Power quality vs. voltage sags
The various factors that make up power quality have developed together in the course of time and in step with the overall development of society and the electrical industry. Interest in power quality has moved from long interruptions and undervoltage towards shorter-duration phenomena, such as shorter interruptions and voltage sags.

Nowadays, for some special customers, the economic losses caused by voltage sags may even be higher than the costs associated with interruptions. Voltage sag analysis should thus be considered as one essential input in the technical and economic optimization of distribution network design and operation.
In this thesis, the main interest is the voltage sags experienced by customers connected to power distribution networks.
The increase in understanding obliges power distribution companies to provide their customers with more information regarding voltage sags. Power distribution companies should be aware of the characteristics of voltage sags experienced in their network.
In addition, they should be able to evaluate the effect of alternative system configurations on voltage sags and their possibilities to reduce the inconvenience caused by sags.
In addition, examples of calculated and measured voltage sag distributions are presented. Voltage sag characteristics are expected to change if certain specified network improvements are carried out.
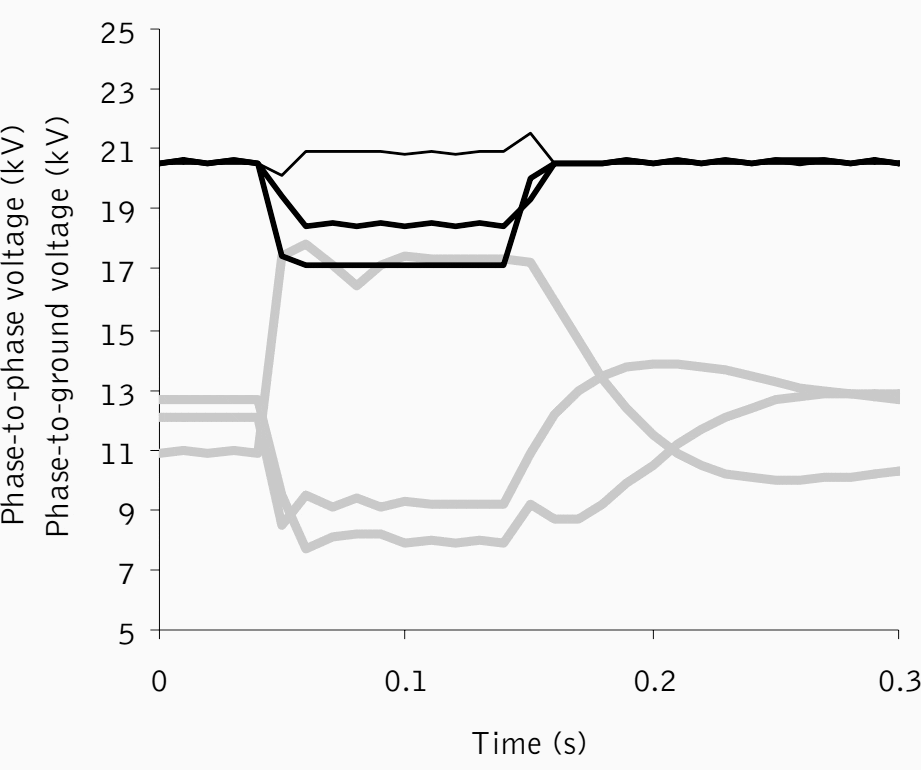
In this thesis, typical power system characteristics are judged in terms of voltage sags. This thesis introduces as main contributions:
- An extended method of fault positions to calculate the voltage sag distribution experienced by customers in power distribution networks.
- Examples of calculated and measured voltage sag distributions.
- Analysis of the influence of various network characteristics on experienced voltage sags. This part includes the analysis of network characteristics such as:
- Overvoltage protection of power distribution transformers (spark gaps / surge arresters / externally gapped metal-oxide surge arresters)
- Medium voltage feeder type (bare overhead line / covered overhead line / underground cable / mixed feeder types)
- Power distribution automation (various levels of automation implemented in different network types).
The thesis consists of a summary with six Chapters and the original papers, Publications I-VIII, which are enclosed as Appendices. Chapter 2 defines voltage sags and the causes of voltage sags. Chapter 3 introduces the calculation of a voltage sag distribution and the main aspects to be taken into account in the calculations.
Chapter 4 applies the developed model and gives examples of calculated and measured voltage sag distributions. Chapter 5 is the main chapter of this thesis. It introduces how the overvoltage protection of power distribution transformers, different MV feeder types and distribution automation affect the sag distribution.
The summary ends with Conclusions in Chapter 6.
| Title: | Analysis of voltage sags in power distribution networks (Doctoral Dissertation) – Pirjo Heine at Helsinki University of Technology; Department of Electrical and Communications Engineering; Power Systems and High Voltage Engineering |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 671.4 KB |
| Pages: | 68 |
| Download: | Right here | Video Courses | Membership | Download Updates |



is very helpful please try to upload all data needed analytically to calculate all power quality problems with example