Power Distribution
Power, generated at a power plant and stepped up to a high transmission voltage, is brought to a local substation. Here, it is stepped down to a lower distribution voltage. When it reaches its final destination at a residential customer, it is stepped down to 240 volts.
Only single-phase power is used in a typical residential application.
Power Supply
The most common supply system used in U. S. residential applications today is a single-phase, three-wire supply system. In this system, the voltage between either hot wire and neutral is 120 volts and the voltage between the two hot wires is 240 volts. The 120-volt supply is used for general purpose receptacles and lighting.
The 240 volt supply is used for heating, cooling, cooking, and other high-demand loads.
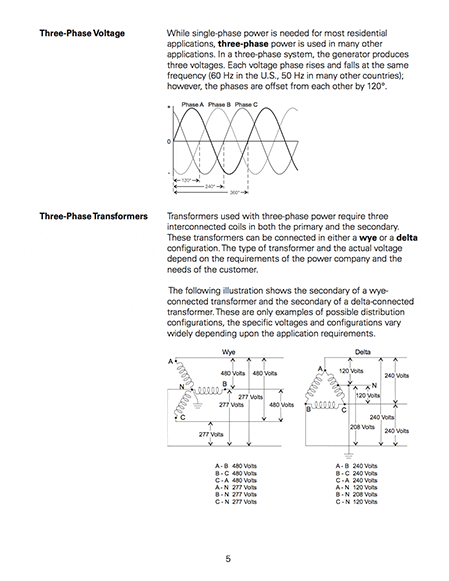
Three-Phase Voltage
While single-phase power is needed for most residential applications, three-phase power is used in many other applications. In a three-phase system, the generator produces three voltages.
Three-Phase Transformers
Transformers used with three-phase power require three interconnected coils in both the primary and the secondary. These transformers can be connected in either a wye or a delta configuration. The type of transformer and the actual voltage depend on the requirements of the power company and the needs of the customer.
Power, purchased from a utility company, enters the house through a metering device and connects to a load center. This is the service entrance. Service can come from an overhead utility transformer or from a lateral service run underground.
| Title: | Basics of Meter Mounting Equipment – SIEMENS |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 4.7 MB |
| Pages: | 64 |
| Download: | Right here | Video Courses | Membership | Download Updates |