Good protection of MV networks
This booklet aims at illustrating the basic criteria needed for good protection of machines and plants in medium voltage networks. Selection of the protection system and relays depends on and is correlated with the plant characteristics, type of industrial process and its service continuity requirements, with the status of the neutral, characteristics of the machines, levels and duration of the fault currents, etc.

An excessive number of protections may also be harmful, since, even if they operate correctly in the case of a fault, they can operate in an untimely way when there is no fault, causing more or less widespread disturbance and out-of-order conditions, sometimes more damaging than the faults themselves, as the cause cannot be found (even protections can go wrong).
It is important to underline at once that trip selectivity must always be looked for, but must only be looked for after having ensured protection of the network component.
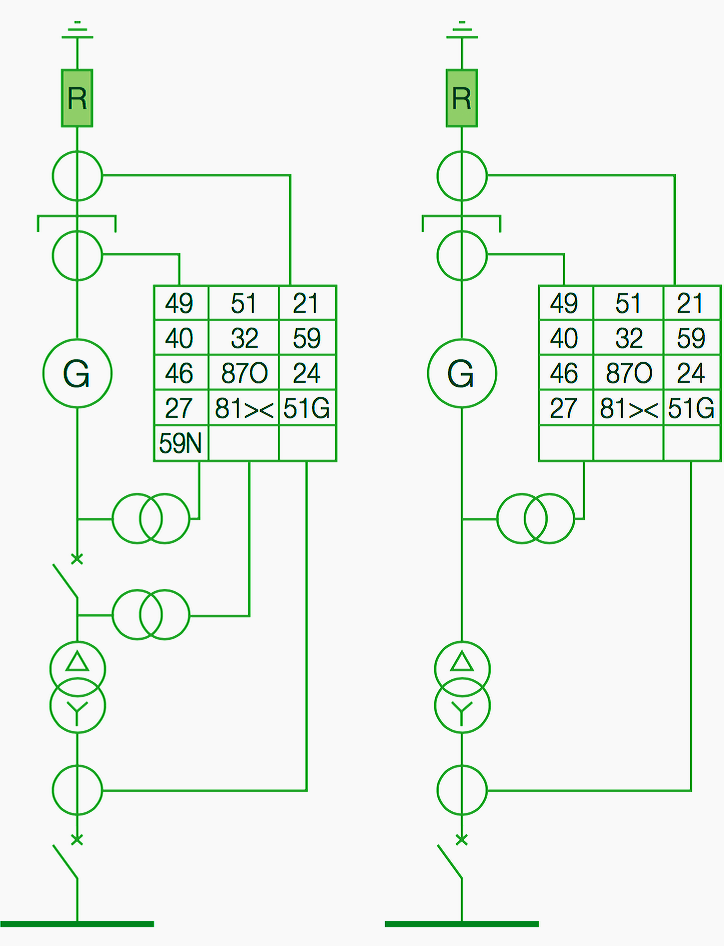
The protection relays are normally provided for different objectives and aims!
In some cases a protection relay is used with the aim of activating automatisms to manage the electric network. The latter is a special application although normal in plants, but in this case the relays cannot be considered as network and plant protections.
The main objectives of protection relays are:
- To provide the operator with an alarm indication under particular network or machine service conditions (for example protection against negative sequence for generators)
- To put the line or faulty machine out of commission within a short time, as defined in the selectivity study
- To carry out automatisms under particular service conditions (for example, undervoltage protections which activate automatic changeover or automatic reclosing of the lines)
- Control of the network parameters to prevent false operations (for example, synchronism check)
- To activate network parameter recording to memorise the network disturbances (for example, the starting contacts of the overcurrent relay)
- To carry out protection of the interface with the external network (with contractual not protection settings)
Identification of the abnormal conditions mentioned is made by the protection relays, which operate to separate the faulty part of the network from the rest of the plant.
The protection relay setting must be calculated to give the plant the highest possible service continuity to avoid damage to network components. The setting values must be selected above the transient conditions which can occur in the network without requiring disconnection.
| Title: | Technical guide – Protection criteria for medium voltage networks By ABB |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 3.9 MB |
| Pages: | 52 |
| Download: | Here 🔗 (Get Premium Membership) | Video Courses | Download Updates |
Suggested Guide – Testing & Commissioning Procedures for Substation Equipment
Testing and Commissioning Procedures for Substation Equipment

