Electric Power Transmission System
The electric power transmission system comprises a grid of high voltage transmission lines and substations, which establish connections between distant power plants and substations located in close proximity to populous regions or loads. To minimize power losses over long distances, electricity is transported at high voltage.

Electricity is converted from high voltage to medium voltage and finally to low voltage near the consumers or loads, in order to be used. Most of the electric energy in Alberta is transmitted as alternating current (AC) through aluminum conductors. In alternating current (AC) systems, the direction of electric charge periodically changes.
An AC system offers a significant benefit in its ability to efficiently convert between low and high voltage utilizing a power transformer. High voltage direct current (HVDC) is a good technique for transmitting large amounts of power.
Direct current refers to the flow of electric charge in a single direction. At the transmitting and receiving ends of an HVDC transmission line or cable, converter stations “convert” direct current back into alternating current and vice versa, where it can be distributed for consumption by normal AC distribution systems.
In an electric transmission line (AC or DC), electric current flows through insulated metal conductors (usually aluminum), and power is delivered via the electric and magnetic fields around these conductors. In an overhead transmission line, the surrounding air acts as an insulating medium between the conductor and the ground.
The live conductors are then supported and insulated from the transmission line construction using insulator units made of porcelain, glass, or polymers.
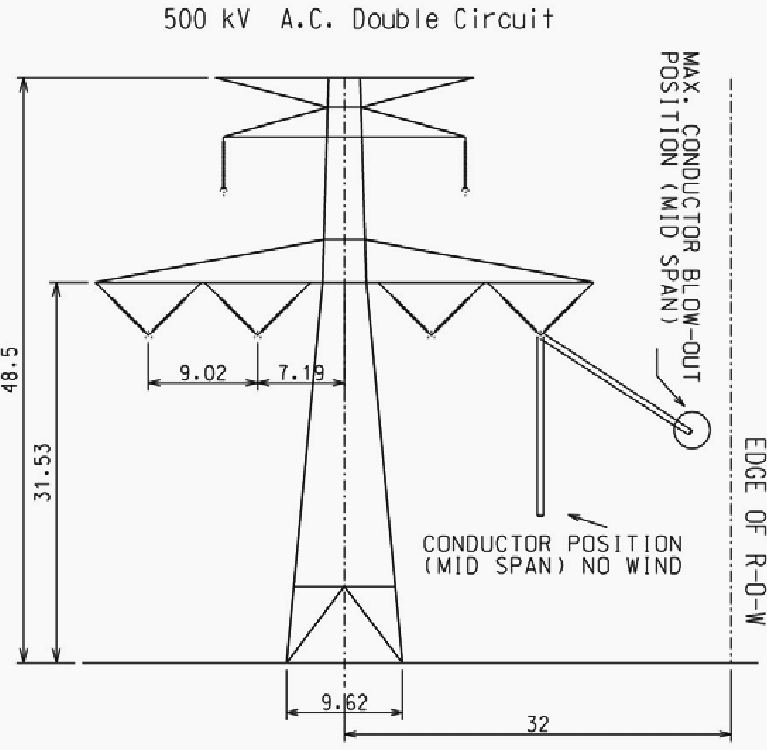
Figure 1 – 500kV AC Double Circuit Tower for 380m span
Underground power lines are increasingly being used to transmit electricity in highly populated urban areas. Metal conductors in power cables are completely wrapped by an insulating media, which is typically oil and paper or polymers such as polyethylene or cross-linked polyethylene.
In certain situations, very short transmission lines can be built with pressurized SF6 gas as an insulating medium. These gas-insulated transmission lines are made up of an inner aluminum conductor tube, insulating spacer rings, and an outer aluminum sheath tube. Because of the high capital, operating, and maintenance costs, this form of pressurized SF6 construction has limited applications.
To far, the highest length of any installed HTS system is less than 1 km, and these were mostly research and development programs with significant government funding.
The above-mentioned electric power technologies use metal conductors to connect a power or generation source to an electrical load. Wireless power transfer using the same physical principles as those employed in the telecommunications and broadcasting sectors is also feasible.
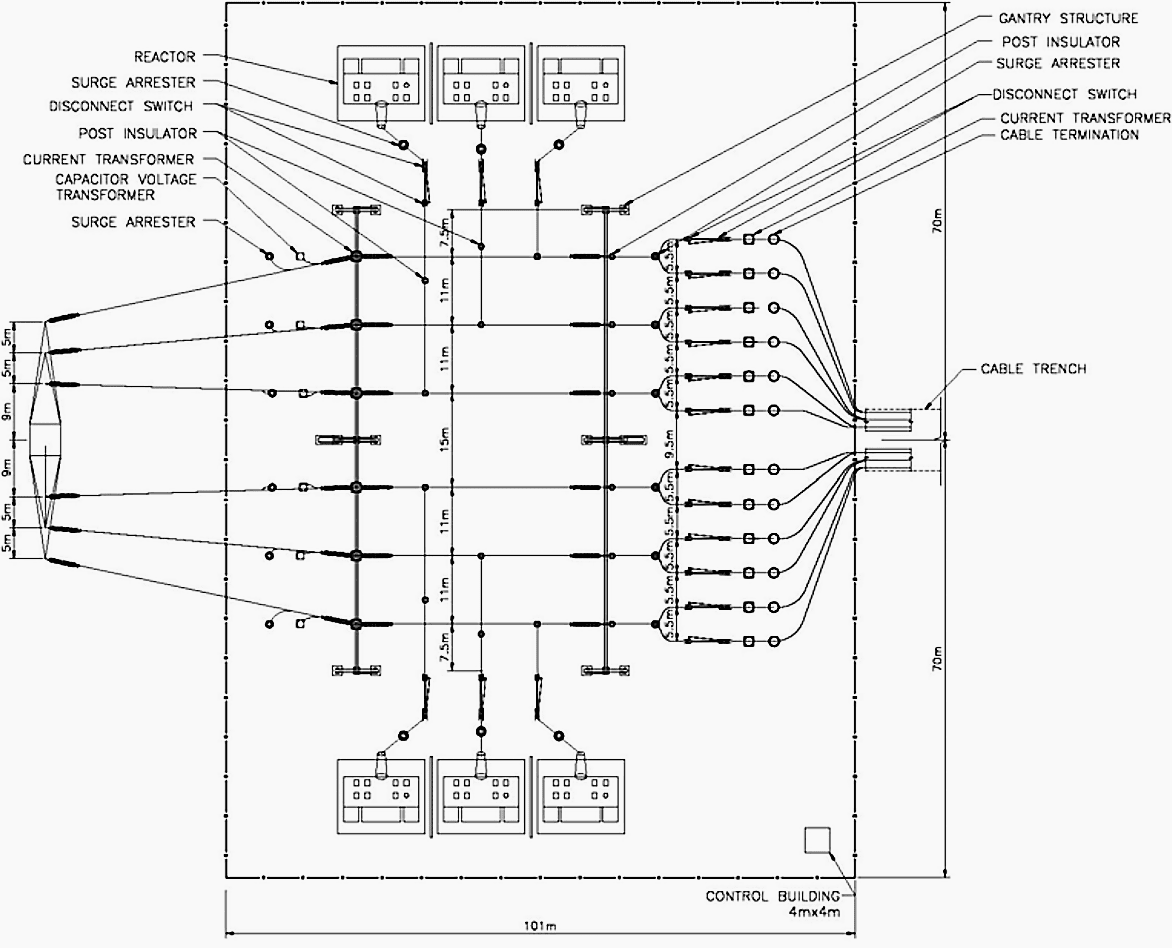
Figure 2 – Transition Station with shunt reactors- double circuit overhead line to underground cable
This sort of wireless power transmission is accomplished by electromagnetic induction, microwaves, or lasers. The three major needs of a power transmission system are listed below.
- Large amount of power to be transmitted,
- Long transmission distance between generation and load, and
- High efficiency requirement for a commercial installation (low losses)
Taking into account the specific local characteristics, it is obvious that at current time, only four electric power technologies can be evaluated for application in Alberta:
- AC Overhead Transmission Lines
- AC Underground Cables
- HVDC Overhead Transmission Lines
- HVDC Underground Cables
| Title: | Review of power transmission systems, HVDC, underground and others – ADOE |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 2.50 MB |
| Pages: | 137 |
| Download: | Here 🔗 (Get Premium Membership) | Video Courses | Download Updates |
Good Reading – Critical factors to bear in mind when designing IEC 61850 communications for digital substations
Critical factors to bear in mind when designing IEC 61850 communications for digital substations

