Distribution substation
Distribution substation is a substation from which electric supply is distributed to the different users. In a substation there are numbers of incoming and outgoing circuits each having its isolator, circuit breaker, transformers etc. connected to bus-bar system.

These equipment are mostly static type.
Safety and protection of equipment as well as working personnel is also a considerable factor. Lightening arresters, earthing of equipment and fencing is done for this purpose.
The following equipment are installed in distribution substations:
- Distribution Transformer
- Circuit breaker
- Lightning Arrester
- Air Break (AB) switches / Isolator
- Insulator
- Busbar
- Capacitor Bank
- Earthing
- Fencing
- Distribution panel board
1. Distribution Transformer
The distribution transformer is a main and largest equipment of distribution substation.
It is basically a static electrical device which steps down the primary voltage of 33kV or 11 kV to secondary distribution voltage of 415-440 volts between phases and 215 volts between phase and neutral through delta-star windings by electromagnetic induction without change in frequency.
Transformer consists of the following parts and components.
- Primary winding
- Transformer tank
- Cooling tubes
- Buchholz Relay
- Tap changer
- Oil outlet valve
- L.T. terminals
- Temperature gauge
- Secondary winding
- Conservator
- Breather
- Explosion vent
- Oil inlet valve
- Oil level indicator
- H.T. terminals
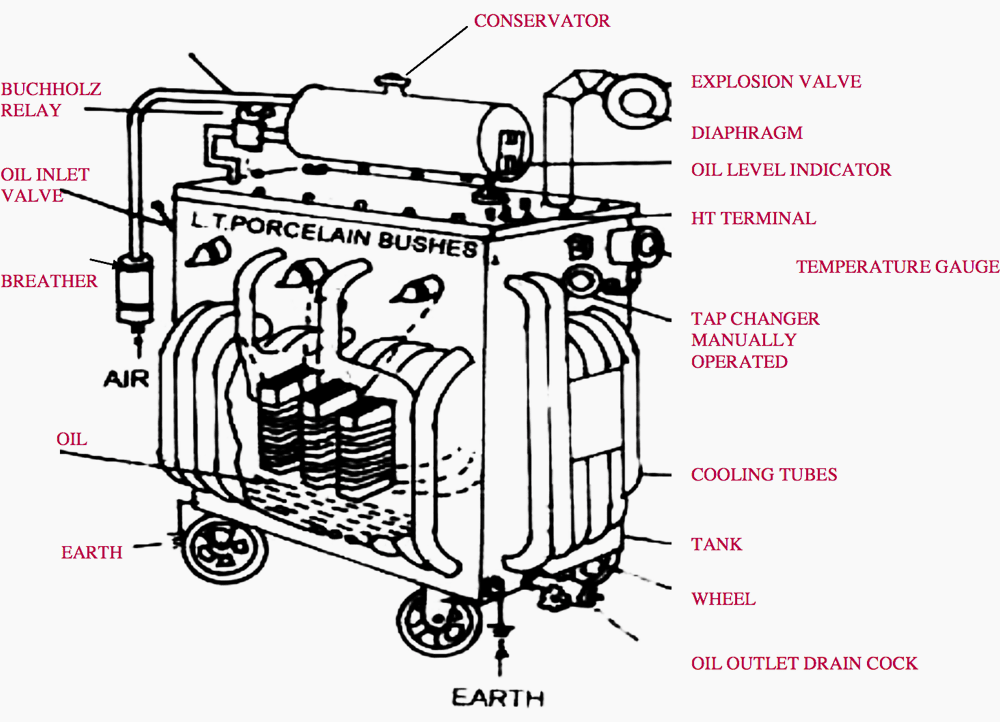

Important Transformer Components
Conservator
(Equipped with transformer of rating 500 kVA and above)
It is a drum containing transformer oil and mounted at the top of the transformer and connected to the main tank by a pipe. As the volume of oil of transformer tank expands and contracts according to heat produced, this expansion and contraction of oil causes the level of the oil in conservator to rise and fall.
The aim of conservator is to:
- Maintain the oil level in tank
- Provide space for the expanded oil


Breather
It is attached to conservator tank and contains silica gel, which prevents the moist air from entering into the tank during contraction of oil. When oil is hot there is expansion and gas passes to atmosphere through it. When oil is cooled, it contracts and the air enters in it.
It prevents transformer oil from moisture contamination.
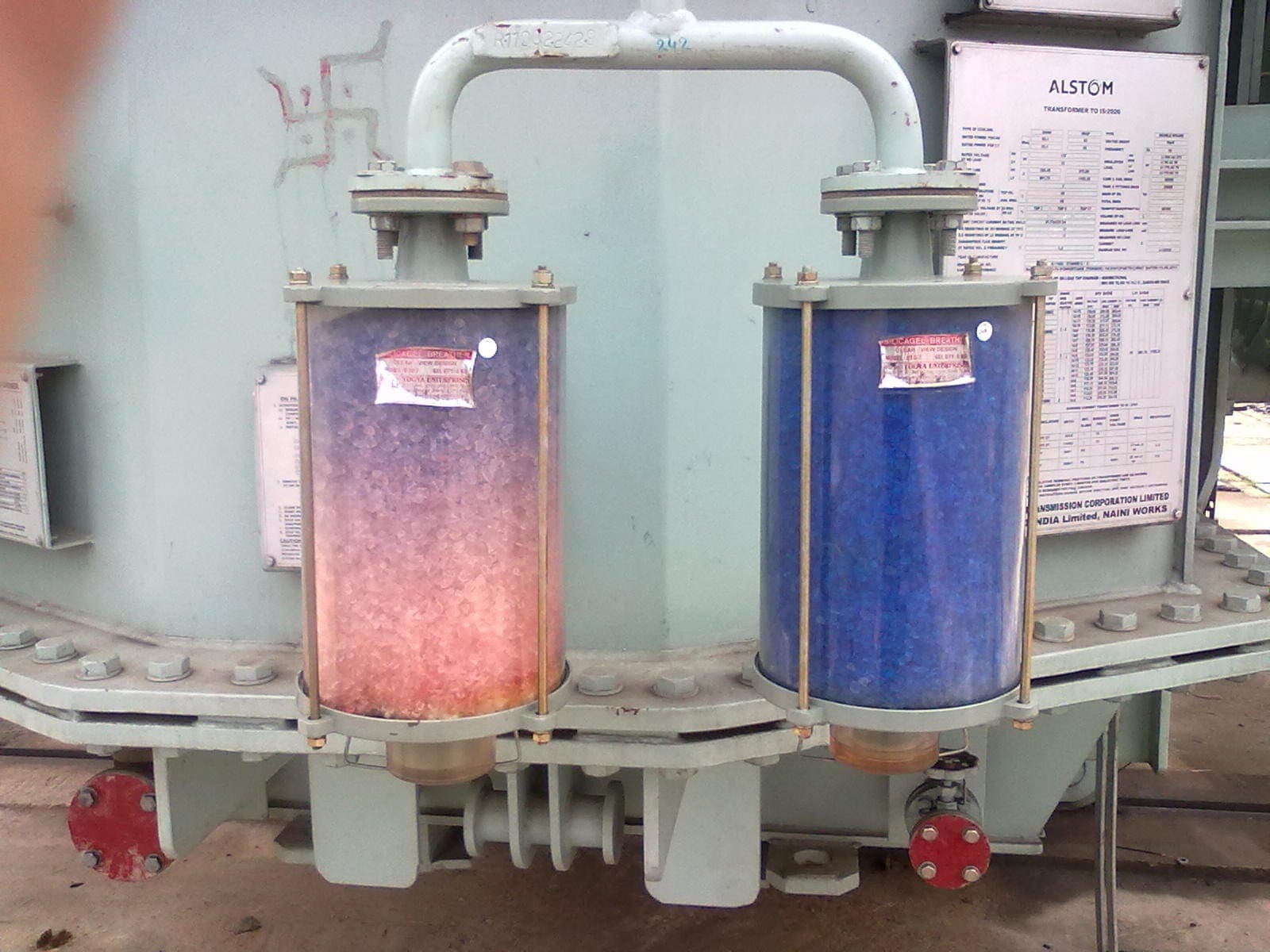


Buchholz Relay
It is protective relay of transformer. This device signals the fault as soon as it occurs and cuts the transformer out of the circuit immediately. This is gas operated protective relay. It is installed in between the pipe connecting the tank and the conservator.
It consists of two operating floats A and B. These are operated by two mercury switches separately provided for each float. The float A is for bell alarm and float B is for operating the tripping circuit.
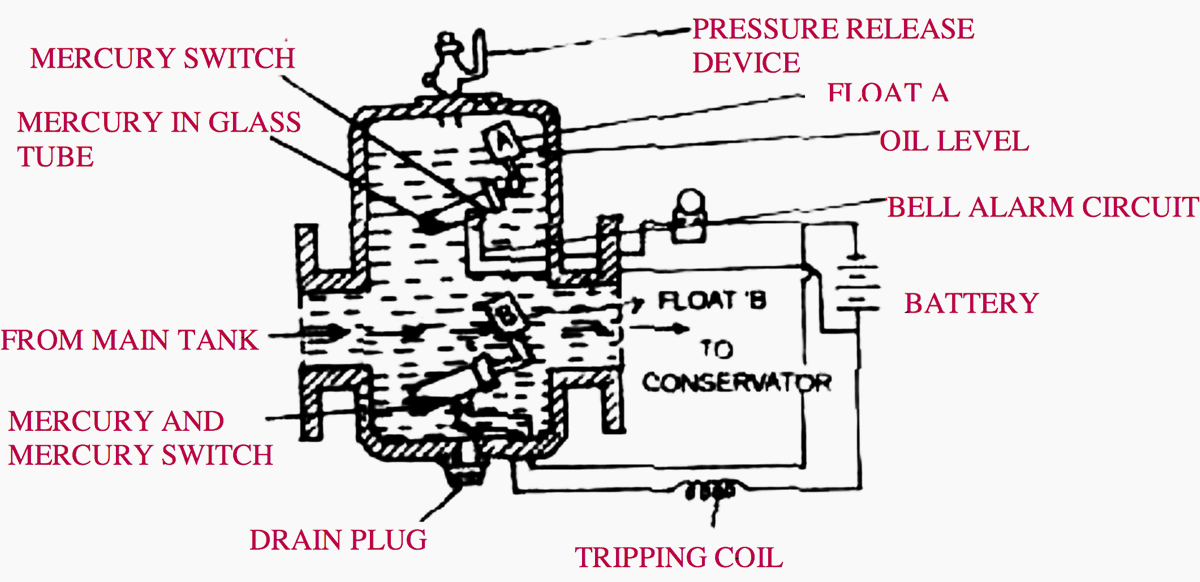

Whenever there is a minor fault or low level of oil, the bell alarm operated by float ‘A’ and whenever there is severe fault in the transformer, float ‘B’ operated due to excessive gases. It trips the circuit breaker and transformer is put out of circuit.
Explosion Vent
A major fault inside the transformer causes instantaneous vaporization of oil, leading to extremely rapid buildup of gaseous pressure. If this pressure is not released with in few milliseconds, the transformer tank can rupture, spilling oil over a wide area.
An explosion vent provides instantaneous releasing of such dangerous pressure and protects the transformer.
Oil level Indicator
It indicates level of transformer oil at the conservator of the transformer. It has markings on transparent sheet for maximum and minimum levels.


Inlet Valve
It provides passage to pour the transformer oil in the tank during purification or in case of shortage found in the tank.
Outlet Valve
It provides passage to drain the oil during overhauling or as and when required oil sample for testing.
Cooling Tubes
These tubes provide better and effective cooling of transformer oil by increasing the surface area of tank to the atmosphere.
Tap changer
The tap changer is used to regulate the output voltage manually according to line voltage. The taps of transformer can be changed by the tape changer manually. It is provided on HV side so that the voltage on LV side feeding to the load can be maintained.
Normally tap selection range is ± 15 % in steps of 2.5 %.
2. Circuit Breaker
The circuit breaker is an equipment which automatically cut off power supply of the system when any fault or short circuit occurs in the system. It detect and isolate faults within a fraction of a second thereby minimizing the damage at the point where the fault has occurred.
The circuit breakers are specially designed to interrupt the very high fault currents, which may be ten or more times the normal operating currents.
In distribution substation, generally oil circuit breakers, vacuum and air circuit breakers are used.


3. Lightning Arrester
Lightning arrester is a most important protective device of distribution substation to protect valuable equipment as well as working personnel. It arrests and discharges over voltage to earth during lightning strokes. These are installed between line and earth near equipment.
Representative values of a lightning stroke:
- Voltage: 2 × 10-8 volts
- Current: 2 × 104 Amps
- Duration: 105 seconds
- Power: 8 × 105 kW
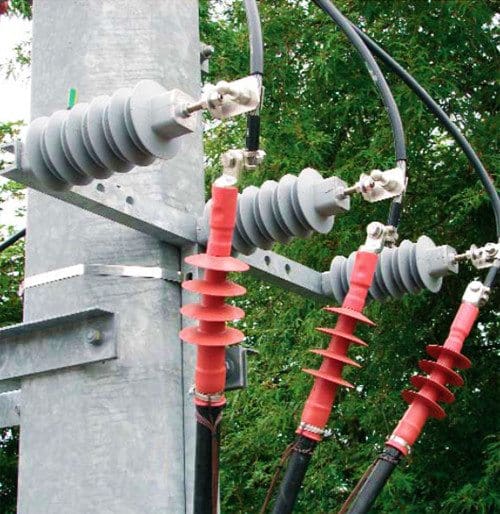


4. Air Break (AB) Switch / Isolator
Air break switches are used to isolate equipment for maintenance and also for transfer of load from one bus to another. Lay-out of substation depends upon type of Air break switches.
These switches are of two types viz. vertical break type or horizontal break type. Horizontal break type normally occupies more space than the vertical break type.
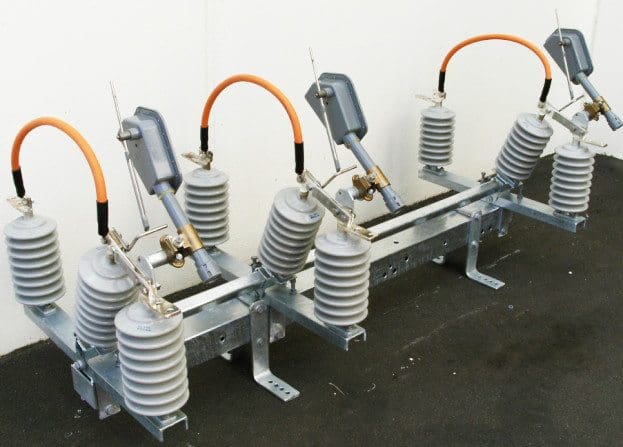


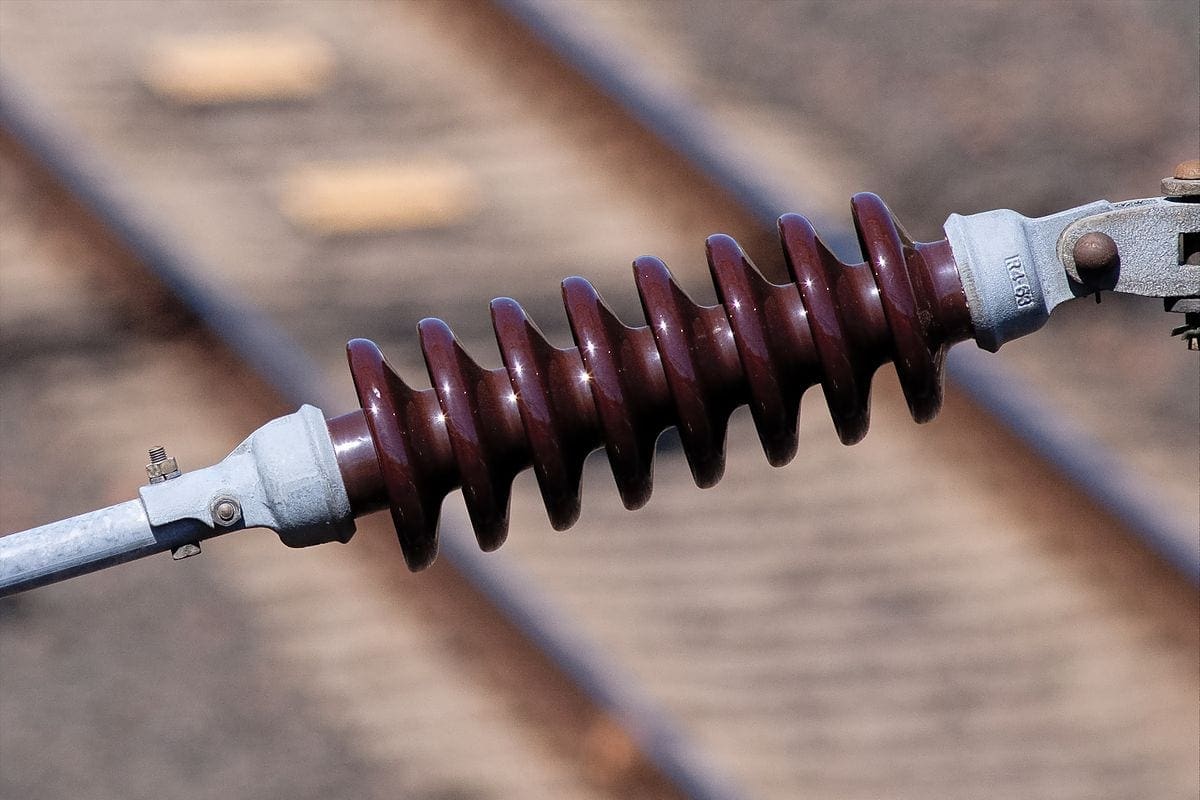
5. Insulator
The main function of an insulator is to insulate live conductor or equipment at different voltages with reference to the ground structures as well as provide mechanical support.
Provision of adequate insulation in a substation is of primary importance from the point of view of reliability of supply and safety of personnel.
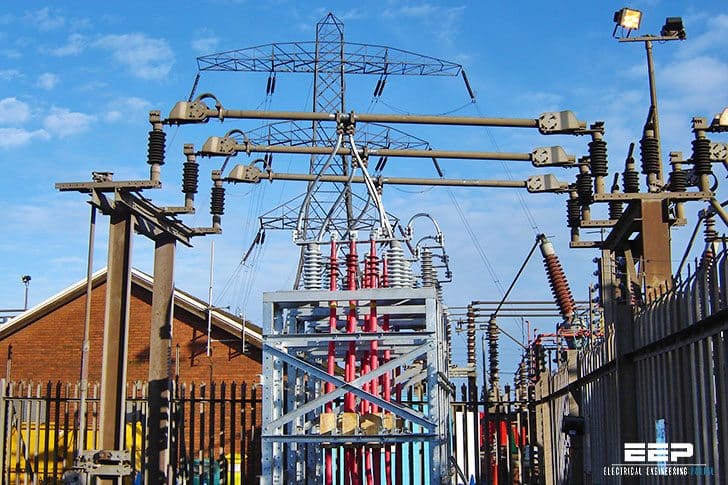




6. Busbar Arrangement
The busbar is a conductor used to connect two and more equipment located side-by-side when the currents are very high. These are usually rectangular, sometimes tubular, bare copper bars supported on insulators. The outdoor busbars are either of the rigid type or of the strain type.
In the rigid type, pipes are used for making connections among the various equipment. The strain type busbars are an overhead system of wires strung between two supporting structures and supported strain type insulators. Since the busbars are rigid, the clearances remain constant.
7. Capacitor Bank
It is a series parallel combination of capacitors required to improve power factor of the system. They act as reactive power generators, and provide the needed reactive power to accomplish active power of circuit. This reduces the amount of reactive power, and thus total power (kVA) or the demand.
The bank should be provided as near as possible to load.
8. Earthing
Provision of an effective, durable and a dependable earthing in a substation and switching stations is very important for the safety of operating personnel as well as electrical devices. The voltage levels do not rise above tolerable thresholds and that the earth connection is rugged to dissipate the fault to the earth.
Earthing has a very low resistance and connects the electrical equipment to the general mass of the earth.
9. Fencing Arrangement
Fencing is provided at outdoor substation yard for restricting entry of unauthorized person and livestock. It must be earthed/ grounded separately. Height of fencing normally should not be less than 1.8 metres. Fencing should be painted once in a year by suitable paint.
10. Distribution Panelboard
Distribution panelboard consists of MCCBs, control equipment, meters and relays are housed in the control room. The panel frame shall be connected to the earth grid by an earthing conductor. A rubber mat of prescribed size and quality shall lay in front of panel.
Reference // Handbook on Maintenance of Electrical General Services Substation by GOVERNMENT OF INDIA











Excellent explainetion I see it is!
This is an interesting and brilliant site of all engineering students.
This is a brilliant site for me as an Electrical Engineer employed by a Power Utility.
I am a an electrical student I found sense in this when I graduate am wishing to be working from distribution substation I just like that work place.
I need more learning about the transformer power
Contact me (Engr. Sunday) for all your power, transmission station and switch yard related Civil Engineering works, I’m a certified Engineer with over a decade experience. Email: [email protected]
The images in the exported PDF files are blurry.
I found the information very educative, I got the information I want. Thanks
Very informative as am now joining substation maintenance team this month.
i need more inform about 330kv substation
Material required of 33KV substation materials
plz contract 03322398775
I have seen a 2.5MVA power transformer recently which has no conservator and no Buchholz relay, but has certain sensors. What do you make of this and what is your take on such a design?
what are the things required to make a best 6.6 KV indoor substation.
This is a very informative and educational article on substations. Thanks for taking time to write it. Let’s not forget that none of the protection circuits will work without a battery. Sadly, it’s frequently ignored and more than one substation has burned to the ground because it was not being maintained. If you’d like a short article on the topic I’d be happy to contribute. Best regards.
Edvard,
Sorry to carp, but there are minor typos in the lightning values (section 3):
Voltage should be 10^8 volts (100MV) – if it were really 10^-8 V (ten nanovolts) lightning would hardly be a problem!
Duration should be 10^-5s (10 microseconds); we should be rather thankful it’s not 10^5 sec. (i.e. lasting all day)!
Power should therefore be (2×10^8) x (2×10^4) = 4×10^12W (or 4×10^9kW) – though this would certainly be an extreme case.
Thanks for the article; regards, David Renshaw
I am a boy of 28years old of age
I am Electrician I work under contrat in (UBTH) university of Benin teaching hospital. I work on line
I will look e to work with you sir.
But I am also a graduate, I have Bsc computer science.
But I electrical work Right from my technical School
Plz sir help me