What are harmonics?
The harmonics allow to represent any periodic waveform. In fact, according to Fourier’s theorem, any periodic function of a period T may be represented as a summation of:

- A sinusoid with the same period T;
- Some sinusoids with the same frequency as whole multiples of the fundamental;
- A possible continuous component, if the function has an average value not null in the period.
The harmonic with frequency corresponding to the period of the original waveform is called fundamental and the harmonic with frequency equal to “n” times that of the fundamental is called harmonic component of order “n”.
A perfectly sinusoidal waveform complying with Fourier’s theorem does not present harmonic components of order different from the fundamental one.
Therefore, it is understandable how there are no harmonics in an electrical system when the waveforms of current and voltage are sinusoidal. On the contrary, the presence of harmonics in an electrical system is an index of the distortion of the voltage or current waveform and this implies such a distribution of the electric power that malfunctioning of equipment and protective devices can be caused.
Figure 1 below shows a graphical representation of this concept.


How harmonics are generated?
Harmonics are generated by nonlinear loads. When we apply a sinusoidal voltage to a load of this type, we shall obtain a current with non-sinusoidal waveform. The diagram of Figure 2 illustrates an example of nonsinusoidal current waveform due to a nonlinear load:
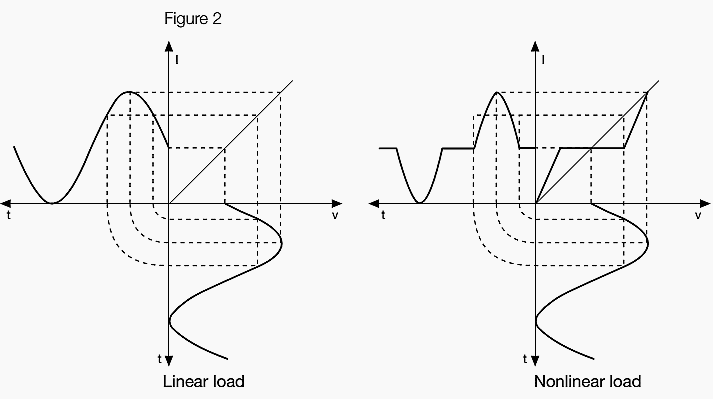

This nonsinusoidal waveform can be deconstructed into harmonics. If the network impedances are very low, the voltage distortion resulting from a harmonic current is low too and rarely it is above the pollution level already present in the network. As a consequence, the voltage can remain practically sinusoidal also in the presence of current harmonics.
The main equipment generating harmonics are:
- Personal computer
- Fluorescent lamps
- Static converters
- Continuity groups
- Variable speed drives
- Welders
In general, waveform distortion is due to the presence of bridge rectifiers (inside of these equipment), whose semiconductor devices carry the current only for a fraction of the whole period, thus originating discontinuous curves with the consequent introduction of numerous harmonics.
Also transformers can be cause of harmonic pollution. In fact, by applying a perfectly sinusoidal voltage to a transformer, it results into a sinusoidal magnetizing flux, but, due to the phenomenon of the magnetic saturation of iron, the magnetizing current shall not be sinusoidal.
Figure 3 shows a graphic representation of this phenomenon:


The resultant waveform of the magnetizing current contains numerous harmonics, the greatest of which is the third one. However, it should be noted that the magnetizing current is generally a little percentage of the rated current of the transformer and the distortion effect becomes more and more negligible the most loaded the transformer results to be.
5 really nice effects of harmonics
The main problems caused by harmonic currents are //
1. Overloading of neutrals
2. Increase of losses in the transformers
3. Increase of skin effect
The main effects of the harmonics voltages are //
4. Voltage distortion
5. Disturbances in the torque of induction motors
1. Overloading of neutrals
In a three phase symmetric and balanced system with neutral, the waveforms between the phases are shifted by a 120° phase angle so that, when the phases are equally loaded, the current in the neutral is zero.
The presence of unbalanced loads (phase-to-phase, phase-to-neutral etc.) allows the flowing of an unbalanced current in the neutral.
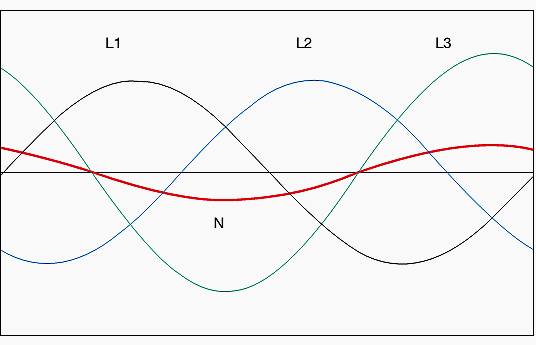

Figure 4 shows an unbalanced system of currents (phase 3 with a load 30% higher than the other two phases), and the current resultant in the neutral is highlighted in red. Under these circumstances, the Standards allow the neutral conductor to be dimensioned with a cross section smaller than the phase conductors.
In fact, although the currents at fundamental frequency in the three phases cancel each other out, the components of the third harmonic, having a period equal to a third of the fundamental, that is equal to the phase shift between the phases (see Figure 5 below), are reciprocally in phase and consequently they sum in the neutral conductor adding themselves to the normal unbalance currents.
The same is true also for the harmonics multiple of three (even and odd, although actually the odd ones are more common).


Go back to Effects of harmonics ↑
2. Increase of losses in the transformers
The effects of harmonics inside the transformers involve mainly three aspects //
- Increase of iron losses (or no-load losses)
- Increase of copper losses
- Presence of harmonics circulating in the windings
The iron losses are due to the hysteresis phenomenon and to the losses caused by eddy currents. The losses due to hysteresis are proportional to the frequency, whereas the losses due to eddy currents depend on the square of the frequency.
The copper losses correspond to the power dissipated by Joule effect in the transformer windings. As the frequency rises (starting from 350 Hz) the current tends to thicken on the surface of the conductors (skin effect). Under these circumstances, the conductors offer a smaller cross section to the current flow, since the losses by Joule effect increase.
These two first aspects affect the overheating which sometimes causes a derating of the transformer.
The third aspect is relevant to the effects of the triple-N harmonics (homopolar harmonics) on the transformer windings. In case of delta windings, the harmonics flow through the windings and do not propagate upstream towards the network since they are all in phase.
3. Increase of skin effect
When the frequency rises, the current tends to flow on the outer surface of a conductor. This phenomenon is known as skin effect and is more pronounced at high frequencies.
At 50 Hz power supply frequency, skin effect is negligible, but above 350 Hz, which corresponds to the 7th harmonic, the cross section for the current flow reduces, thus increasing the resistance and causing additional losses and heating.
In the presence of high-order harmonics, it is necessary to take skin effect into account, because it affects the life of cables. In order to overcome this problem, it is possible to use multiple conductor cables or busbar systems formed by more elementary isolated conductors.
Go back to Effects of harmonics ↑
4. Voltage distortion
The distorted load current drawn by the nonlinear load causes a distorted voltage drop in the cable impedance. The resultant distorted voltage waveform is applied to all other loads connected to the same circuit, causing harmonic currents to flow in them, even if they are linear loads.
Go back to Effects of harmonics ↑
5. Disturbances in the torque of induction motors
Harmonic voltage distortion causes increased eddy current losses in the motors, in the same way as seen for transformers. The additional losses are due to the generation of harmonic fields in the stator, each of which is trying to rotate the motor at a different speed, both forwards (1st, 4th, 7th, …) as well as backwards (2nd, 5th, 8th, …).
High frequency currents induced in the rotor further increase losses.
Go back to Effects of harmonics ↑
Reference // Electrical installation handbook Protection, control and electrical devices by ABB











Absolutely benefit! I always keep following
The article provides a lot of of information about harmonics.
Thankyou so much for the article.
excellent article, I liked it, very enlightening, congratulations
Good Insights on harmonics !!
Good information… Thank you for sharing
Thanks
This is the best explanation . Thanks.
Thanks
Dear Ed. Very useful article especially for the students of EEE and beginners of this harmonics studies. Is it possible to update with a pdf document as other articles
Wonderful !!!
How to download Ref: Electrical installation handbook Protection, control and electrical devices by ABB
good work Edvard
Very good . Thanks
Edvard, I found your article interesting and insightful. It help better clarify several points that I have simply accepted as I always found the a bit confusing of felt uncertain about them. So thanks for helping me become a better engineer.
That said, grammar and mechanics errors made reading and understanding at several points difficult. I presume by your writing style that English is not you first language. As such, I applaud your dedication to learning one of the world’s most complex and changing languages. Should you wish for help or proofing of your English work I would be happy to assist. It would be an honor to help such a clearly talented man have his work shine as brightly and clearly as his mind.
Hi Edward,
A good article on harmonics. However, the relation of different waveforms on graphs is not clear. Wonder if it is possible to update this article with this information.
Regards,
Munibullah Wahdy
Why are we always talking about odd harmonics (3rd, 5th,…) and not about even ones (2nd, 4th,…)?
Great article very informative, keep it up!
Thank you, how we could compensate this effect?
Thank you for the article. (y)
I would like to get a copy of the autocad electrical 2016 , I already have the autocad autodesk student version with just architectural , I tried to download the electrical , it keeps saying the .net 4.5 is not installed although I have it already in my computer , please advise ..
Thanks
Raoul, the autiocad electrical full version (by the way it has a 2019 last versio) has to be boughtfrom the dofficial distributor for autocad in your country. here it can be leased with a monthly payment system which includes full support
there is effect of harmonics – generally 3rd, 5th, 7th and some times 9th.
What are the basic reason of generation and means of control by which these can be controlled or reduced.
Good article.
thanks
Nicely complied. In my view impact on Capacitor banks should in top 5 effects of Harmonics.
This is the best explanation of harmonics I’ve come across. Thanks!
Thank you Lisa :)