22kV Distribution System
The 22kV distribution is primarily directed at urban and other densely populated areas, and our efforts are focused on reducing overall costs (by making the equipment more compact and reducing equipment costs), by enhancing the distribution system to ensure improved reliability and better availability.

To optimize the distribution efficiency from substations, 22kV power may be distributed to the point of demand where it is stepped down to 6kV, or in other cases such as industrial zones and sparsely populated regions, power may be supplied by 6kV distribution systems.
Let us first consider the 22kV supply side equipment that is currently available.
22kV Low Voltage Direct Supply
1. Main and backup line system and loop systems
This is the most common system for receiving 22kV power. Since it has somewhat smaller transformer capacity than spot networks (SNWs), it is more economical both in terms of space and cost, and is therefore extensively deployed (see Figure 1).
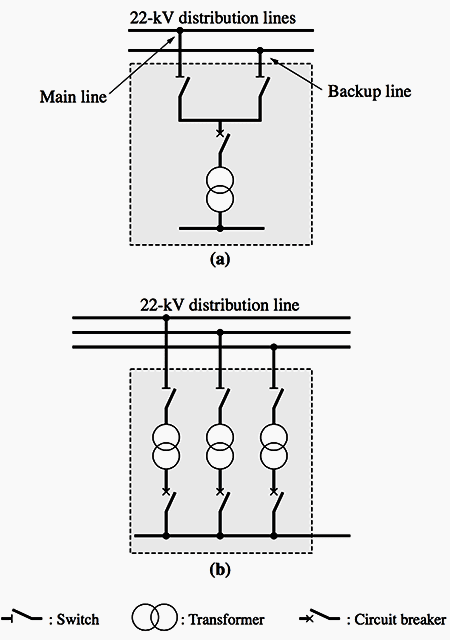
2. Spot network (SNW) systems
A spot network consists of the secondaries of three transformers connected together to maintain a constant source of supply even if one transformer fails.
SNWs are generally deployed as low voltage SNWs in which transformer secondaries supply low voltage power or as high voltage SNWs in which transformer secondaries supply 6kV to support efficient distribution within a single building (see Figure 1).
3. Regular network (RNW) systems
By interconnecting several RNWs on the low voltage side, load can continue to be supplied from another system in the event one system fails.
RNW systems maintain a constant source of supply and are generally applied in bustling shopping areas such as Ginza and Shinjuku in Tokyo.
However, this system is not being expanded because of the numerous requests from customers for 6kV power and because the system is insufficient in maintainability, operability and expandability.
| Title: | Development of 22kV Distribution Systems and Switchgear – Shuichi Kikukawa, Kenji Tsuchiya, Satoru Kajiwara and Akira Takahama |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 1.4 MB |
| Pages: | 7 |
| Download: | Right here | Video Courses | Membership | Download Updates |


Hi,
We can analized distribution networks in many way ;
-interconection in power station in fails way condition, for supply the customers without drop down energy;
-pass energy from an line to other in different condtition;
There are a lot relays protection for analize the function conditions in each electrical distribution station;
– the relays protection for transformers cells(settings and communication protocols);
– the relay protection for the lines(settings and communication protocols);
-local controls of the cells(the interupters of cells);
-the controls by remote of the cells (the interupters of cells );
-the analize of events local( in relays) or to distances( control centers through SCADA);
We can discuss a lot about an distribution system.
For designs I consider that you can use the Electrical Solidworks software which it is very good for such projects.
Thank you
Hi,
Thank you for uploading this file. The number of pages does not match what is posted (7 vs 84), is this a typo or there might be more than one document?
Thank you,
It’s a typo. Sorry for the confusion, this is the document and number of pages is 7.
Hi
I need a design program for 20kV overhead transmission lines.
Thank you