Power losses & tap changer operation
Power quality is an important issue for the distribution network companies. They must guarantee the electricity supply fulfilling the requirements for the consumers. In this thesis we investigate specifically voltage requirements. We use transformers and tap changers to see how the voltage works in an electric system and we analyze the relationships with other aspects of the system’s performance, like power losses or tap changer operation.

Voltage settings
Power quality is an important issue for distribution network companies. They must guarantee the electricity supply for the customers, while fulfilling certain quality requirements. Public institutions are involved in this topic as well.
There are European standards and, usually, every country has specific regulations for power quality too. One of these requirements is the voltage level. It has to be kept between the established limits. In order to do that, the distribution network companies should decide the best strategy using the technology within reach.
Also, they supply the loads profiles of one day which are made up of 24 values, one per hour. With PowerWorld, first we build a generic system that could help to find useful information related to the real system. Based on the real data, we build the models and we run several simulations of them.
Once we have the results of the simulations, we analyze them in order to discover potential problems. Then, we modify the settings of the model, especially in the transformer side, to investigate any change in the system that could improve the voltage quality.
Another aim of this thesis is to confirm theoretical aspects of the voltage, related to the set point and the deadband. So, with help of the simulation results, we look for relations between the voltage and others parts of the system like the losses or the tap changer operation.
Voltage control
There are several methods to control the voltage in order to keep high quality electricity supply. Some of them are introduced below:
Tap-changing transformers
A tap changer can vary the number of turns in one side of the transformer and thereby, change the transformer ratio. Normally, this can vary between 10-15% in steps of 0.6-2.1%.
There are several options to design the control of the voltage. One of them is to set a nominal value of the voltage with a deadband in a point of the line, and to control it with an integral controller.
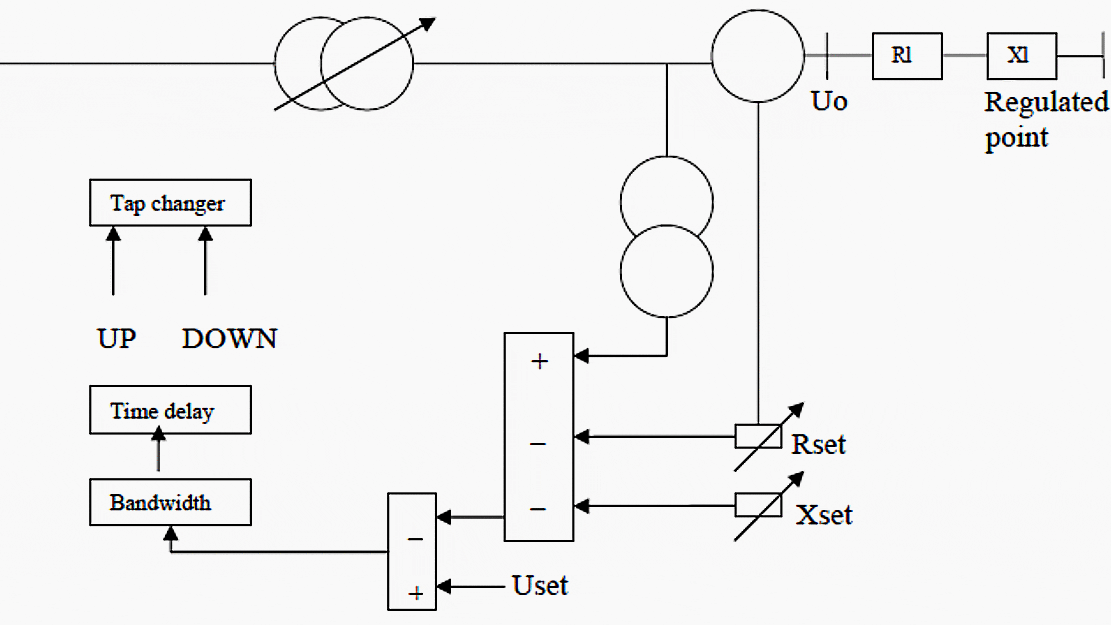
LDC system (Line Drop Compensation)
It is based on calculating the voltage drop knowing the reactance and resistance of the line and then, applying the set voltage based on these values with the tap changers of the transformers.
Figure 1 shows the main operation of the LDC system.
Compensation with reactive elements
For mainly reactive networks voltage is correlated with the reactive power so, one way to control it is to connect compensators and reactors in the nodes.
In distribution lines, there are several methods to control the power from the reactive elements like switched fixed capacitors/inductors, Static Var Compensator (SVC) or the static synchronous compensator (STATCOM). They are based on measuring the line voltage and comparing it with a given reference.
So, we connect capacitive compensators if we have to increase the voltage or we connect reactive compensation if we have to decrease it.
| Title: | Voltage regulation in distribution systems – Tap changer and Wind Power – David Sáez Romero at DIVISION of Industrial Electrical Engineering and Automation, Faculy of Engineering, Lund University |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 1.4 MB |
| Pages: | 59 |
| Download: | Right here | Video Courses | Membership | Download Updates |


Just discovered your existence through an accidental article I was reading on Facebook. Very impressed with your professionalism and your ability to guide people, novices as well as veteran professionals.
Thank you
Will browse a (good) few more articles before I surely will become a member
In great appreciation
Dirk