
Testing and Commissioning Procedures //
1. Objective
2. Test Equipment Required
3. Test procedures
- Mechanical Check and Visual Inspection
- Insulation Resistance Test
- Polarity Test
- Secondary/Loop Resistance Test
- Burden Test (optional test)
- Magnetization Curve Test (optional test)
- Turns Ratio Test (optional test)
- Primary Injection Test
- High Voltage Test
- Commisioning Test
4. Applicable Standards
5. Live VIDEO CT Testing (6 Testings)
1. Objective
To confirm the physical condition and electrical characteristics of current transformer installed in the installation. Ensure the CT is connected to system properly in all respect (primary and secondary).
2. Test Equipment Required
Required equipment for testing:
- Insulation tester
- Polarity tester
- Digital low ohmmeter
- Current source, multimeter
- Variac, step-up transformer (0-2kv)
- Primary current injection set
3. Test Procedures
3.1. Mechanical Check and Visual Inspection
- Verify nameplate ratings are in accordance with the approved drawings and specifications.
- Inspect for physical damage/ defects and mechanical condition.
- Verify correct connection of transformers with system requirements.
- Verify that adequate clearances exist between primary and secondary circuit wiring.
- Verify tightness of accessible bolted electrical connections by calibrated torque-wrench method.
- Verify that all required grounding and shorting connection provided.
- Verify all shorting blocks are in correct position, either grounding or open as required.
- Verify single point grounding of eachcore done properly. Grounding point shall be nearer to the CT location. However grounding shall be at relay point in case of several CT secondaries connected together like differential protection.
3.2. Insulation Resistance Test
The voltage shall be applied between:
- Primary to secondary plus ground (covered during switchgear test).
- Secondary to primary plus ground.
- Secondary core to core.
Test voltage limits mentioned in table below. The ambient temperature shall be noted down during test.
Table – Test Voltage Limits
| Rated voltage | Test voltage |
| 100-1000V AC/DC | 1000V DC |
| >1000 to 5000V | 5000V DC |
3.3. Polarity Test
Polarity test is to confirm the polarity marking on the CT primary and secondary and verify it is matching with drawing. More ever it is giving an idea, how to connect the secondaries to make the protection (like directional, differential) and metering function properly.
Isolate CT secondary from the load and make circuit connection as shown in Figure 1.
Close and open the battery switch connected on the primary. Observe the pointer is moving +ve direction, while closing and –ve direction while opening for correct polarity.

3.4. Secondary / Loop Resistance Test (optional test)
Secondary resistance test is to verify the CT secondary winding resistance with specified one and no discontinuity in the winding. This value can be used in other calculations.
Loop resistance to ensure load is connected properly and circuits not left open. The circuit connection shall be made as shown Figure 2 for secondary resistance. Measure the dcresistance value and record. The same shall be done for all taps and cores. These values are influenced by temperature, so ambient temperature must be recorded during this test. The circuit connection shall be made as shown Figure 2 for loop resistance.
Measure the dc resistance including CT and load, phase by phase and values can be compared between them.
Limits:
The value must be with in specified on nameplate after the effect of temperature taken in to account. If not factory test results shall be taken as reference.
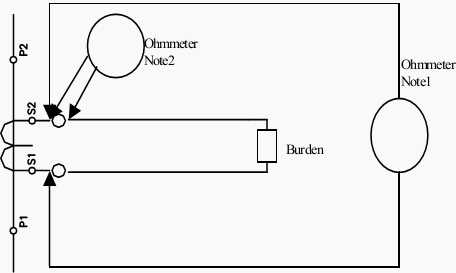
Notes:
- Ohmmeter connection for CT resistance excluding burden.
- Ohmmeter connection for CT loop resistance including burden.
3.5 Burden Test (optional test)
Burden test is to ensure the connected burden to CT is with in the rated burden, identified on the nameplate.
Injected the rated secondary current of the CT, from CT terminals towards load side by isolating the CT secondary with all connected load and observe the voltage drop across the injection points. The burden VA can be calculated as
Burden VA = Voltage drop x rated CT sec. Current.
Limits:
The calculated burden should be less than rates CT burden.
Note:
- Ammeter selector switch should be at respective phase during test.
- High impedance relays shall be shorted during the test.
3.6. Magnetization Curve Test (optional test)
Magnetization Curve test is to confirm the magnetisation characteristics of CT with nameplate specification.
This test shall be conducted before ratio test and after secondary resistance and polarity test, since residual magnetism left in the core due to DC test (polarity, resistance), which leads additional error in ratio test. The meters used for this test shall be having true RMS measurement.
The circuit connection shall be made as shown Figure 3. The primary should be open during test.
Demagnetisation
Before start the test demagnetise the core by Inject voltage on secondary terminals and increase up to where considerable increment in current with small voltage increment. Now start decreasing the voltage to zero, the rate at which increased.
Magnetisation test
Now increase the voltage and monitor the excitation current up to the CT reaching near to saturation point. Record the reading of voltage and current at several points. Plot the curve and evaluate the Vk and Img from the graph.
Limits:
Class X CT:
The obtained Vk should be greater than specified one; mag current should be less than specified one.
Protection class CT:
The secondary limiting voltage can be calculated as follow:
Vslv = Is * ALF (Rct + (VA/Is*Is))
Where:
Is – rated secondary current
Rct – CT secondary resistance
VA – rated CT burden
ALF – Accuracy limit factor
The mag current (Img) drawn at Vslv can be obtained from graph. The following criteria should be satisfied.
Img < accuracy class * ALF * Is
Metering Class CT:
Accuracy can be ensured as follow:
Img at Vs (= 1.2 * VA / Is) should be less than (accuracy class * Is)
And instrument security factor to be verified.

3.7. Turns ratio Tests (optional test)
This test is to ensure the turn’s ratio of CT at all taps. The circuit connection shall be made as shown Figure 4. The primary current of minimum of 25% rated primary current to be injected on primary side of CT with secondaries shorted and the secondary current can be measured and recorded for all cores.
Limits:
The obtained turn’s ratio should match with rated nameplate ratio.
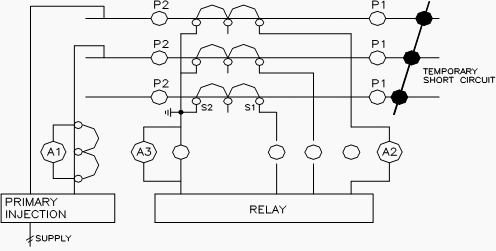
3.8. Primary Injection Test
This test is to ensure the CT circuits are properly connected with respected cores and there is no mix up in the circuit (phase identification).
The circuit connections shall be made as shown in Figure 4. Single point grounding shall be verified for CT circuits, before starting this test. Inject 25% of rated primary current between one phase and earth with all connected burden. Measure secondary current at all points of CT circuits. It shall be done for other phases.
Core identification:
When one CT is having several cores used for different purposes. The cores can be identified during primary injection test by shorting the one of the core at CT terminal itself and check there isno current only at relevant load. The same can be verified for other cores.
Inject 25% of rated primary current between phase to phase with all connected burden. Measure secondary current at all points of CT circuits. It shall be done for other phases.
Limits:
- Secondary current should only be observed at respective phase and neutral leads during Phase to earth injection.
- Secondary current should only be observed at respective phases and no current on neutral during Phase to phase injection.
3.9. High Voltage Test
This test is included with switchgear high voltage.
Objective of HV test is to determine the equipment is in propercondition to put in service, after installation for which it was designed and to give some basis for predicting whether or not that a healthy condition will remain or if deterioration is underway which can result in abnormally short life.
Test Instruments Required for HV Test
Calibrated AC hi-pot test set for switchgear with leakage current indicator and overload protection. Calibrated DC hi-pot test set for cables with leakage current indicator and overload protection.
3.10. Commisioning Test
After commissioning, secondary current measurement shall be carried out in CT circuits. Phase angle check shall be done for correct direction. Go to Content ↑
4. Applicable Standards
- IEC 60044-1: Instrument transformers – current transformer.
- IEC 60694: common specifications for HV switchgear.
5. Live VIDEO CT Testing (6 Testings)
1. CT Tests – Ratio and Polarity
Cant see this video? Click here to watch it on Youtube.
2. CT Tests – Burden Secondary Side
Cant see this video? Click here to watch it on Youtube.
3. CT Tests – Excitation Curve
Cant see this video? Click here to watch it on Youtube.
4. CT Tests – Winding or Burden Resistance
Cant see this video? Click here to watch it on Youtube.
5. CT Tests – Voltage Withstand Test
Cant see this video? Click here to watch it on Youtube.
6. CT Tests – Polarity By Pulses
Cant see this video? Click here to watch it on Youtube.
Resource: Testing and Commissioning of Electrical Equipment – Schneider Electric Service Dpt.











Suggestion: you may consider to introduce the single point ground verificaiton for the CT circuit as a test.
I always want to confirm that. We check and verify that the neutral of the CT is grounded at one point only, as per the drawing (confirm that the drawing identifies that correctly) and then check the continuity w.r.t ground with the ground connected and disconnected to verify that the grounding is proper and that removing the ground isolates the CT from it.
Please inform me how many type of test need for oil type CT and PT.
Anyone can you please explain the procedure and required testing equipment to conduct the thermal stability and thermal co-efficient test on 66kV & 110kV Current Transformer.
New to your excellent engineering portal.
Nice to know your background and engineering wisdom to the power systems.
Nice article. Very helpful for me, thanks and wish many more such articles.
Very nice article.
Can anyone answer plz.
Why burden test is mentioned to be optional?
and what is need of shorting the high impedance relay during the test?
nice article
I am JE of Nagbhir sub station of 132/25 kv newly electrified section and testing started of current transformer when test CT ratio by injecting current in primary bushing of old CT which was 20 years old CT installed in circuit,after testing values not found according to ratio,100 amps inject and found in secondary terminal 3.9 amps please send me solution.
First open links in jb then measure ratio ,same repeat even after links open directly measure on secondary across terminals ,if same repeat primary terminals have to be checked properly (one should earth another shouldn’t) eventhough repeat …have to replace
I am a planning Engineer. Recently I came in a situation of our New substation which is in commissioning phase. I was tasked to prepare a detailed L7 schedule by cubicles and activities. We have a permanent grid power source from an existing substation. 2 incoming feeder from old substation supply permanent power to New Substation.
I am wondering if there is a sequence b/w various steps mentioned above and duration for each of them, will help to plan a detailed schedule and also track them as well. Please supports
tHANKS FOr yoUR VAluaBLE InfO OVer tTHE yeARS MR. Edvard Csanyi……
Very helpful. Thanks Sir
sir i can’t download this article because download link is not available .plz help me
Yes, I am a Electrical Engineer from SriLanka and I have been reading your valuable technical Articles for more than one year period and I have learned a lot from them and wish to add some articles in the near future. Thanks for your great service.
appreciate the article and the vedios thanks very much if you could include the test formate please
Can you provide me with a test format or a sample of test report please.