The frequency spectrum
The frequency spectrum is a practical graphical means of representing the harmonics contained in a periodic signal. The graph indicates the amplitude of each harmonic order. This type of representation is also referred to as spectral analysis.
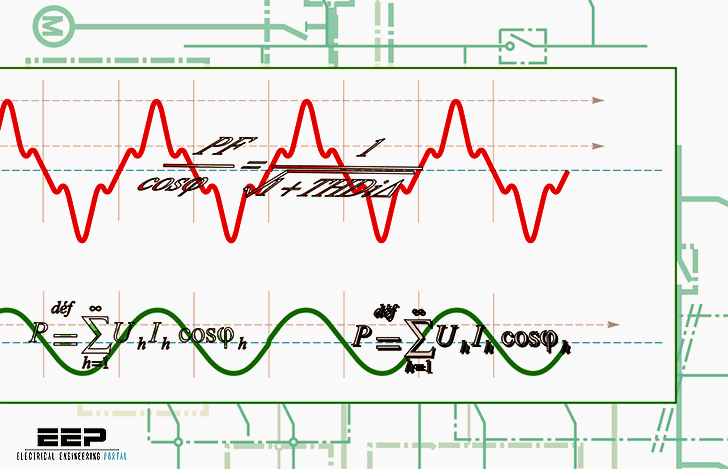
The frequency spectrum indicates which harmonics are present and their relative importance. Devices causing harmonics are present in all industrial, commercial and residential installations.
Harmonics are caused by non-linear loads.
Definition of non-linear loads
A load is said to be non-linear when the current it draws does not have the same wave form as the supply voltage.
Examples of non-linear loads
Devices comprising power electronics circuits are typical non-linear loads. Such loads are increasingly frequent and their percentage in overall electrical consumption is growing steadily.
Examples include:
- Industrial equipment (welding machines, arc furnaces, induction furnaces, rectifiers),
- Variable-speed drives for asynchronous and DC motors,
- Office equipment (PCs, photocopy machines, fax machines, etc.),
- Household appliances (television sets, microwave ovens, fluorescent lighting, etc.),
- UPSs.
Saturation of equipment (essentially transformers) may also cause non-linearcurrents.
| Title: | Harmonic Detection And Filtering by Schneider Electric |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 350 KB |
| Pages: | 45 |
| Download: | Right here | Video Courses | Membership | Download Updates |


Thank you.
Good effort for engineer’s refreshing their knowledge along with new developments.
Thanks a lot.