Low Voltage Circuit Breakers
An electric system shall be protected by the damages which may result from overcurrents. An overcurrent can be divided into short circuit and overload. In both cases (short circuit as well as overcurrent), the cables overheat and, if there is not adequate protection, the temperature rise damages the electrical system and the connected equipment, with the risk of causing fires and subsequent serious damage to people and things.

Among overcurrent protective devices used as protection against overcurrents, there are circuit breakers which, in case of fault, open the circuit based on their tripping characteristics and on the overcurrent value.
The circuit breaker is a mechanical switching device, capable of making, carrying, and breaking current under normal circuit conditions and also, making and carrying for a specified time and breaking current under specified abnormal circuit conditions such as those of short circuit.
Each circuit breaker is equipped with a trip unit which actuates the circuit breaker release mechanism and allows opening on the basis of the current flowing through it.
Two types of trip units are used in low voltage circuit breakers: Thermal magnetic (thermal magnetic trip unit) and Electronic (electronic trip unit).
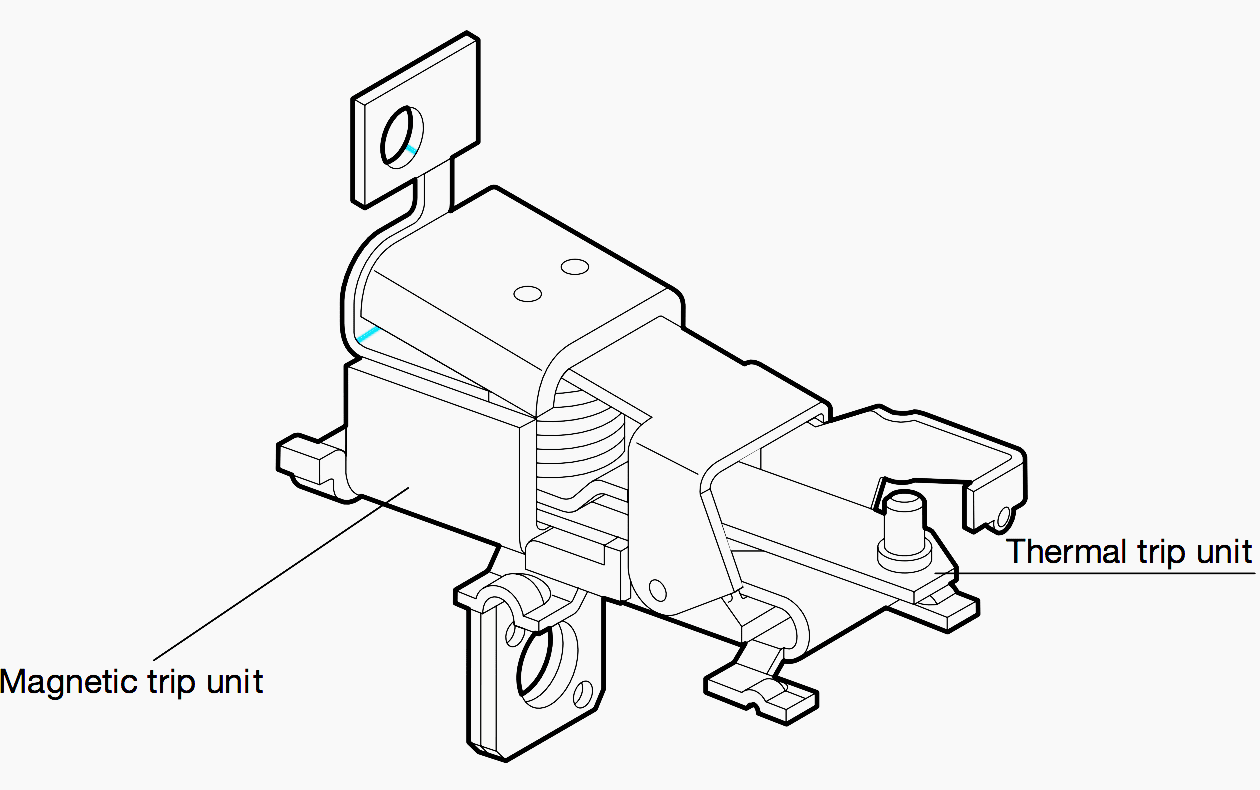
The thermal magnetic trip unit consists of two parts:
The thermal trip unit – Made up of a bimetallic thermal device which actuates the opening of a circuit breaker with a delay depending on the overcurrent value; for overload protection.
The magnetic trip unit – Made up of an electromagnetic device, with a fixed (fixed instantaneous trip) or adjustable (adjustable instantaneous trip) threshold, which actuates the instantaneous trip of the circuit breaker on a pre-determined overcurrent value (multiple of the In) with a constant trip time (about some tens of milliseconds) for short circuit protection.
By digital processing of the signal, they provide the following protection functions:
- The long time-delay trip function (ANSI code: 51, AC time overcurrent relay);
- The short time-delay trip function (ANSI code: 51, AC time overcurrent relay);
- The instantaneous trip function (ANSI code: 50, instantaneous overcurrent relay);
- The ground-fault trip function (ANSI code: 51 N, AC time ground fault overcurrent relay).
| Title: | Low voltage circuit breakers – Working with trip characteristic curves by ABB |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 948 KB |
| Pages: | 40 |
| Download: | Right here | Video Courses | Membership | Download Updates |


It is good
Thanks for information
Please explain for Ground Settings of PR222DS the formula of K=I^2*t. Thanks
I am expecting about relays like ref 542 615 functional depends on the protection how it manipulates and notify the alarms due to interrupt
I want to more about relay REF 542
GRACIAS¡¡¡¡ EXCELENTE INFORMACION… GRACIAS POR COMPARTIR…SALUDOS DESDE MEXICO¡¡¡
A good manual and while acknowledging the good content and presentation these features are available on other manufacturers breakers. The explanations associated with the curves and showing the Maximum and minim settings on one graph adds value to the information.