
In principle a frequency converter consists of a rectifier, a d.c. link converter, an inverter and of the control electronics (Figure 1 above).
At the input of the inverter the single phase or interlinked, three-phase a.c. voltage is changed into a pulsating d.c. voltage and is pushed into the d.c. link converter that also serves as energy store (buffer). Capacitors in the d.c. link converter and the LC networks connected to earth in the a.c. line filter, can cause problems with the residual current devices (RCD) connected in series.
The problems, however, result from the short-term induction of fault currents by the frequency converter. These are sufficient to activate sensitive earth leakage circuit breakers (RCDs).
A surge-proof RCD circuit breaker available for a tripping current IΔn = 30 mA and a min. discharge capability of 3 kA (8/20 μs) provides a remedy.
By the control electronics, the inverter delivers a clocked output voltage. The higher the clock frequency of the control electronics for the pulse-width-modulation, the more sinusoidal is the output voltage. With each cycle, a peak voltage is created that is superimposed on the curve of the fundamental frequency. This peak voltage reaches values of 1200 V and higher (according to the frequency converter).
The better the simulation of the sine curve at the output, the better is the performance and control response of the motor. This means, however, that the voltage peaks appear at the output of the frequency converter more frequently.
It specifies the maximum permissible operating voltage a surge protective device may be connected to. This means that surge protective devices with a correspondingly higher Uc are used at the output side of the frequency converter.
This avoids faster ageing due to gradually heating of the surge protective device under normal operating conditions and the consequential voltage peaks. This heating of the arrester leads to a shorter service life and consequently to a disconnection of the surge protective device from the system to be protected.
The voltage at the output of the frequency converter is variable and adjusted a little bit higher than the nominal voltage at the input. Often it is approx. + 5 % during continuous operation, in order to compensate the voltage drop at the connected line, for example.

Example with Dehn devices
1 – DEHNguard S DG S 275
2 – DEHNguard S DG S 600
3 – BLITZDUCTOR XT
Otherwise, one can simply say that the maximum voltage at the input of the frequency converter is equal to the maximum voltage at the output of the frequency converter.
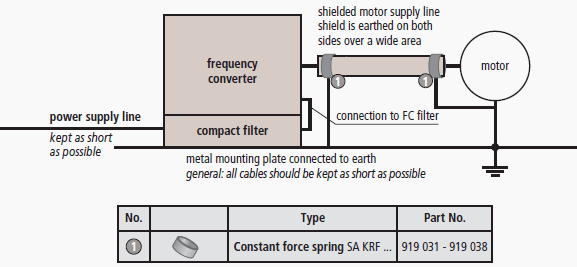
The high clock frequency at the output of the frequency converter generates fieldborne interferences and therefore, requires necessarily a shielded cabling so that adjacent systems are not disturbed.
For shielding the motor power supply line, a bilateral shield earthing at the frequency converter and the drive motor has to be ensured. The large-surface contacting of the shield results from the EMC requirements.
By means of intermeshed earth-termination systems, i.e. the earth-termination system the frequency converters and the drive motor are connected to, potential differences are reduced between the parts of the installation and thus equalising currents via the shield are avoided.
Figure 3 shows the example of use of surge protective devices Type DEHNguard on the power supply side and type BLITZDUCTOR for 0 – 20 mA signals. The protective devices have to be individually adapted according to the interface.
For the integration of the frequency converter into the building automation it is absolutely essential that all evaluation and communication interfaces are connected with surge protective devices in order to avoid system failures.
Resource: Lightning-Protection-Guide – dehn.de











What is the difference between earthing,grounding and nuetral.
Hello
Very interesting these subject.
You have materials or study regarding rectifier failure in the case of a insulation fault on the output of the frequency converter?
In all FC i’ve seen, this rectifier failure (one or two diode or thyristor, depends on the way is made the rectifier) appear when the insulation problem is on the run time.
You know a way to avoid this failure?
Regards
Cosmin Sahian
Variable speed drive & solar inverter service tech.