Solving DC Circuits
I guess you’re still recovering from an awesome lunches and dinners you’ve had during holidays. Well, now when it’s over – it’s a good moment to plug yourself back and shake your brain cells!

Assuming that you’re very familiar with electric circuits theorems, I advice you to get yourself a good old black coffee and give your brain a training by solving few simple dc circuits :)
Let’s start.
Circuit #1
Using the current division rule, calculate I1 and I2, I being 10 A. Verify the solution, calculating UAB as ReqpI and observing that R1I1 = R2I2 = UAB.


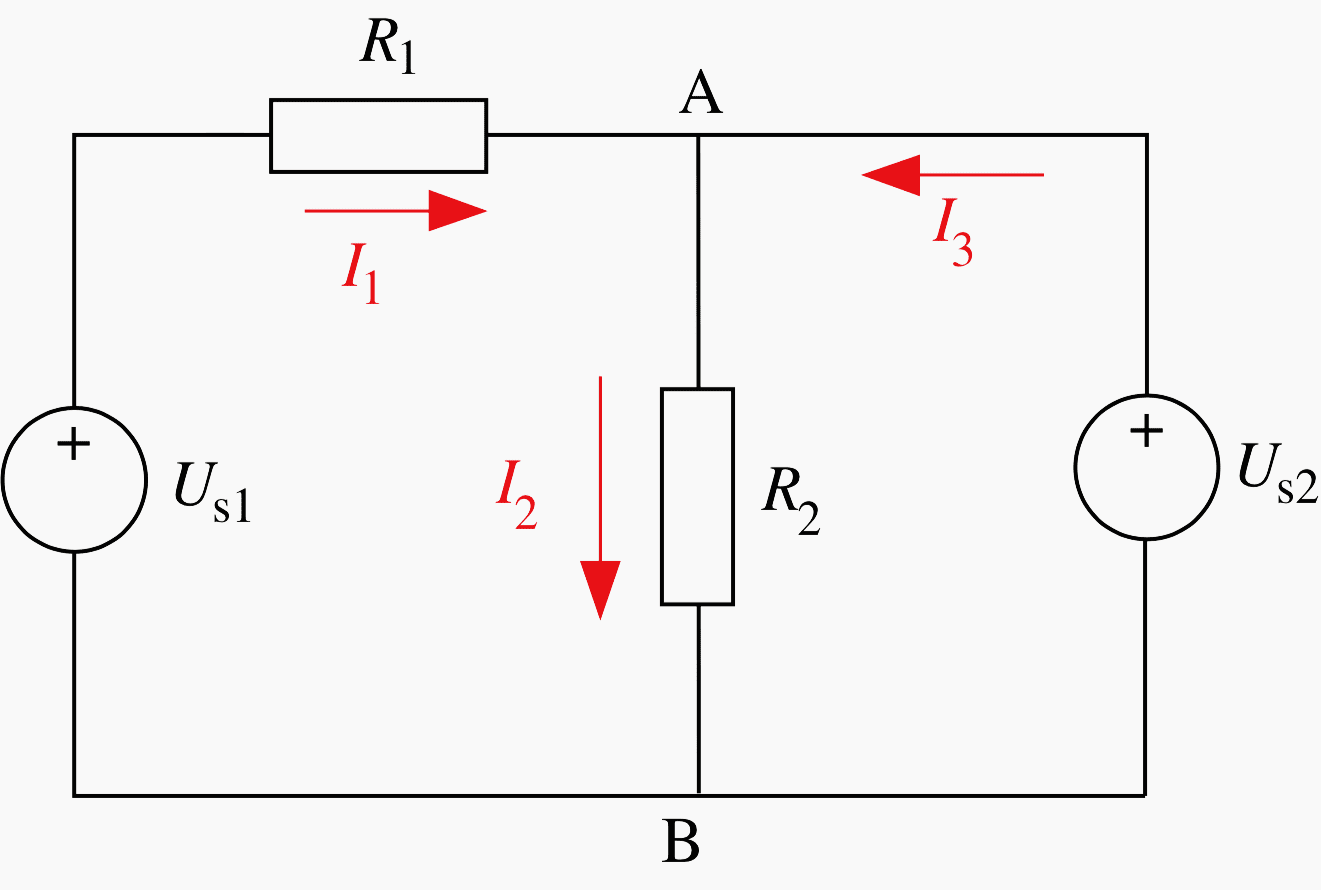
Circuit #2
Determine I and UAB. If Us1 and Us2 represent two ideal batteries, which one charges the other?
- Us1 = 120V
- Us2 = 90V
- R1 = R2 = 10Ω
- R3 = 40Ω


Circuit #3
Calculate the resistance RG seen by the generator, and I1. Then, using the voltage division rule, calculate I2 and I3. Check the conservation of power, comparing what is delivered by the generator and what is absorbed by resistors.
- Us = 12V
- R1 = R2 = 2Ω
- R3 = 8Ω
- R4 = 6Ω
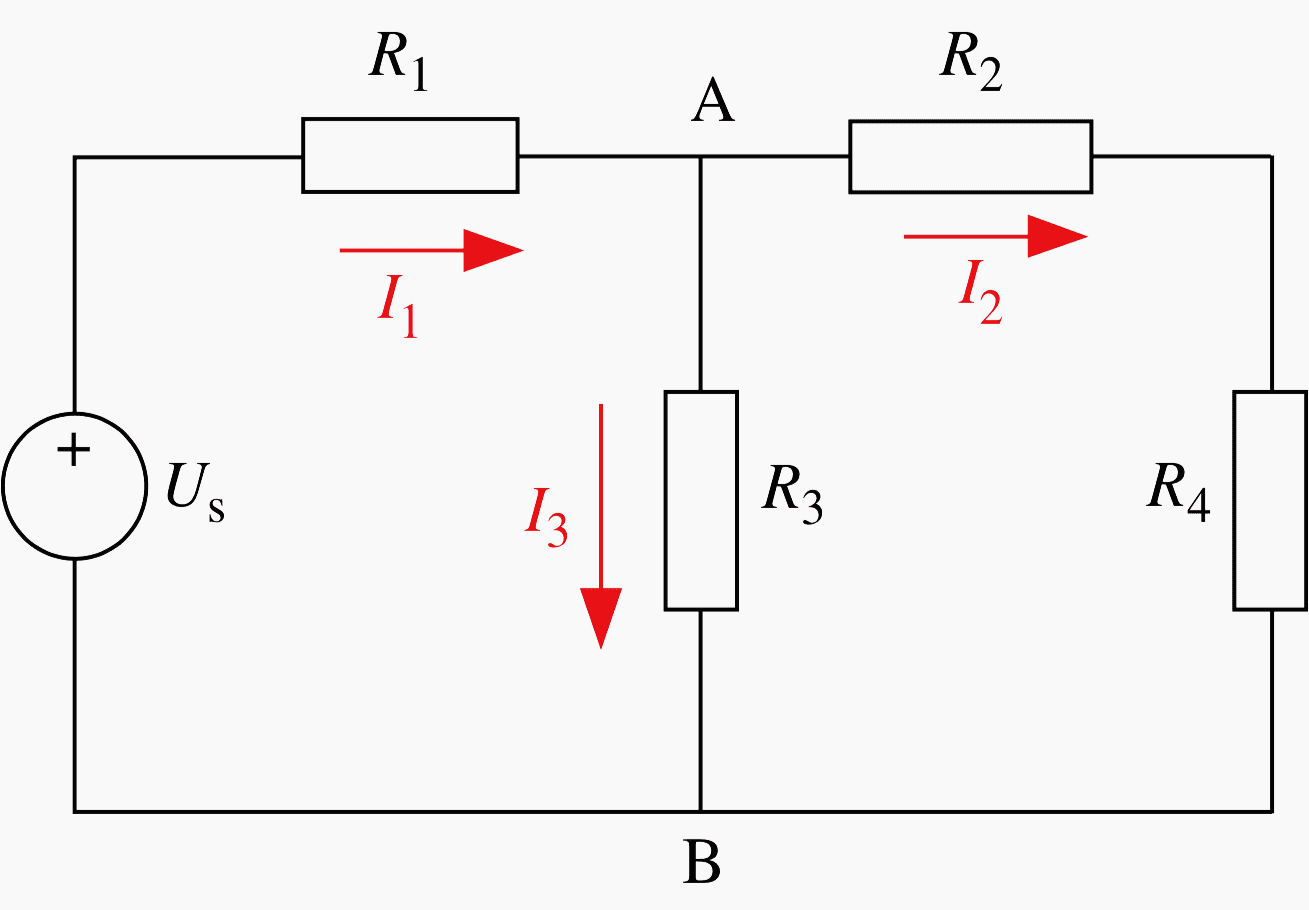

Circuit #4
By applying Thévenin’s theorem between A and B, calculate the equivalent voltage UTh and the equivalent resistance RTh:
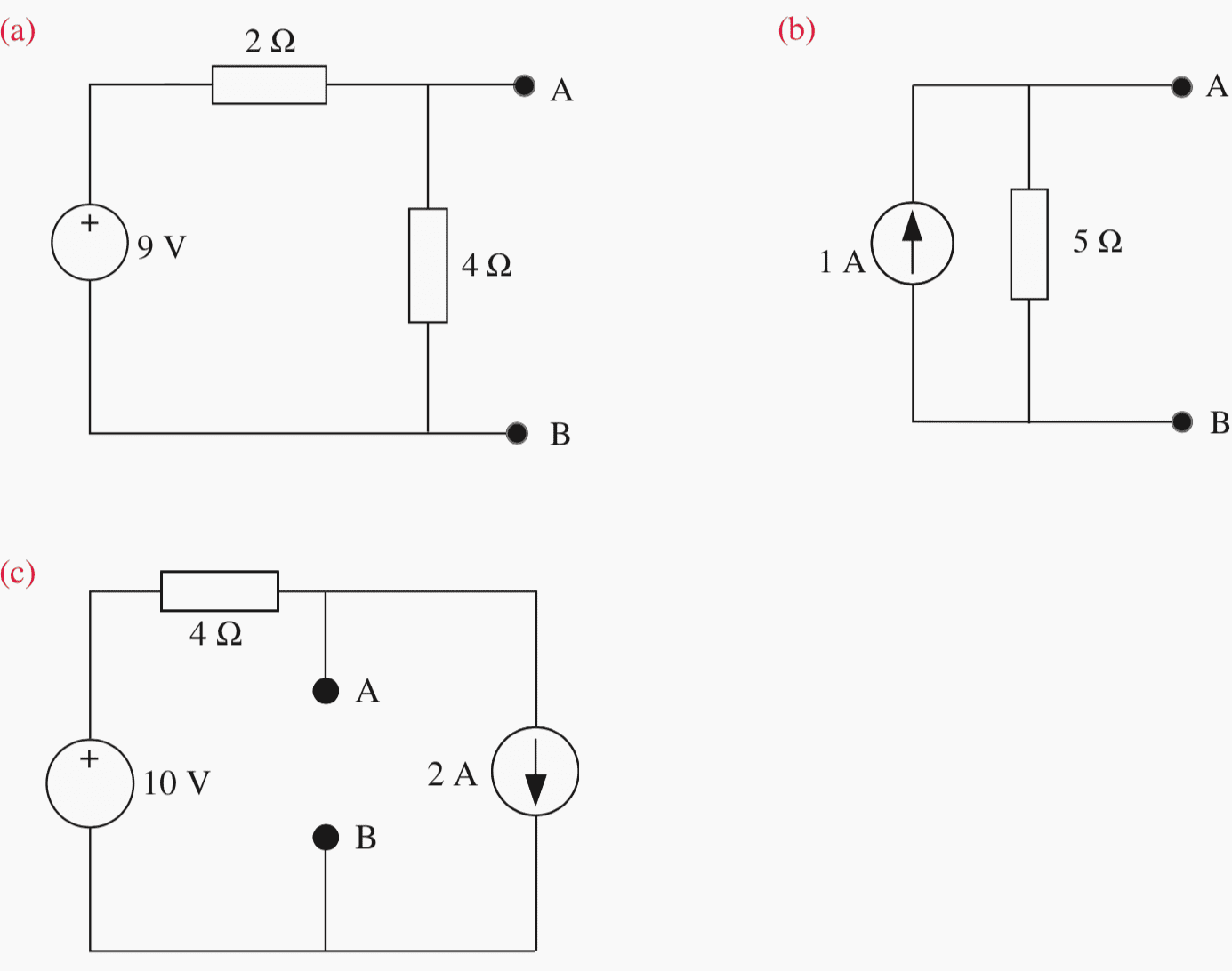

Circuit #5
Solve the following circuit by using:
- The superposition rule;
- KCE;
- Nodal analysis to calculate UAB;
- Thévenin’s theorem to find an equivalent, left-side or right-side section AB.
Input circuit parameters:
- Us1 = 12V
- R1 = 0.5Ω
- R2 = 5Ω
- Us2 = 9V

Circuit #6
Solve the following circuit by using:
- The superposition rule;
- KCE;
- Nodal analysis to calculate UAB (write KCL at node A);
- Thévenin’s theorem to find an equivalent, left-side section AB.
Input circuit parameters:
- Us = 100V
- R1 = 20Ω
- R2 = 30Ω
- Is = 3A


Circuit #7
Find at least three ways to calculate I2 and I3. Is R1 really required to determine currents? And to calculate the power delivered by IS1?
- Is1 = 5A
- Is2 = 1A
- Is3 = 8A
- R1 = 5Ω
- R2 = 1Ω
- R3 = 4Ω


Circuit #8
Calculate current I in the following circuit:
- Us1 = 6V
- Us2 = 2V
- R1 = 1Ω
- R2 = R3 = 2Ω
- Is = 3A


Circuit #9
Calculate the Thévenin equivalent of the following circuit:
- Us1 = 6V
- Us2 = 2V
- R1 = 4Ω
- R2 = 6Ω
- R3 = 2Ω
- R4 = 1Ω
- Is = 1A


Circuit #10
Calculate IA and UAB and determine the power flowing through section AB. Verify the result using the principle of power conservation.
- Us1 = 10V
- Us2 = 4V
- R1 = 1Ω
- R2 = 2Ω
- RI = 1Ω
- Is = 1A


Circuit Solutions
Solution #1
- I1 = 7.5A
- I2 = 2.5A
Solution #2
- I = 0.5A
- UAB = 5V
- Us1 charges Us2
Solution #3
- RG = 6Ω
- I1 = 2A
- I2 = I3 = 1A
Solution #4
- UTh = 6V, RTh = 1.333Ω
- UTh = 5V, RTh = 5Ω
- UTh = 2V, RTh = 4Ω
Solution #5
- I1 = 6A
- I2 = 1.8A
- I3 = 4.2A
Solution #6
- I1 = 0.2A,
- I2 = 3.2A
Solution #7
- I2 = 9.6A
- I3 = 2.4A
Solution #8
I = 2.5A
Solution #9
- UTh = 7V
- RTh = 4Ω
Solution #10
P = 20.22W
Literature for studying:
Basic AC/DC circuit theory, analysis and problems
Theory and problems – Basic circuit analysis by John O’Malley, professor of Electrical Engineering University of Florida.
Lessons In DC Electrical Circuits
Lessons In DC Electrical Circuits by Tony R. Kuphaldt.
Reference // Fundamentals of electrical engineering by Massimo Ceraolo and Davide Poli (Get yourself hardcover from Amazon)











Any electrical relationship