Commercial and industrial distribution systems use several methods to transport electrical energy. These methods may include heavy conductors run in trays or conduit. Once installed, cable and conduit assemblies are difficult to change.
Power may also be distributed using bus bars in an enclosure. This is referred to as busway.
Bus Bars
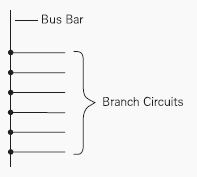
A bus bar is a conductor that serves as a common connection for two or more circuits. It is represented schematically by a straight line with a number of connections made to it. Standard bus bars in Siemens busway are made of aluminum or copper.
NEMA Definition
Busway is defined by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) as a prefabricated electrical distribution system consisting of bus bars in a protective enclosure, including straight lengths, fittings, devices, and accessories.
Busway includes bus bars, an insulating and/or support material, and a housing.
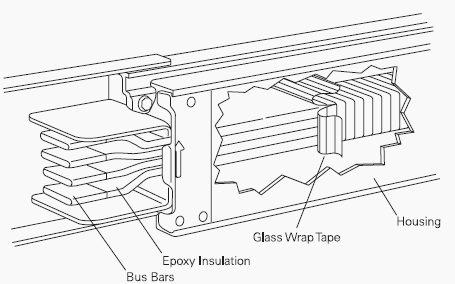
Busway Used in a Distribution System
A major advantage of busway is the ease in which busway sections are connected together. Electrical power can be supplied to any area of a building by connecting standard lengths of busway. It typically takes fewer man-hours to install or change a busway system than cable and conduit assemblies.
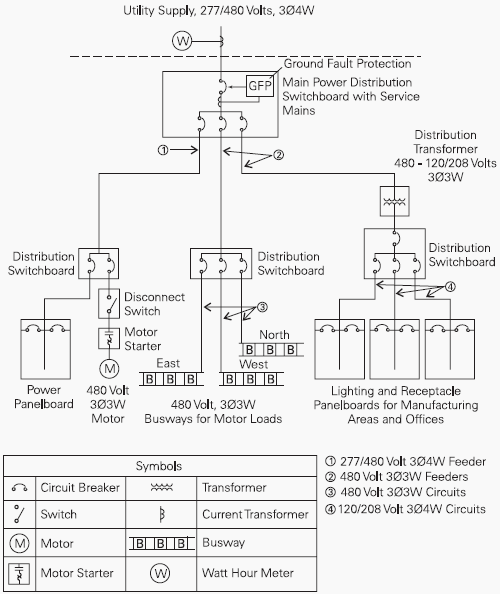
The total distribution system frequently consists of a combination of busway and cable and conduit. In this example power from the utility company is metered and enters the plant through a distribution switchboard. The switchboard serves as the main disconnecting means. The feeder on the left feeds a distribution switchboard, which in turn feeds a panelboard and a 480 volt, three-phase, three-wire (3Ø3W) motor. The middle feeder feeds another switchboard, which divides the power into three, three-phase, three-wire circuits. Each circuit feeds a busway run to 480 volt motors.
The feeder on the right supplies 120/208 volt power, through a step-down transformer, to lighting and receptacle panelboards. Branch circuits from the lighting and receptacle panelboards supply power for lighting and outlets throughout the plant. In many cases busway can be used in lieu of the cable/conduit feeders at a lower cost.
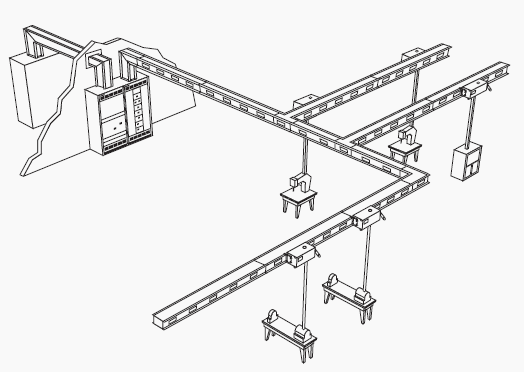
Busway is used in various applications and can be found in industrial installations as well as high-rise buildings. Busway used in industrial locations can supply power to heavy equipment, lighting, and air conditioning.
Busway risers (vertical busway) can be installed economically in a high-rise building where it can be used to distribute lighting and air conditioning loads.











Informative article.