Undeservedly second…
Despite some gains in recent years, renewable energy sources make only a modest contribution to the provision of modern energy services worldwide. Why is it so?
The principal constraints to their growth are their costs and their unrewarded environmental characteristics (the continuing and exclusive use of production costs to compare energy options without adjustment for environmental externalities). Some renewables have also been hampered by siting concerns and intermittent supply.
Moreover, there is a variety of challenges stemming from the inertia in turnover of existing energy infrastructure, the relatively recent development of marketable products based on renewable energy, as well as the costs and difficulties of creating new technical, business and human support structures on a global scale.
Wind power is in close competition in locations with good wind conditions and bioenergy can be cost effective in Combined Heat and Power (CHP) applications if the cost of fuel is low.
Table 1 – Renewable Energy Cost Assessment
| Current Cost | Cost Reductions by 2020 | |
| Bioenergy | High. Cost-effective in CHP applications with low fuel cost. Co-firing is a relatively low-cost retrofit option. | 10-15% |
| Wind onshore | Relatively low; lowest compared to other renewables. | Up to 15-25% |
| Wind offshore | High. | 20-30% |
| Solar Photovoltaic | Very high. Cost-effective only in niche markets. | 30-50% |
| Solar Thermal | Very high. | 30% + |
| Geothermal | High. | 10% |
| Hydro | Relatively low for large hydro. | 10% |
- Source: IEA (2001), IEA World Energy Outlook 2001 Insights, OECD/IEA.
- Note: This table presents a quantitative assessment of current costs and the likely average reductions by 2020. Estimates can vary significantly depending on site conditions.
Recent analyses indicate that the costs of electricity generated through renewable sources are a function of the cumulative installed capacity. Thus, if a larger market could be identified, economies of scale could lower prices and accelerate demand. And that is not happening…
The competitive position of renewable energy vis-à-vis fossil fuels would improve substantially if a market price were attached to carbon dioxide and other air emissions.
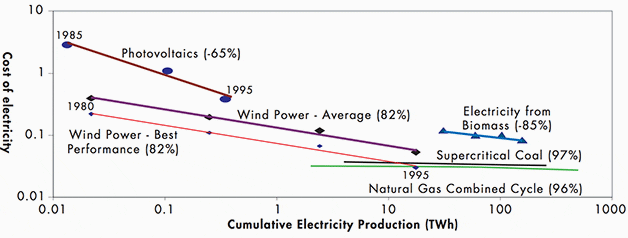
* ECU 1990/kWh.
- Note: Numbers in brackets represent “progress ratios”. A figure of 85% means that the price of the technology is reduced to 0.85 of its previous level after a doubling of its cumulative sales.
- Source: IEA (2000), Experience Curves for Energy Technology Policy, OECD/IEA.
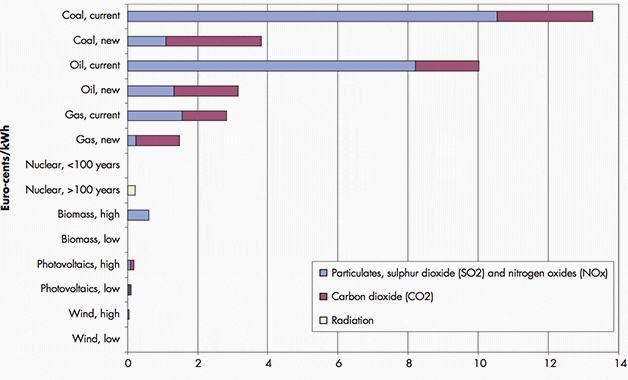
Figure 3 below shows that full valuation of CO2 emissions would raise the price of power generation based on coal, gas and oil by 2.7, 1.2 and 1.8 Euro-cents per kWh, respectively. Similar valuation of particulates, SO2 and NOx would add 0.3 to 1.1 Euro-cents per kWh to the cost of new fossil fuel-based power generation.
Energy technology perspective
Secure, reliable and affordable energy supplies are fundamental to economic stability and development of the nation.
That can only be met through innovation, adoption of new cost-effective technologies, and a better use of existing energy efficient technologies.

Resource: Renewable Energy book