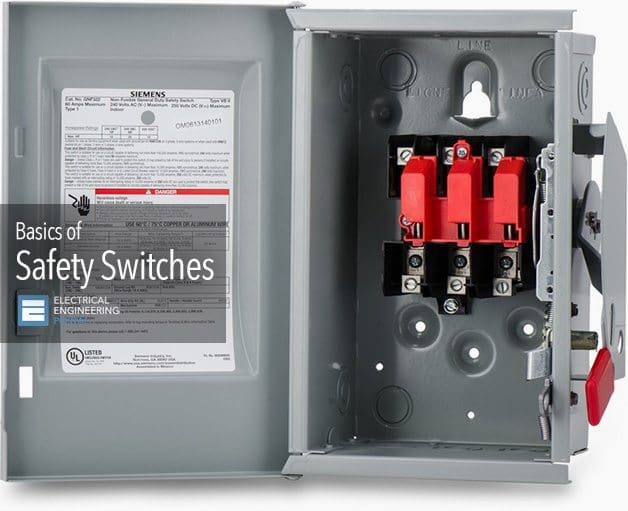

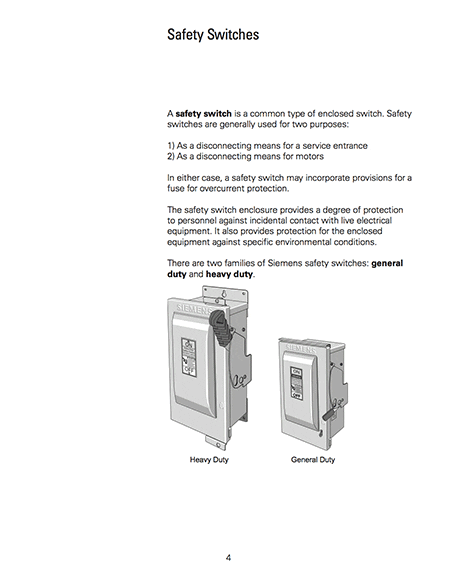
Safety Switches
A safety switch is a common type of enclosed switch. Safety switches are generally used for two purposes:
- As a disconnecting means for a service entrance
- As a disconnecting means and fault protection for motors
The enclosure provides a degree of protection to personnel against incidental contact with live electrical equipment. It also provides protection for the enclosed equipment against specific environmental conditions. Safety switches may consist of a switch only or may consist of a switch and fuses.
Application
Safety switches can be used in any number of applications. The National Electrical Code® (NEC®), for example, requires that a disconnecting means shall be located in sight from the motor location and the driven machinery location (Article 430.102(B)). The NEC® defines “in sight” as visible and not more than 50 feet (15.24 m) distant (Article 100 – definitions).
Non-Fusible Safety Switch
A safety switch with no associated fuses is referred to as a non-fusible safety switch. A non-fusible safety switch has no circuit protection capability. It simply provides a convenient means to open and close a circuit.
Opening the circuit disconnects the load from its source of electrical power, and closing the circuit connects the load. Circuit protection must be provided by external overcurrent devices such as a circuit breaker or fuses. In the following illustration, power is supplied to a motor through a non-fusible safety switch and a separate fuse.
Fusible Safety Switch
A safety switch can be combined with fuses in a single enclosure. This is referred to as a fusible safety switch. The switch provides a convenient means to manually open and close the circuit, and the fuse provides overcurrent protection.
| Title: | Basics of Safety Switches – SIEMENS |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 3.9 MB |
| Pages: | 72 |
| Download: | Right here | Video Courses | Membership | Download Updates |


Can a double throw non-fusible safety switch be used as service entrance rated manual transfer switch?
A electrical safety switch is a device that quickly interrupts an electrical circuit to prevent serious harm from an ongoing electric shock.
We have older Square D type safety switches installed for some of our machinery where I work. The front panels can be opened while the switch is in the “ON” position. The newer types have a switch interlock that prevents this. My question is, is there a current safety requirement that requires this interlock be installed, and do we need to change out all of our old safety switches with ones that have the interlock?