Busbar schemes
The commonly used busbar schemes at substations are single busbar, main and auxiliary busbar, double busbar, double main and auxiliary busbar and one and a half breaker scheme.

Single busbar arrangement
This is the simplest switching scheme in which each circuit is provided with one circuit breaker. This arrangement offers little security against busbar faults and no switching flexibility resulting into quite extensive outages of busbar and frequent maintenance of busbar isolator(s).
The entire substation is lost in case of a fault on the busbar or on any busbar isolator and also in case of maintenance of the busbar.
Typical single busbar arrangement is shown in Figure 1.
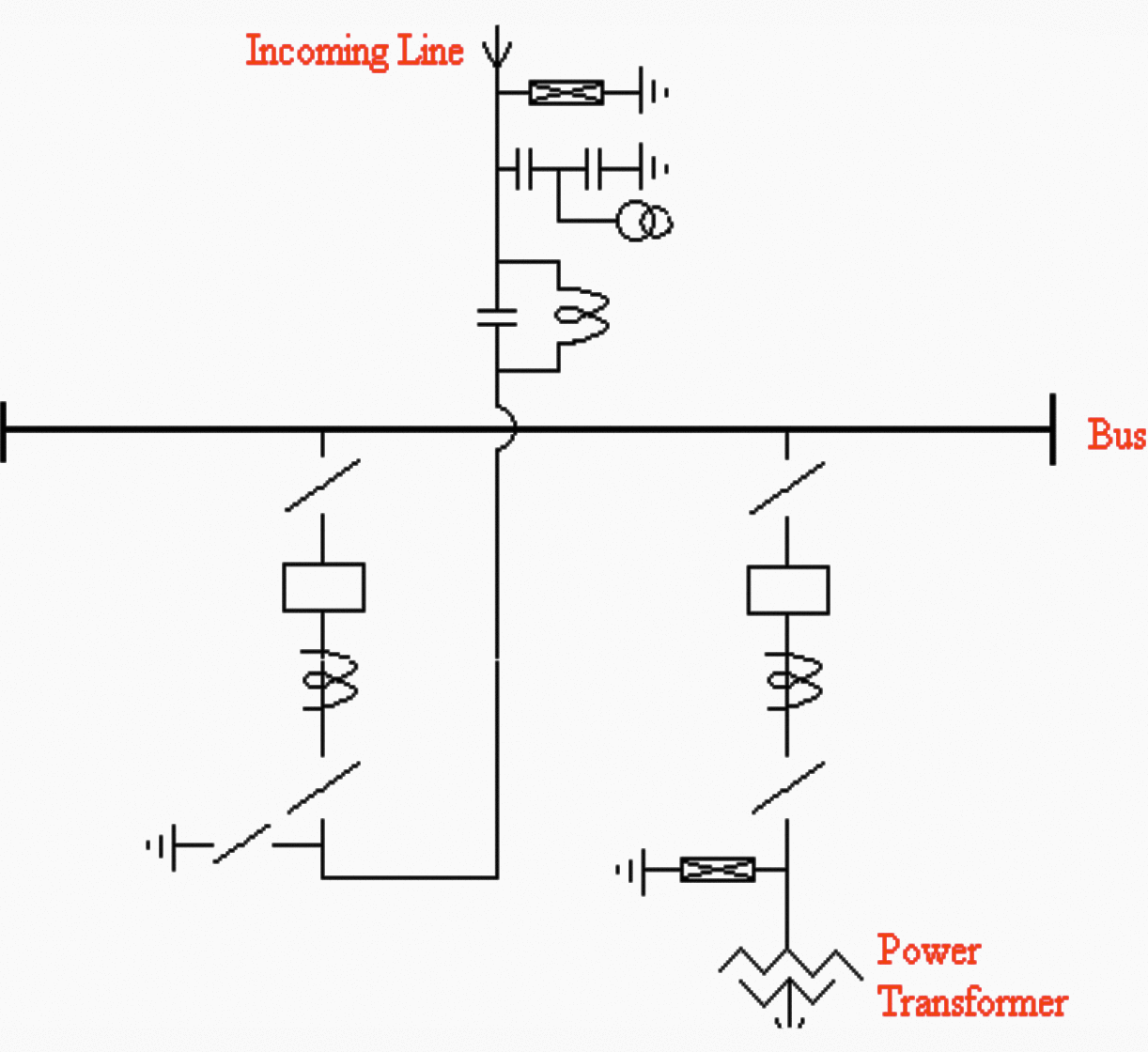
Main and auxiliary bus arrangement
This is technically a single busbar arrangement with an additional busbar called “Auxiliary bus” energized from main busbars through a bus coupler circuit, i.e., for ‘n’ number of circuits, it employs ‘n + 1’ circuit breakers.
Each circuit is connected to the main busbar through a circuit breaker with isolators on both sides and can be connected to the auxiliary busbar through an isolator.
As in the case of single bus arrangement, this scheme also suffers from the disadvantages that in the event of a fault on the main busbar or the associated isolator, the entire substation is lost. This bus arrangement has been extensively used in 132 kV substations.
Typical main and auxiliary busbar arrangement is shown in Figure 2.
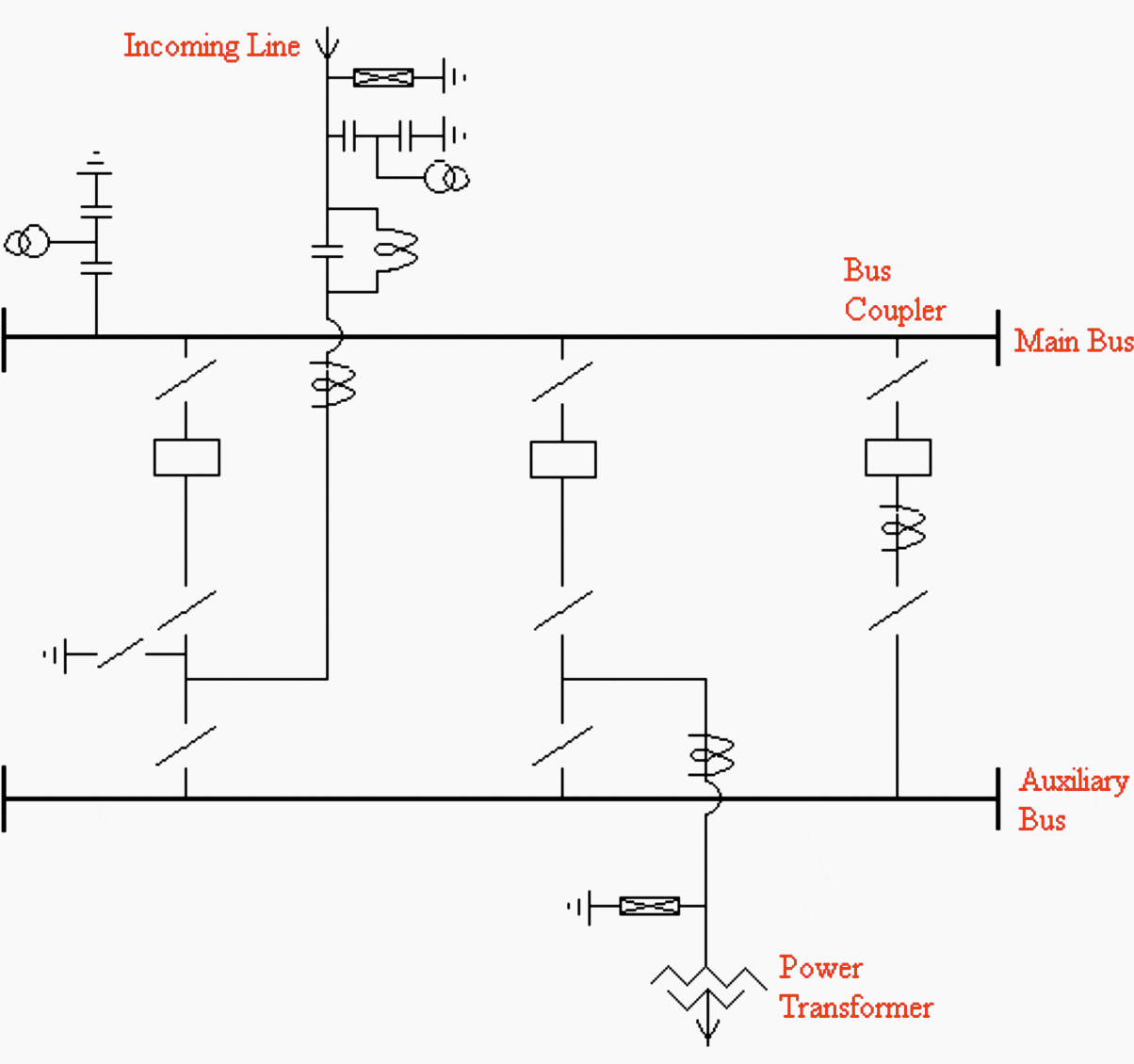
One and a half breaker arrangement
In this scheme, three circuit breakers are used for controlling two circuits which are connected between two busbars. Normally, both the busbars are in service.
Typical one and a half breaker arrangement is shown in Figure 3.
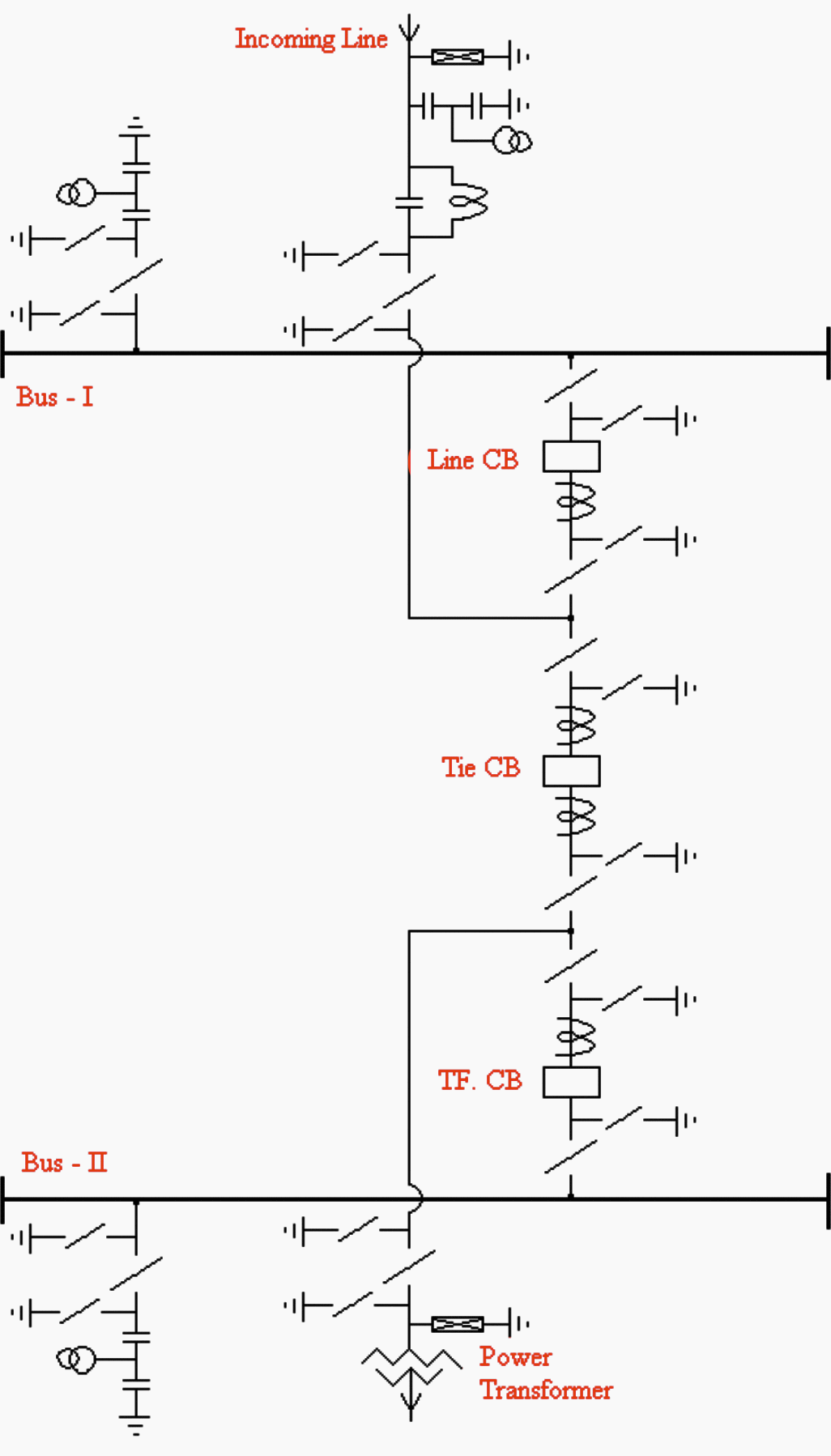
Load transfer is achieved through the breakers and, therefore, the operation is simple. However, protective relaying is somewhat more involved as the central (tie) breaker has to be responsive to troubles on either feeder in the correct sequence.
Besides, each element of the bay has to be rated for carrying the currents of two feeders to meet the requirement of various switching operations which increases the cost.
The breaker and a half scheme is best for those substations which handle large quantities of power and where the orientation of out going feeders is in opposite directions. This scheme has been used in the 400 kV substations.
| Title: | Construction of a grid substation for engineers and technical supervisors – RAJASTHAN RAJYA VIDYUT PRASARAN NIGAM LTD. |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 4.70 MB |
| Pages: | 150 |
| Download: | Right here | Video Courses | Membership | Download Updates |



Very impressive work
I want to know about simulation of an Escalator using Embedded system