Introduction to substation automation
Substations in electrical grids are devices which are used for connecting transmission and distribution lines. They are used in transmission and distribution of power. Typical substation receives the electricity and based on the its location it either needs to step up the voltage or step down the voltage and transmit the power down the line.

Correspondingly, substations have either a step up transformer or step down transformer and lines to distribute the load. Hence we can compare the substation to a router in a communication network. Both of them receive data, process them and send it to the destination. In case of anomalies, the router can just discard the data or perform some action but a substation cannot do such tasks.
So with the involvement of power, a substation needs to have some kind of fault detection, fault tolerance and recovery mechanisms.
This combined with the fact that some substations are deployed in rough and inaccessible terrains, Substation Automation Systems (SAS) was introduced.
IEC 61850
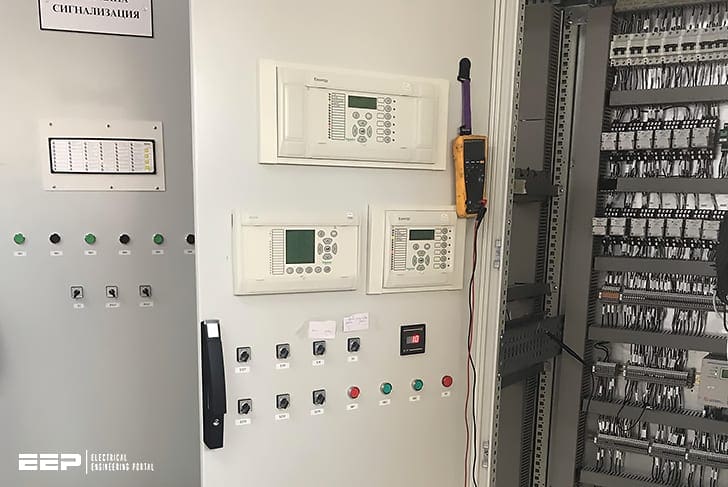
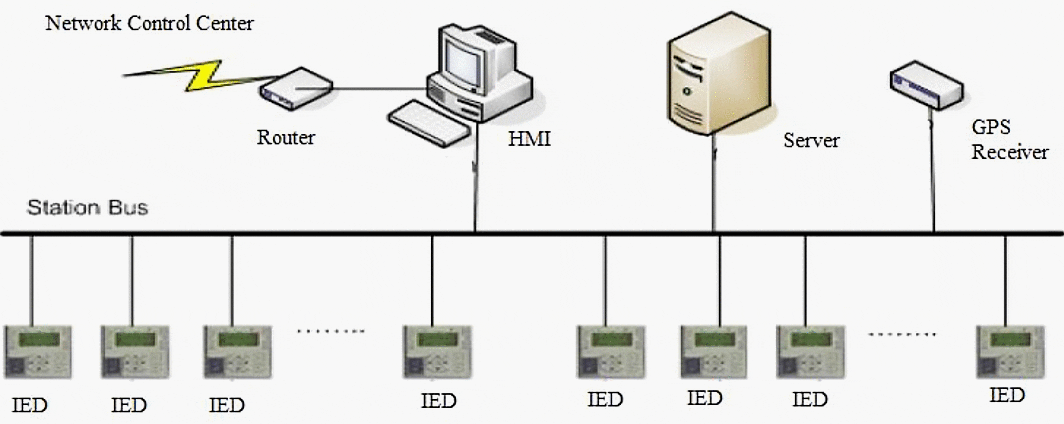
SAS uses Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) to control it’s functionalities. These IEDs are nothing but a microprocessor based controller that are capable of performing various functions. Various types of IEDs were designed to perform specific tasks.
Each of these IEDs used to follow different protocols to communicate based on the type of task they were supposed to perform. This led to a lot of complexities when the IEDs tried to operate together. Costly protocol converters were used to ensure interoperability of IEDs. These protocol converters also introduced delay in the network.
IEC 61850 used ethernet based technology to be the communication network. This protocol also defines the requirements for various communication and even takes care of substation automation in terms of project management, conformance testing, etc.
Thus IEC 61850 reduces the cost of the substation by avoiding protocol converters. It also establishes interoperability with minimum delay.
Role of IEDs
There are many types of IEDs in the substation network. Some of the IEDs include the Merged Unit (MU) IED, Protection IED, Control IED and the Breaker IED. As said before, each type of IED has a specific set of tasks to perform.
The MU IED is connected to the current and voltage transformers. The function of the MU IED is to receive the analog current and voltage values from the current and the voltage transformers. It then samples those values and sends the digitized values to the Protection IED.
All the three messages discussed here namely, the sample values, the trip message and the GOOSE message are all considered to be high priority and time critical messages.
Excessive delays in these messages mean failure to detect fault or failure to open the circuit and so the consequences are severe.
Apart from these IEDs, there is a Circuit Breaker Monitor (CBM) that monitors the breaker to see if they have been opened properly. These CBMs and the Protection IED records the event associated with the failure and sends out those records to the substation computer.
| Title: | Design and analysis of digital communication protocols in substation automation systems – ELANGOVAN KEMBANUR NATARAJAN at Texas A&M University |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 905 KB |
| Pages: | 60 |
| Download: | Here 🔗 (Get Premium Membership) | Video Courses | Download Updates |



very well, thank you