Testing Power Transformers
High voltage transformers are some of the most important (and expensive) pieces of equipment required for operating a power system. The purchase, preparation, assembly, operation and maintenance of transformers represent a large expense to the power system.
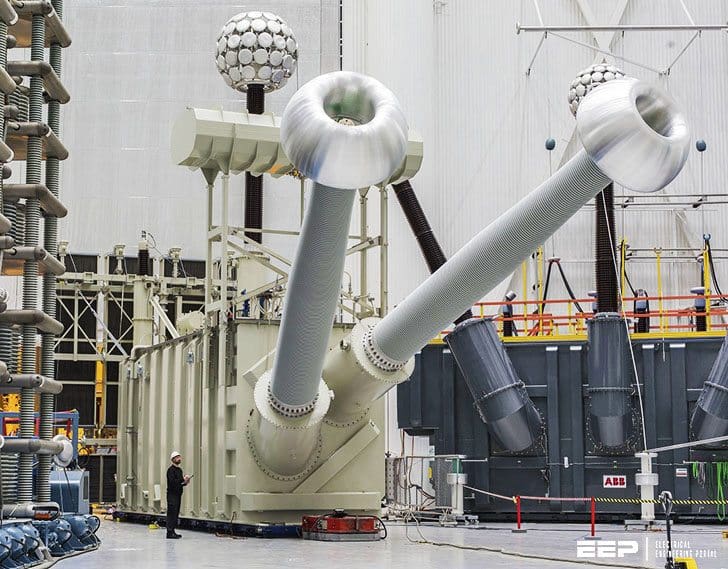
When transformers are received from the factory or reallocated from another location it is necessary to verify the following: that each transformer is dry, no damage has occurred during shipping, internal connections have not been loosened, the transformer’s ratio, polarity, and impedance agree with its nameplate, its major insulation structure is intact, wiring insulation has not been bridged, and the transformer is ready for service.
Physical size, voltage class, and kVA rating are the major factors that dictate the amount of preparation required to put transformers in service. Size and kVA rating also dictate the kind and number of auxiliary devices a transformer will require.
There are a multitude of checks and tests performed as a transformer is being assembled at a substation. The test engineer may not directly perform all of the following tests and inspections but must be sure they are satisfactorily completed, so that the final decision over transformer bank readiness for energization can be made.
Some tests and procedures may be performed by specialists during the assembly phase. Special tests, other than those listed, may also be required. Many require special equipment and expertise that construction electricians do not have and are not expected to provide.
Some tests are performed by an assembly crew, while other tests are done by the person(s) making the final electrical tests on the transformers.
The following information is not intended to describe, or include, the details for performing the entire array of tests needed to prepare transformers for service, only the tests that may be performed by field personnel. Even though details have been limited, descriptions should allow field personnel to perform, or assist in performing, the basic tests they may be asked to do.
The following items are discussed or described:
- Nameplate Data
- Power Meggering
- Auxiliary Components and Wire Checks
- Lightning Arrestors
- Hand Meggering
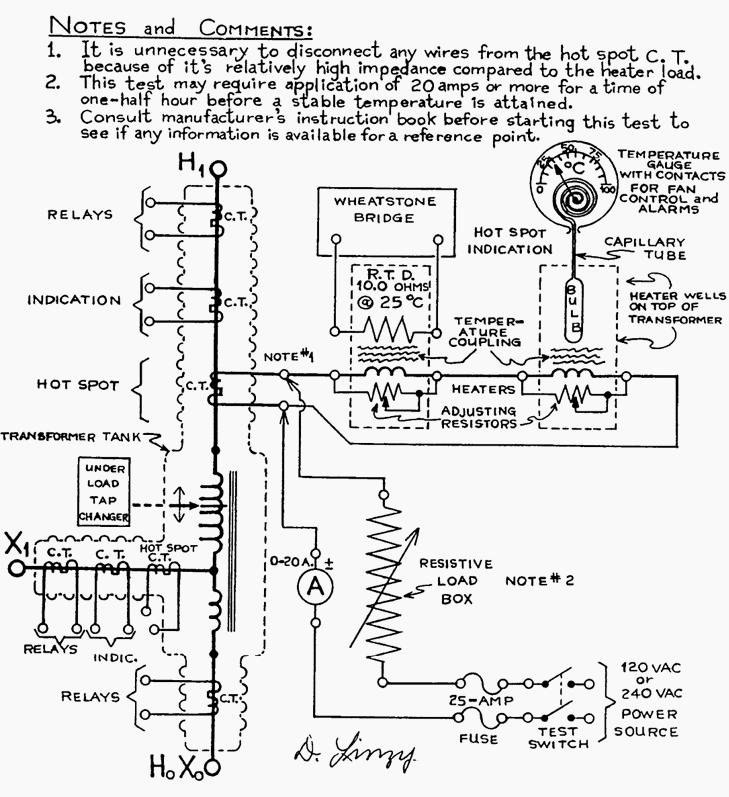
- Temperature Devices
- CT Tests
- Winding Temperature and Thermal Image
- Bushing Power Factoring
- Remote Temperature Indication
- Transformer Power Factoring
- Auxiliary Power
- Voltage Ratio
- Automatic Transfer Switch
- Polarity
- Cooling System
- Transformer-Turns Ratio
- Bushing Potential Device
- Tap Changers
- Auxiliary-Equipment Protection and Alarms
- Short-Circuit Impedance
- Overall Loading
- Zero Sequence
- Trip Checks
- Winding Resistance
Procedures and tests are described somewhat generically, but apply to most transformers in one way or another. Also, the following test descriptions provide an anchor point from which to ask for help when needed.
| Title: | 25 High Voltage Transformer Tests and Commissioning Procedures (Before Energizing) |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 2.8 MB |
| Pages: | 83 |
| Download: | Here 🔗 (Get Premium Membership) | Video Courses | Download Updates |


