The art of lockout in control circuitry
Lockouts and auto-reclosures are apprentices of power systems protection that have long served to regulate power supply and safeguard important components from probable catastrophes. But are we taking them seriously enough? In implementing the lockout features, apart from their placements in control circuitry, operating principles, construction, and functionalities remain almost the same over decades, while their counterparts have seen massive overhauls.
This article will focus on the practical applications of lockout relays on mainstream switchgear and protection. The primary goal is to discuss the transition from the current mode of application to possible upgrades and adaptations in modern digital power substation protection.
The terminologies lockout relay, master trip relay, and 86-relay are used interchangeably in this article.
- What does lockout relay do exactly?
- Operation in protection circuit
- What makes lockout relay indispensable in substation protection
- An analogy with auto-reclosure
- Next-generation implementation of lockout features
1. What does lockout relay do exactly?
Protection relays are undoubtedly the soul of substation protection and require multiple auxiliary relays to support them for the overall functionality of protection, control, and monitoring. Master trip relay or lockout relay, also known by ANSI code 86, holds a significant position as an intermediator between the protection relay and control points, even though it is not self-equipped with fault sensing capabilities.
The master trip relay can operate as a hub of multiple protection relays trip commands and drive multiple subsequent contacts. This makes the relay a protagonist to execute simultaneous commands like breaker trips, interlocks, alarms, data display, SCADA extensions, and lockouts.
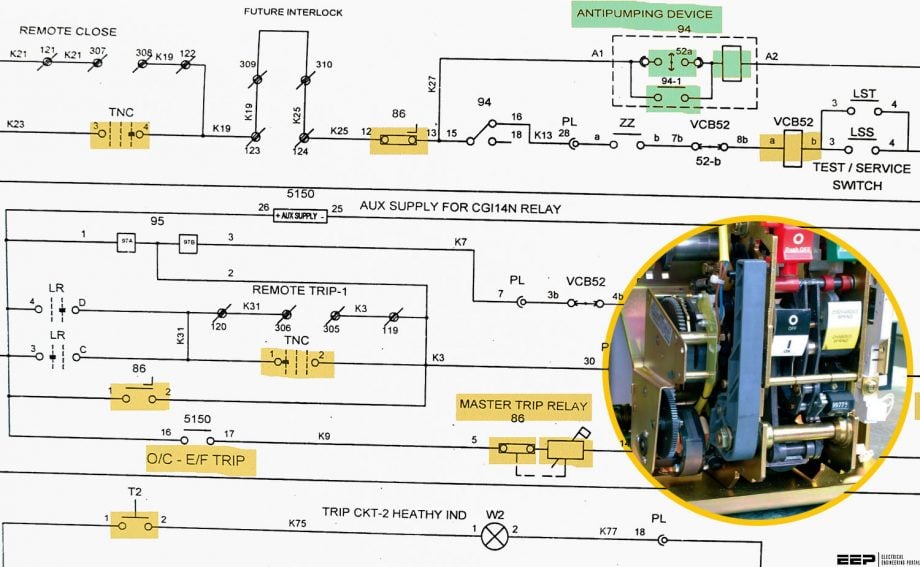
Figure 1 – Trip function interface: Soft Logic to a hard-wired connection
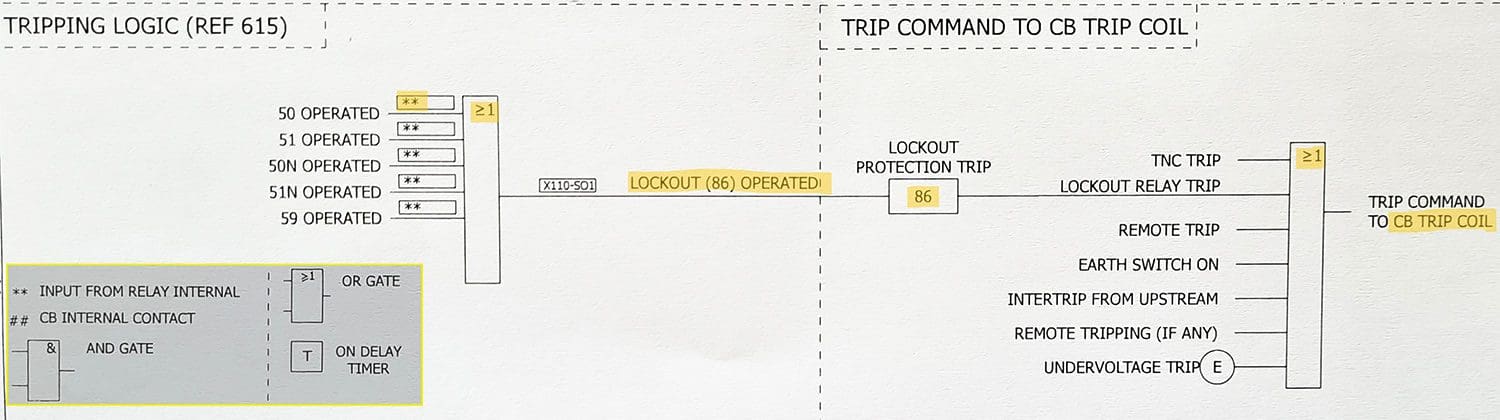

In absence of a master trip relay, imagine connecting individual trip circuits of each protection relay to circuit breaker trip coils. Along with the obvious extra cost incurred, this would be a mess for operation and troubleshooting. The concept of lockout relay as an intermediator of protection is illustrated in Figure 1.
Initiation of fault signals in modern-day protection IED activates the lockout relay to perform the trip command of associated breakers. Likewise, the command for a closing coil of breaker only receives the close signal upon confirmation from the lockout relay.
The sequence of operation for medium voltage switchgear with numerical protection relay to execute closing command is illustrated in Figure 2.










