Split-phase induction motor
The capacitor-start (CS), or more precisely, capacitor-start, induction-run motor, is a modified split-phase induction motor used for hard-to-start loads. CS motors are efficient and require starting currents about 5 times their full-load currents.
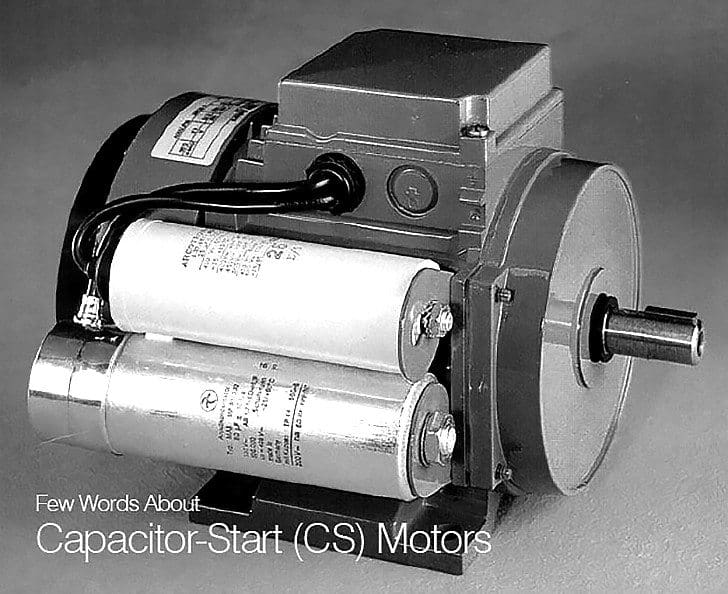
The schematic Figure 1 shows that the CS motor circuit is the same as the SP motor circuit, except that it includes a centrifugal starting switch and a small-value AC electrolytic capacitor in series with its starting winding.
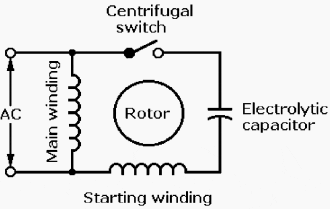
The typical torque–speed curves for a CS motor, Figure 2, show that it provides about twice the starting torque of an SP motor. The capacitor lowers the motor’s starting current and increases the phase difference between currents in the running and starting windings to 90°.
(This is about 60° more than the phase difference in SP motors.)
The capacitor functions only when the CS motor is started, so it can be relatively small and inexpensive. Both the starting winding and capacitor are disconnected by the centrifugal starting switch when the CS motor reaches about 80 percent of its running speed.
The motor then continues to run with only its main winding energized.
CS motors are rated from 1/8 to 3/4 HP.
They run at constant speed under varying loads, offer high running and starting torques, and high overload capacity. Their range of full-load synchronous speeds matches that of SP motors—865 to 3450 rpm when powered from a 120/240-V AC line.
The major components of a fan-cooled CS motor are identified in the exploded view Fig. 10-6. The capacitor in this motor is mounted outside the motor frame in a removable protective housing, to make it easier to replace if necessary.
Replacing a Motor Start Capacitor (VIDEO)
Reference: Handbook of electrical design details – Neil Sclater, J. E. Traister
(Get this book from Amazon)











Thank you for your clear and concise video. I’m an EE, and have a oil burner pump motor which won’t start, just hums when trying to start. It will run if I apply power and spin it up manually, which would indicate to me that the problem is the start capacitor. There is expected resistance across the cap leads without the cap attached, and, with the motor disconnected from power and my Fluke attached to either the cap leads OR the main power leads, when I manually spin the motor fan rotor, the resistance DOES change as it’s spinning. Both the run and start windings read around 20 ohms at idle. My Fluke reads the cap as dead on the money at 4uf, but I’m still suspect that with the 240v applied (I’m a Gringo now in the UK) the cap isn’t happy, so I await arrival of the replacement. Have you seen caps that appear physically OK and read accurately at the low voltage used by the Fluke, yet are actually faulty with full AC applied? Just wondering. As there’s only one external cap on this motor, I don’t believe there’s a run cap inside. Interestingly, the motor tag shows that the cap SB 3uf, and the one found on the motor is 4uf, so I suspect it’s been changed prior to my ownership. Ideas?
Szep Napot!
Jo leiras, eppen egy kompresszor motorral van problemam.
Minden jot, jo egeszseget!
Tibor
Excellent write up. Short and sweet.
Quality information (awesome)
Awesome