Surge arresters against lightning
Description of the installation
The site consists of offices (computer hardware, lighting and heating unit), a security post (fire alarm, burglar alarm, access control, video surveillance) and three buildings for the manufacturing process on 10 hectares in the Avignon region of France (probability of lightning is 2 strikes per km2 per year).

There are trees and metal structures (pylons) in the vicinity of the site. All of the buildings are fitted with lightning conductors. The MV and LV power supplies are underground.

Problems encountered
A storm struck the site, destroying the LV installation in the security post and causing 36.5 kE of operating losses. The presence of lightning conductors prevented the structure from catching fire, but the electrical equipment which was destroyed was not protected by surge arresters, contrary to the recommendation in standards UTE C-15443 and IEC 62305.
Solutions with surge arresters
After analysing equipotentiality and earthing of the power system, followed by verification of the installation of lightning conductors and checking of the values of the earth electrodes, the decision was taken to install surge arresters.
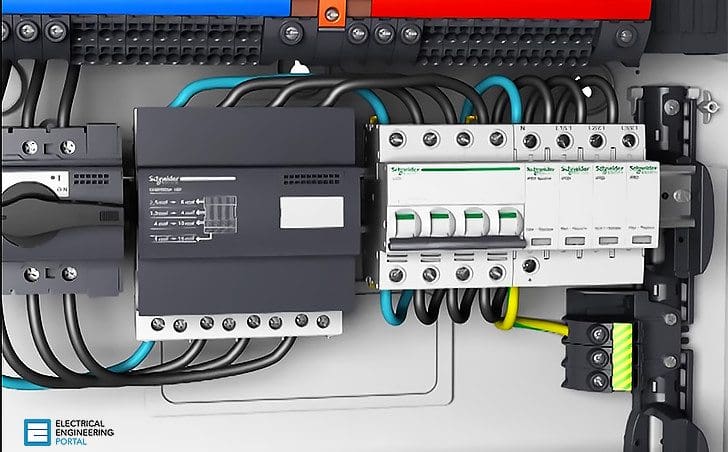
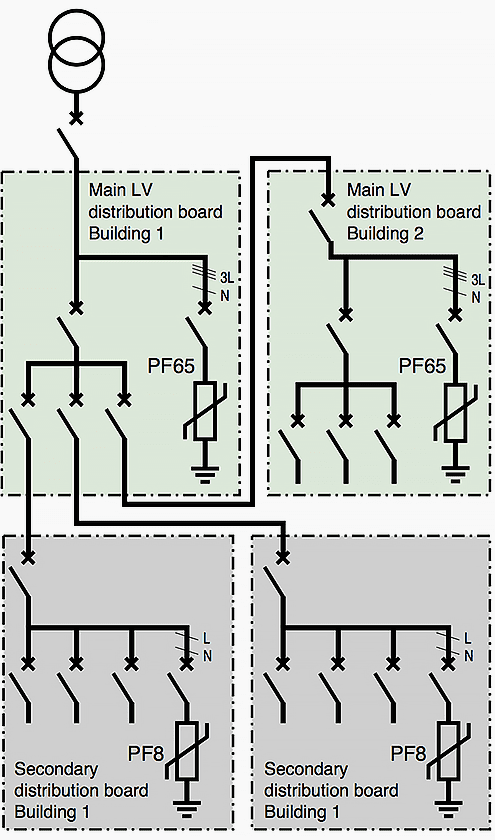
Surge arresters were installed at the head of the installation (main LV distribution board) and in cascade in each manufacturing building (see figure 1 above). As the neutral point connection was TNC, protection would only be provided in common mode (between phases and PEN).

Figure 2 – SPD Type 2 and 3 standa alone – Surge/transient overvoltage power network protection
- Imax from 8kA to 65kA (8/20)
- In from 2.5kA to 20 kA (8/20)
- Up from 1kV to 2.5kV
- Uc = 320V, 350V, 460V
- 1P to 4P
- Monobloc(F) and pluggable (D)
- TT, TNS, IT
- Remote transfer
In conformity with guide UTE C-15443 regarding operation in the presence of lightning conductors, the characteristics of the Schneider Electric SPDs iPF65 and iPF8 surge arresters (see figure 2) are as follows:
- At the head of the installation
In = 20 kA – Imax = 65 kA – Up = 2 kV - In cascade (at least 10 m apart)
In = 2 kA – Imax = 8 kA – Up = 1.5 kV
In cascade, good protection is provided for the secondary distribution boards (offices and security post).
As the neutral point connection was converted to TNS, protection had to be provided in common mode (between phase and PE) and differential mode (between phases and neutral). The disconnection devices in this case are circuit breakers with a breaking capacity of 22 kA.
Tutorial // Installation of a Surge Protector
The Video shows the correct installation of surge protection, associating with backup protection (circuit breaker). The “50 cm wiring rule” explanation will help you to understand correct wiring according the installation standard IEC 60364-5-534.
Reference // Cahier Technique Schneider Electric no. 199 – Power Quality by Philippe FERRACCI











i want to ask
what is difference between lightning Arrester and surge Arrester? beacuse i want to design 400 kV Transmission line i dint no any one used
thank you
Hello Dear
is there any diffrent between phases and nole arresters in a400V battery charger panel in general? or they can be same in specifications?
Hello Mahmoud,
Could you please send quotation for the below specs or send a catalogue?
Rated Voltage Continuous Operating Voltage Short Circuit Current Withstand Frequency
<690V 690V 100 KA 50HZ
I like EEP very much. it is a good source however on this i will have to comment, as even big companies make errors.
In this video the phases are tangled and even touching the rails, that is bad practice.
i would recommend to have the wiring from the switch straight down to the various components of the system, this will also help to reduce wirelength to a minimum.
the single line diagram is queried with five circuit breakers in cascade, it would be most difficult to effectively grade the protection system. I suggest the isolators on each distribution board should be non-auto. I note also there is no RCD protection which is more or less mandatory in Australia at least.
I suggest that circuits be realistic rather than a generic set up to develop a particular theme as the real world does require grading and earth leakage (RCD) protection of circuits.