Increase of the magnetizing current
Overexcitation of a transformer means that the magnetic flux in the core is increased above the normal design level. This will cause an increase of the magnetizing current and the transformer can be damaged if this situation isn’t taken care of.

Overexcitation of transformers in transmission and distribution networks is caused by overvoltages in the network.
For step-up transformers connected to generators during start-up, overexcitation can occur since the flux is dependent of the factor voltage/frequency. This means that the voltage must be gradually increased, with increasing frequency, in order not to overexcite the transformer.
The overexcitation is not an internal transformer fault, although can lead to one.
The differential protection must therefore be stabilized under these conditions as tripping of transformers and thus load will only mean that the overvoltage condition in the network is becoming worse.
The current during overexcitation has a lot of fifth harmonic, see figure 1. This fact is utilized in modern transformer protection to stabilize the transformer against unwanted functions during these kind of conditions.
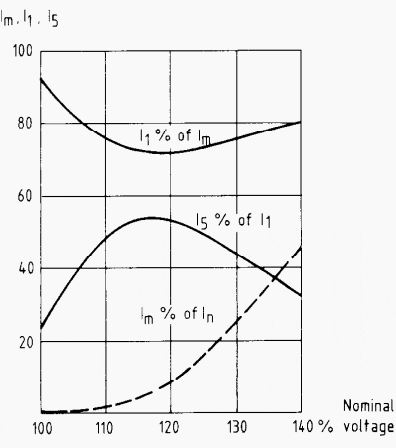
If overexcitation of the transformer due to overvoltage or underfrequency is likely to happen, a separate overexcitation protection should be supplied. This protection has inverse characteristics according to the transformers capability to restrain overexcitation “V/Hz”.
This protection must be connected to a transformer winding with fixed number of turns.
If the transformer is supplied with tap changer the protection must be connected to a side without tap changer. The side with the tap changer can withstand different voltages depending on the tap changer position and is therefore not suitable for overexcitation protection.
Reference: Protection application handbook – ABB BA THS / BU Transmission Systems and Substations











Hi all,
In the case that we have a step-up transformer installed after a converter( the converter is protected against frequency changes and the system is protected against overvoltage fault by surge arrester) please let me know if we still need an overexcitation protection for the transformer.
Hello everyone
Any one know about over excitation protection of transformer, which side of transformer are we usually connect the over excitation relay(i-e primary side or secondary side)?
and my other question is that for relay setting which side of transformer voltage is used?
Over excitation relay has to connect to the transformer winding with fixed number of turns. Hence it has to connect on transformer side where there is no tap change is connected.
nice
Hi,
With due respect, I would like to point that on your website there is a link to Jignesh Parmar blog( Excel sheets, Notes-books, Articles-codes) which is totally misleading in regard to fault levels calculation KVA Base method.
kind Regards
Anna
how about under-excitation?
What do you recommend for Over fluxing relay setting of a Power Transformer?
What do you recommend for Over Fluxing relay setting?
over voltage is the only reason of overexcitation of a transformer? over load is not the reason of overexcitation