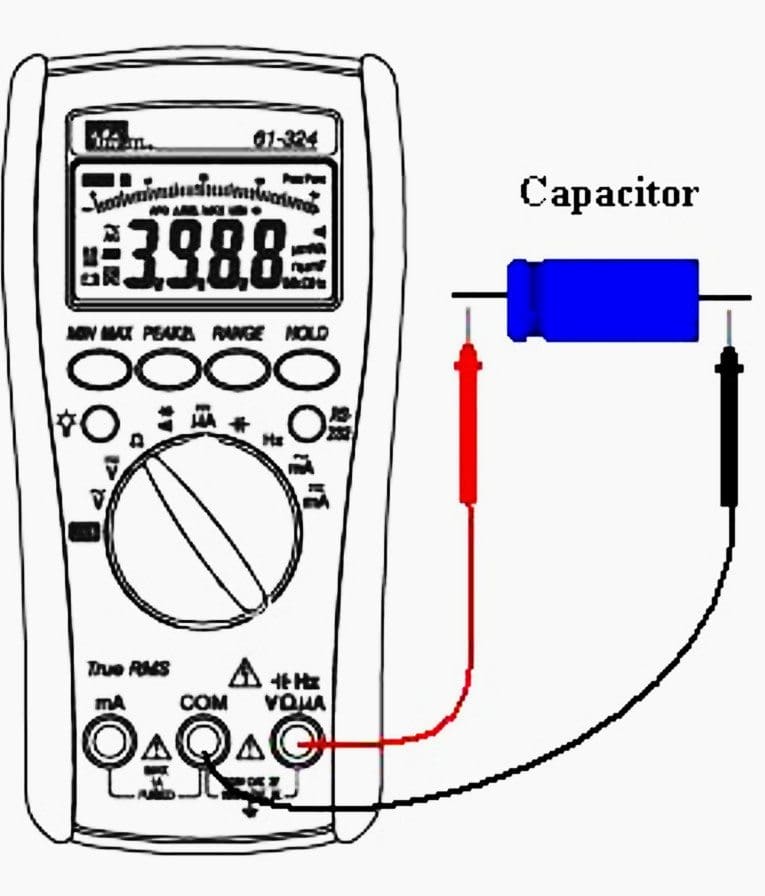
Capacitance measurement
A capacitor is a device that stores energy. It is widely used to give a boost of energy at start up when power is applied to lighting and motor systems. To test a capacitor, first remove power from the device.
Before making a measurement on a capacitor, make sure it is not holding a charge! Discharge the capacitor, using a 10,000 to 20,000 ohm 2 or 5 watt resistor.
| Title: | A guide to help you understand the basic Features and Functions of a Digital Multimeter by Patrick C Elliott at IDEAL Industries, Inc. |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 935 KB |
| Pages: | 25 |
| Download: | Right here | Video Courses | Membership | Download Updates |



In the above article, what is the meaning of ‘current potential’. Thank you for giving such new technical words. Please clarify it.
An excellent article, i will share with my community. Is important to know the power of the basic in tthe technology
This is a good knowledge sharing on us.