Substation equipment in buildings
This guide enables its readers to assess electrical load of a building and thus enabling to find out the required capacity of the switchgear, transformers etc. It deals with 33 kV/11 kV, 33 kV/0.433 kV & 11 kV/0.433 kV substations and includes HV panels, transformers, bus ducting, LV panels (essential & non-essential), APFC panels, SCADA panels, DG sets, DG synchronizing panels, UPS, solar PV panels, IBMS, rising main etc. for offices, hospitals and institutional buildings.

Objective of modern power distribution system
The main objective of a modern modern power distribution system is to provide quality and uninterrupted power supply to the building so that there is no disruption to the productive operation of various services operating in the building to ensure human comfort.
Design considerations
Indoor Substations and Underground Cable power distribution
Substation specifications in this guide are based on Indoor substations with standby equipment and UG cabling for ensuring service with minimum breakdowns to overcome the disadvantages of outdoor substations as:
Outdoor substations are subject to dust, rain, storm, extreme heat and theft leading to breakdowns and higher maintenance. During winds, cyclones and storms, the entire distribution system including poles, and conductors collapse taking long time to restore the power supply.
The indoor substations work at much lower ambient, say at 28 Degree C, when the outside temperature may be above 40 degree C. Similarly the UG cable of power distribution is far superior to overhead system.
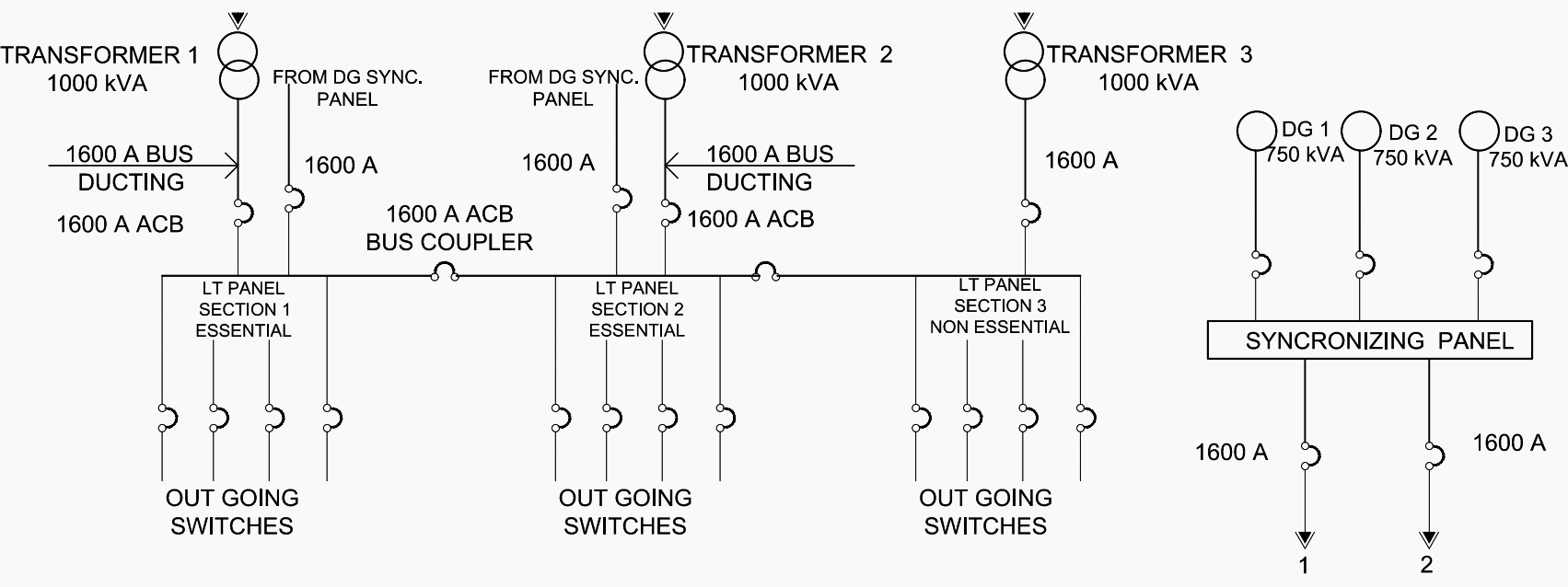
Notes:
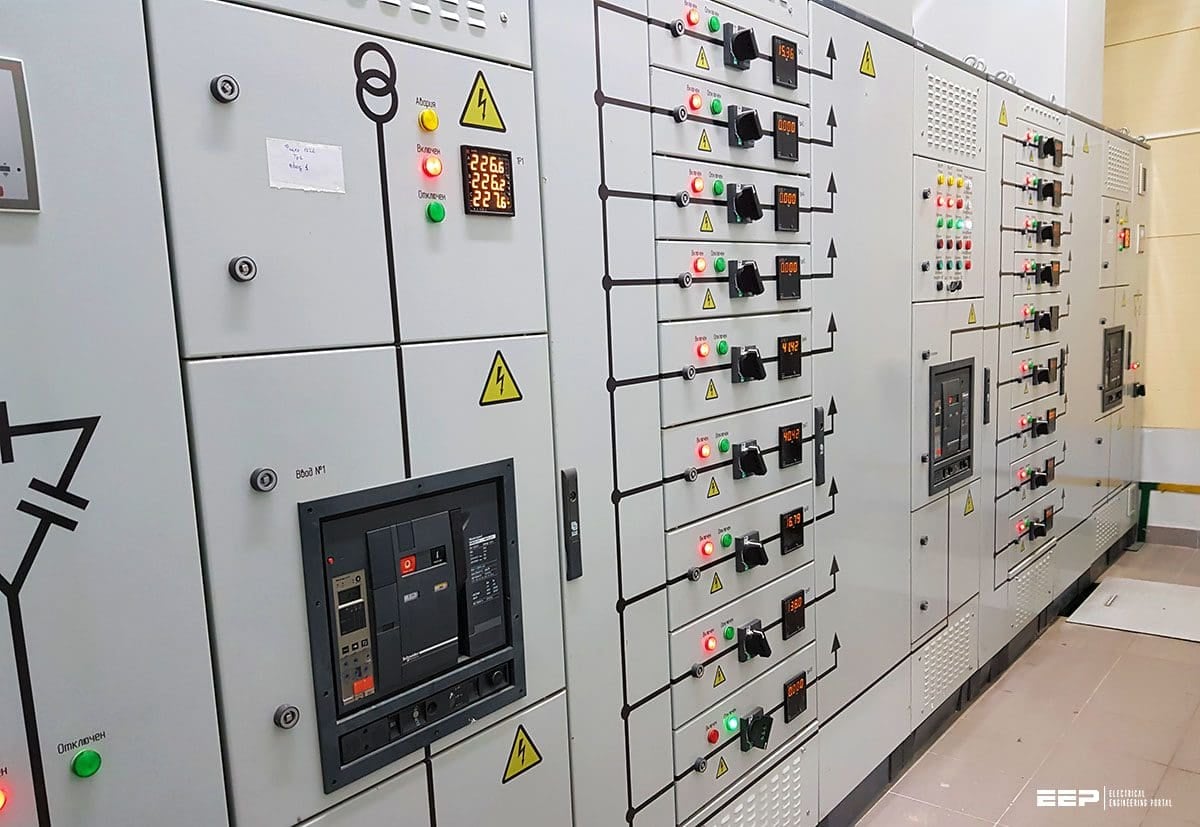
- The entire system is controlled / monitored through PLC/SCADA panels
- All switches above 800 a will be ACB and up to 800 a will be MCCB.
Substation with DG Backup
Uninterrupted power supply is supplied by the substation to cater to various loads based on DG Backup and UPS backup. The decision on central vs. building wise UPS provisions are to be taken after careful technical and economical consideration and user requirements.
DRY versus Oil cooled transformer
Oil cooled transformers are not allowed to be located inside the building. They are allowed when the substation is away from the main building. However it is recommended to go for dry transformer in place of oil cooled transformer for following reasons:
- Not prone to fire and explosion thereof.
- Practically maintenance free.
No wall enclosure for transformer required and substation space requirement is reduced. For example, with VCB HT Panel, dry transformers, the substation layout can be one hall.
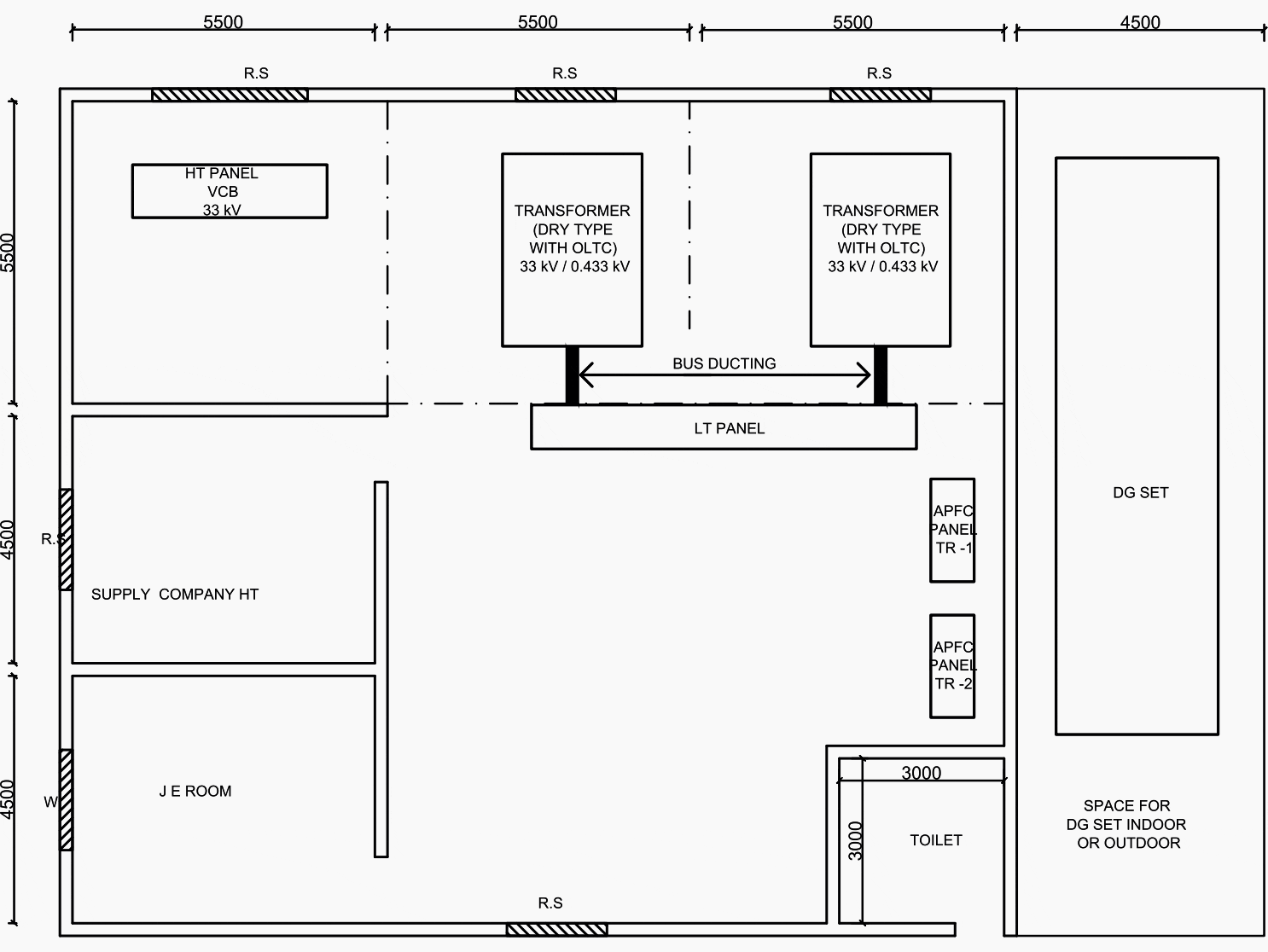
Voltage stabilization with Transformers with OLTC
Fluctuating voltage is quite harmful to the substation equipment. As a standard practice if the supply voltage is less than 380 volts and more than 440 volts, the equipment should be shut down. Therefore transformer with OLTC should be provided as a standard practice for the safety of the equipment.
Distribution substation DG Back up
It is recommended that each distribution substation should have its own DG Backup so that in case of mains power failure local DG sets are available as backup as per the normal practice.
It is not recommended to have a centralized DG Backup to supply 11 KV DG Power to the distribution substations. This will not allow for segregation of essential and non-essential supply. Also in case of any fault in 11 KV feeder cable the whole campus will have no DG Backup.
Indoor Vs Outdoor DG Sets
Indoor DG sets can be installed indoors or outdoors as decided by technical sanctioning authority after taking into account all relevant considerations. Indoor DG sets can be provided subject to proper smoke exhaust and provision of required quantum of ventilation air. Often, site conditions do not permit installation of DG Sets outdoor.
It has become common practice to install DG sets indoors for architectural, aesthetic and security reasons and also for limited outdoor space availability.
| Title: | Design notes of substation and power distribution systems of buildings |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 1.1 MB |
| Pages: | 51 |
| Download: | Here 🔗 (Get Premium Membership) | Video Courses | Download Updates |


The latest trend in highrise buildings especially in load profiling and frequency distribution. Share published works on the same.
You lecture is understood.Please what is the difference between circulating current and magnetizing current.
How does circulation current will affect a standalone distribution transformer say : 2.5MVA,0.415KV transformer ?
I really want to go deal into this course and get certified.
Please how do I go about it.
Regard
Joseph Ilegah
Mody University
So excited to have suddenly run into u this evening. Pls always keep me up dated.
Excellent to have such ideas and I admire
Latest trends in highrise buildings electrical designs including building systems