DG Electrical Interconnection
The interconnection with the network is a complicated procedure that involves the realization of a distributed generation (DG) application. The DG operation is usually referred to as synchronised or parallel operation.
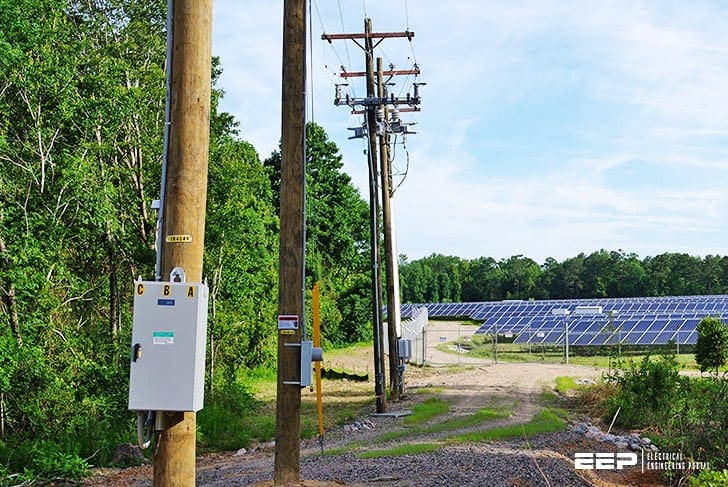

In this configuration the DG is connected to the network the same time that it’s producing power and in the case that the load is met any excess energy is also transmitted to that.
The parallel DG operation is the most complicated in contrast with a stand-alone DG application. The complexity of DG operation generally depends on the level of interaction with the existing network.
Isolated, stand alone source
In this case the load is met by DG only with no network connection.
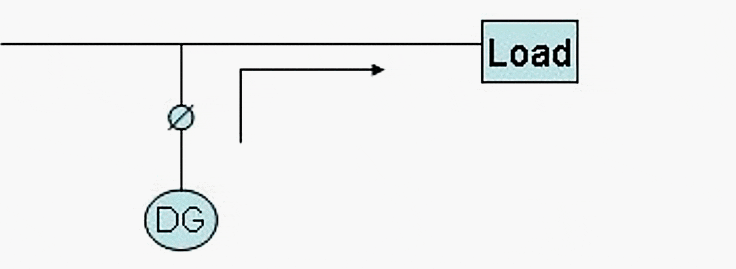
Isolated system with automatic transfer
DG provides power in Load 2. The network covers Load 1 and Load 2 when needed. DG does not work in parallel except for a few seconds.
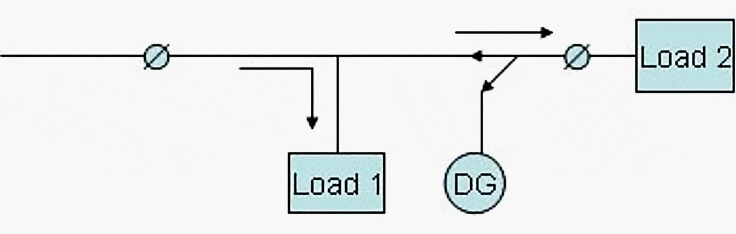
DG connected to the network with no power export
DG operates in parallel to the grid by transmitting power to one or more loads without sending any excess energy to the grid.
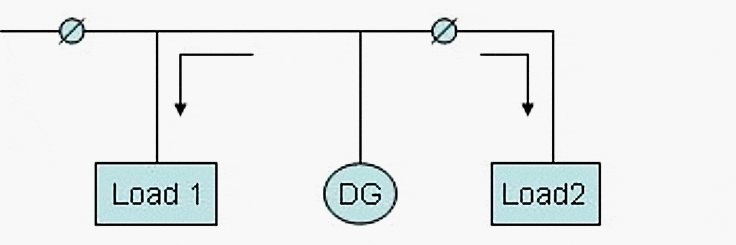
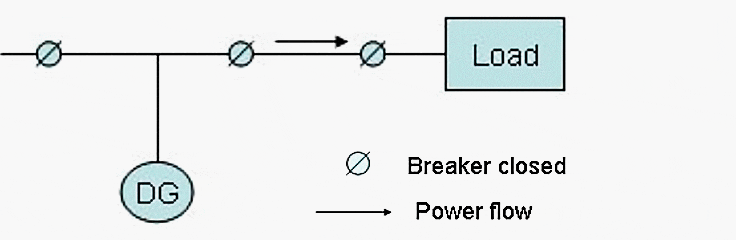
DG grid interconnected with power export
DG operates in parallel to the grid and there exists the option to supply any excess power to the grid.
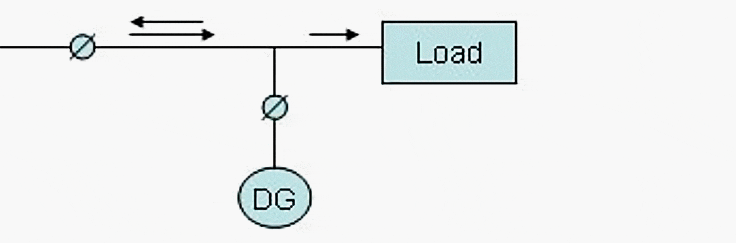
Grid interconnected with power export- utility side
The system supplies the base load, standby power, and peak load. DG operates in parallel.
Technical issues
The main technical issues for DG connection relate to reliability and quality of supply, protection, metering, and operating protocols for connection and disconnection, islanding and reactive power management.
The DG protection issues depend on the type of generator and the characteristics of the network. Network protection issues depend on the type and location of the DG installation and network characteristics.
Thus protection design requires good communication between DG project developer and network service provider during the design process.
It may be difficult to develop economically sound policies on how to pay for any required upgrades in the utility infrastructure to protect against those risks.
Experts generally agree that the current risks to the distribution system from the parallel operation of small generators, representing only a small fraction of a local distribution network’s capacity, are usually manageable.
| Title: | Power quality and economics of integration of distributed generation in LV networks – Master of Science Thesis by Konstantinos Angelopoulos, University of Strathclyde in Glasgow, Department of Mechanical Engineering |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 0.93 MB |
| Pages: | 94 |
| Download: | Right here | Video Courses | Membership | Download Updates |


