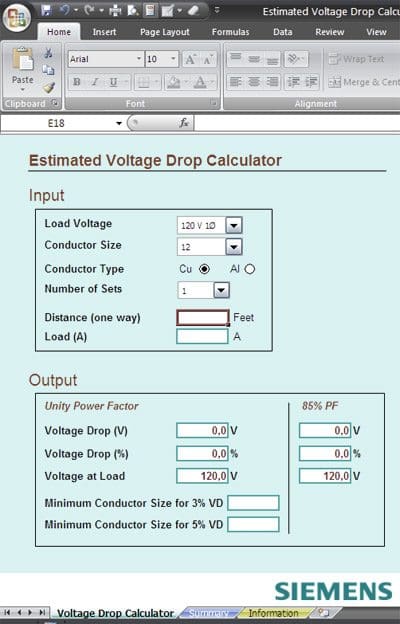
Voltage drop for feeders/branch circuits
This voltage drop calculator is based on public domain formulae and will provide an approximate value for use in project design.

The National Electrical Code Articles 210.19(A)(1) FPN No.4 and 215.2(A)(3) FPN No.2 suggest that a design with no more than 3% voltage drop for feeders and no more than a total of 5% voltage drop in branch circuits to the farthest outlet will “provide reasonable efficiency of operation”.
In fact Section 647, Sensitive Electronic Equipment. requires (not an FPN) that voltage drop for feeders and branches shall not exceed 1.5% and 2.5%. respectively and shall not exceed 1% and 2% respectively for cord-connected equipment. Fire pumps have additional maximum voltage drop requirements and these are outlined in Section 695.
If you do increase the size of your conductors to accommodate for voltage drop, remember to check if the new conductor size is compatible with the lugs to which they will be attached.
The circuit breaker manufacturers make available the acceptable conductor sizes. and in some cases offer optional larger lugs for this purpose. Also, Article 250 requires that if the conductors are upsized, the grounding conductor must also be upsized proportionately.
Vd = (2·K·Q·I·D) / CM for single phase and
Vd = (1.732·K·Q·I·D) / CM for three phase,
where:
- K equals 12.9 for Copper and 21.2 for Aluminum.
- Q is the ratio of Rac/Rdc for conductors larger than 2/0 (this takes into account skin effect at larger conductor sizes).
- I is the current in amperes.
- D is the one-way circuit distance in feet.
- CM is the conductor cross section in circular mils.
This equation assumes a power factor of 1.0, conductor temperature of 75°C, and individual conductors run in steel conduit. The 85% power factor section is based on NEC Chapter 9, Tables 8 and 9.
| Software: | Estimated Voltage Drop Calculator – SIEMENS |
| Version: | 1.1 |
| Developer: | SIEMENS |
| Size: | 67 KB |
| Price: | Free |
| Download: | Here 🔗 (Get Premium Membership) | Video Courses | Download Updates |


Thanks for sharing
The National Electrical Code Articles 210.19(A)(1) FPN No.4 and 215.2(A)(3) FPN No.2 suggest that a design with no more than 3 and no more than a total of to the farthest outlet will .
In fact Section 647, Sensitive Electronic Equipment. requires (not an FPN) that voltage drop for feeders and branches shall not exceed 1.5% and 2.5%. respectively and shall not exceed 1% and 2% respectively for cord-connected equipment. Fire pumps have additional maximum voltage drop requirements and these are outlined in Section 695.
If you do increase the size of your conductors to accommodate for voltage drop, remember to check if the new conductor size is compatible with the lugs to which they will be attached.
The circuit breaker manufacturers make available the acceptable conductor sizes. and in some cases offer optional larger lugs for this purpose. Also, Article 250 requires that if the conductors are upsized, the grounding conductor must also be upsized proportionately.
This equation assumes a power factor of 1.0, conductor temperature of 75°C, and individual conductors run in steel conduit. The 85% power factor section is based on NEC Chapter 9, Tables 8 and 9.
Thanks in advance
Thank you for your calculation tool.
How to calculate mv drop with respect to temp rise
It would be nice if you would develop software in metric for us in the southern hemisphere
IE kW and mm2
thanks for your help
Voltage drop in 11kv 27km long feeder either using dog or osprey conductor for 3000megawatt load?
Thanks for your effort
thanks for software
nice
be happy with u
Thank for free providing such a very useful calculator . We can manage to choose the correct cable size by using this . That will be very very cool .