Forms of internal separation
By form of separation it is meant the type of subdivision provided within the switchboard. Separation by means of barriers or partitions (metallic or insulating) may have several functions.

And these functions:
- Provide protection against direct contact (at least IPXXB) in the case of access to a part of the switchboard which is not live, with respect to the rest of the switchboard which remains live;
- Reduce the risk of starting or propagating an internal arc;
- Impede the passage of solid bodies between different parts of the switchboard (degree of protection of at least IP2X).
A partition is a separation element between two parts, while a barrier protects the operator from direct contact and from arcing effects from any interruption devices in the normal access direction.
The following table from Standard IEC 61439-1-2 highlights typical forms of separation which can be obtained using barriers or partitions:
| Main criteria | Subcriteria | Form |
| No separation | – | Form 1 |
| Separation of busbars from the functional units | Terminals for external conductors not separated from busbars | Form 2a |
| Terminals for external conductors separated from busbars | Form 2b | |
| Separation of busbars from the functional units and separation of all functional units from one another. Separation of the terminals for external conductors from the functional units, but not from each other | Terminals for external conductors not separated from busbars | Form 3a |
| Terminals for external conductors separated from busbars | Form 3b | |
| Separation of busbars from the functional units and separation of all functional units from one another, including the terminals for external conductors which are an integral part of the functional unit | Terminals for external conductors in the same compartment as the associated functional unit | Form 4a |
| Terminals for external conductors not in the same compartment as the associated functional unit, but in individual, separate, enclosed protected spaces or compartments | Form 4b |
Symbols


Where:
- Housing
- Internal segregation
- Functional units including the terminals for the associated external conductors
- Busbars, including the distribution busbars
Form 1
(no internal segregation)


Form 2
(segregation of the busbars from the functional units)
Form 2a
Terminals not separated from the busbars
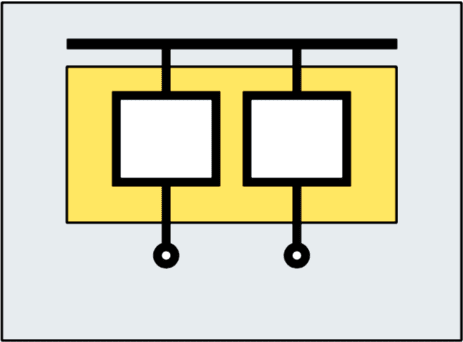

Form 2b
Terminals separated from the busbars


Form 3
(separation of the busbars from the functional units + separation of the functional units from each other)
Form 3a
Terminals not separated from the busbars


Form 3b
Terminals separated from the busbars
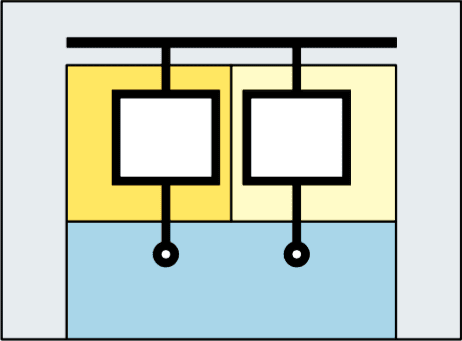

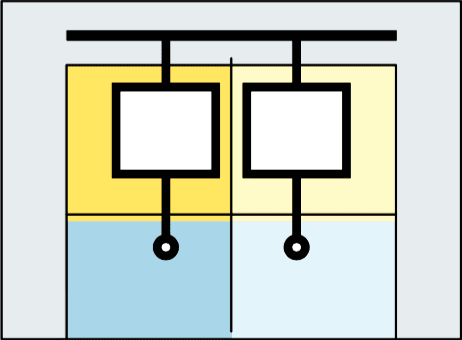
Form 4
((separation of the busbars from the functional units + separation of the functional units from each other + separation of the terminals from each other)
Form 4a
Terminals in the same compartment as the associated functional unit


Form 4b
Terminals in the same compartment as the associated functional unit

Form 2B Segregations assembling (VIDEO)
Animation about segregation form 3b 4b (VIDEO)
Classification of LV switchgears
Different classifications of electrical switchboard exist, depending on a range of factors. Based on construction type, Standard IEC 61439-1 firstly distinguishes between open and enclosed assemblies.
Open switchboards, with or without front covering, which have the live parts accessible. These switchboards may only be used in electrical plants.
External Design
With regard to external design, switchboards are divided into the following categories:
1. Cubicle-type assembly
Used for large scale control and distribution equipment. Multi-cubicle-type assembly can be obtained by placing cubicles side by side.


2. Desk-type assembly
Used for the control of machinery or complex systems in the mechanical, iron and steel, and chemical industries.


3. Box-type assembly
Characterized by wall mounting, either mounted on a wall or flush-fitting. These switchboards are generally used for distribution at department or zone level in industrial environments and in the tertiary sector.


4. Multi-box-type assembly
Each box, generally protected and flanged, contains a functional unit which may be an automatic circuit-breaker, a starter, a socket complete with locking switch or circuit-breaker.
Intended function
With regard to the intended function, switchboards may be divided into the following types:
1. Main distribution boards
Main distribution boards are generally installed immediately downstream of MV/ LV transformers, or of generators; they are also termed power centres.
Main distribution boards comprise one or more incoming units, busbar connectors, and a relatively smaller number of output units.


2. Secondary distribution boards
Secondary distribution boards include a wide range of switchboards for the distribution of power, and are equipped with a single input unit and numerous output units.


3. Motor operation boards
Motor control boards are designed for the control and centralised protection of motors. Therefore they comprise the relative coordinated devices for operation and protection, and auxiliary control and signalling devices.


4. Control, measurement and protection boards
Control, measurement and protection boards generally consist of desks containing mainly equipment for the control, monitoring and measurement of industrial processes and systems.


5. Machine-side boards
Machine-side boards are functionally similar to the above. Their role is to provide an interface between the machine with the power supply and the operator.
6. Assemblies for construction sites (ASC)
Assemblies for construction sites may be of different sizes, from a simple plug and socket assembly to true distribution boards with enclosures of metal or insulating material. They are generally mobile or, in any case, transportable.


Reference // Electrical installation handbook – Protection, control and electrical devices by ABB











Hi,
Is it possible to have higher form of separation for a downstream Distribution Board. I.e: Sub main is 3bih and the downstream 4bih?
Thank you,
Karam Habashy
Hi Karam Habashy,
Yes, the form of separation can be any form decided by the specifiers.
Where I work we test that the form specified by the customer is achieved.
Hope this helps
kA Testing Facility ltd. Nottingham U.K.
Very enlightening in these days where Arc Flash has become an important consideration for working on any form of electrical apparatus
This is a great lesson… Infect every post teaches me more about switchgears
Greetings Edvard from one Hungarian and IET member to another. I need some help. Though, I agree with various Forms for switchgear, it is difficult for high density panels containing numerous starters, instruments PLCs etc. if the controls are inter-wired. Also, detecting fire in the panels. We often fit smoke, IR heat and smoke detectors and should a problem occur CO2 is sprayed from the top with several nozzles, which would quickly extinguish the fire. The cost of sensors would be phenomenal, for say 50 compartments. Also the connecton of multicore cables. But like winklepicker shoes, it became a fashion
thanks a lot. very clear and detail. learn new things.
The article is very useful, but i needed to know how to select between the 4 forms for instance in the MDB. Thx alot
hi
tanks
your description in the above was useful and have new technical information for my reserch in the field of my survey