DC Tests
DC tests are used mainly to do “pressure tests” on high voltage cables. Although the cables operate with AC, AC testing is not practical.
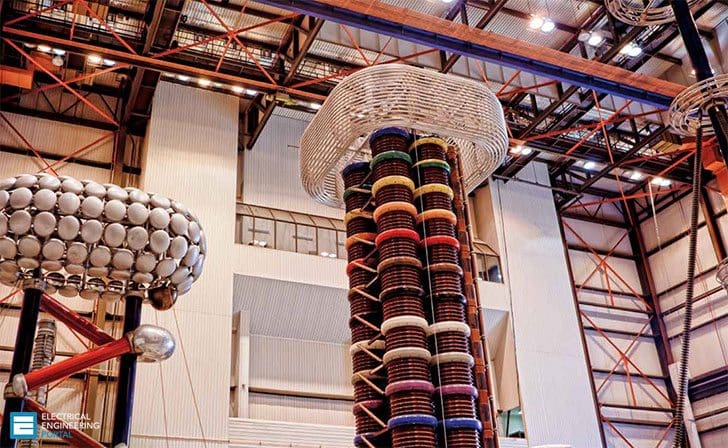

The high capacitance of the cables necessitates AC test sets with a high kVA rating to be able to supply the capacitive current. In the case of DC, once the cable is charged, only the losses have to be supplied.
Typical DC test set-up is shown in Figure 1.
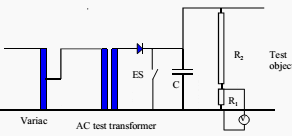
An AC high voltage test transformer is again supplied via a variac and a rectifier is used together with a filter capacitor C to limit the ripple to acceptable values. The earthing switch ES is a safety feature and closes automatically when the power is switched off to discharge the capacitor C.
Note that the peak inverse voltage required of the rectifier is 2 Vm.
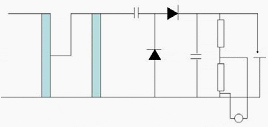
Doubling and multiplier circuits (as used in TV’s and household appliances) are also used to obtain an even higher voltage. A typical Cockcroft-Walton (in Germany: Greinacher) doubling circuit is shown in Figure 2.
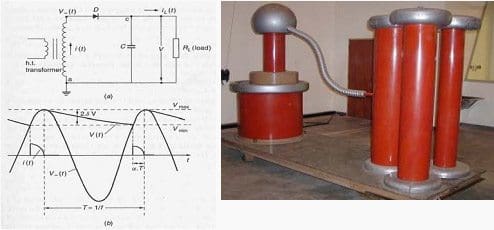
Resource: High Voltage Engineering Practice and Theory – Dr JP Holtzhausen; Dr WL Vosloo











Thanks for providing the complete detail about High voltage testing. Keep it up and keep doing this great work.
1. Why do you double the voltage when you pressure test?
2. 3 Ansi Codes and their meanings.
3. What is the name of the test that checks the tension between clusters and contacts?
4. How do you connect your undervoltage coil to the UPS?
I want know about thermal test and DC high voltage test of PVC cable..
thank you for your information
Slam/Hi,
Love your work @Edvard. Every article is worth spending time on it. I’m final year undergraduate student and my final year project is “Simulation Based Impulse Testing of a Power Equipment”. Do you have anything in store for me regarding my project? It would be of great help. _Thanks
“Power Equipment” can either be transformers, surge arrestors, isolators, Circuit Breaker or switchgear.