LV Busbar Trunking Systems
The object for this guide is to provide an easily understood document, aiding interpretation of the requirements to which Busbar Trunking Systems are designed and how they should be safely installed and used in service.
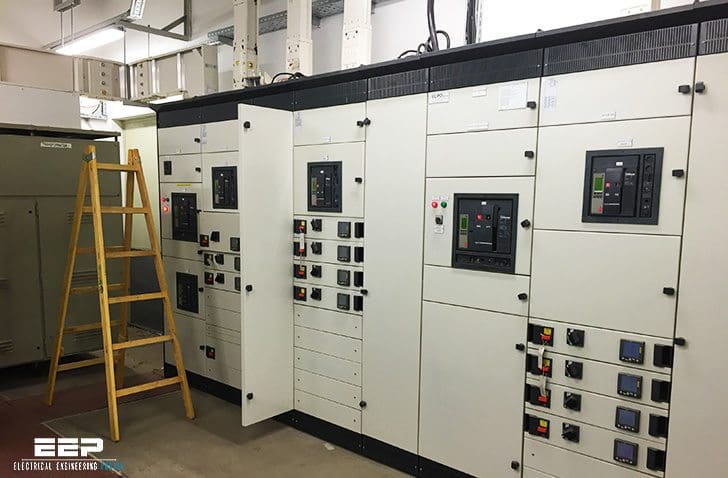

Distribution Trunking Run
This is the most common use of busbar trunking and is applied to distribute power over a predetermined area. Busbar trunking can be run vertically or horizontally, or a combination of both.
Three typical applications would be:
- Supply to large numbers of light fittings
- Power distribution around factories and offices
- Rising main in office blocks or apartment blocks to supply distribution boards serving individual floors or other busbar systems serving individual floors.
Seven biggest of advantages over cable:
- The contractor can achieve savings with respect to material i.e. cable trays and multiple fixings and also labour costs associated with multiple runs of cable.
- Reduced installation time since busbar trunking requires less fixings per metre run than cable.
- Multiple tap-off outlets allow flexibility to accommodate changes in power requirements subsequent to the initial installation (subject to the rating of the busbar trunking).
- Repositioning of distribution outlets is simpler.
- System is easily extendable.
- Engineered product with proven performance.
- Verified to recognised international and national standards. Aesthetically pleasing in areas of high visibility.
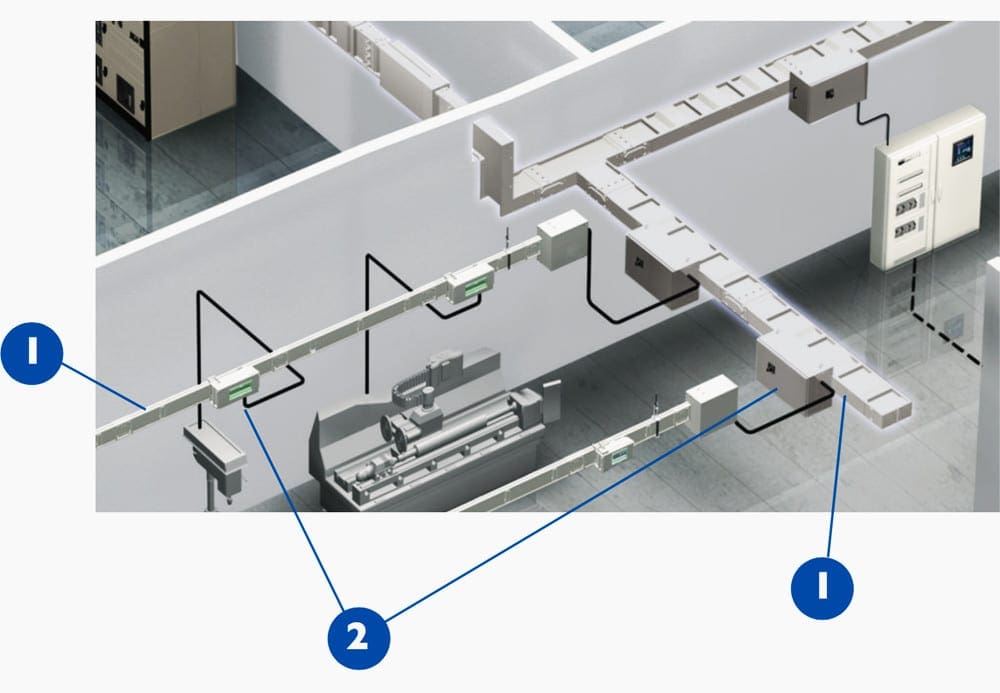
Feeder Trunking Run
Feeder trunking runs are used for the interconnection between switchboards or switchboard and transformer.
The advantages over cable are:
- Greater mechanical strength over long runs with minimal fixings resulting in shorter installation times.
- Replaces multiple runs of cable with their associated supporting metalwork.
- Easier to install compared to multiples of large cables with all of the associated handling problems.
- Less termination space required in switchboards.
- Verified short-circuit fault ratings including joints.
- Takes up less overall space, bends and offsets can be installed in a much smaller area than the equivalent cable space.
- Cable jointer not required.
- Busbar trunking systems may be dismantled and re-used in other areas.
- Busbar trunking systems provide a better resistance to the spread of fire.
- Voltage drop in the majority of cases is lower than the equivalent cable arrangement.
| Title: | Guide to low voltage busbar trunking systems verified to BS EN 61439-6 – BEAMA |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 4.50 MB |
| Pages: | 22 |
| Download: | Right here | Video Courses | Membership | Download Updates |



Hello. I have a question pls.
I saw a documentary on the building of the famous Burj al-Arab. To my utter surprise, for a building well over 300m high cabling and not busbar was used for the LV power distribution – over 5000km of cabling done.
this doesn’t seem electrically shrewd to me. could someone pls explain the electrical or technical reasons for choosing cables over busbar on this project?
I require catalog of different sizes of BBT with ampere capacities for industrial power distribution
Hola gente, si a alguien le interesa colocar sus productos en Argentina, pueden contactarme por privado.
Saludos
Dear Sir
I am looking for BBT to sell to Bangladesh market.
BR
Azhar