Courses and education
Learning and studying have never been easier than nowadays. Since we started the EEP Academy, there are thousands of electrical engineers, students, technicians, and many others who are literally hungry for knowledge and experience. This is where EEP’s contribution comes into the first plan. EEP Academy has over fifty handy and quality electrical engineering courses and bundles.

All video courses at the EEP Academy are pre-recorded and on-demand type. Students have lifetime access to all purchased courses and can access them anytime, there is no time limit.
The instructors are electrical engineers and senior electrical professionals with a minimum level of 10+ years of experience each. Most of them have served at the highest level of various industries throughout the world.
Starting from the fundamentals of electricity and AC/DC circuits, you can learn three-phase power analysis, power transformers, protection & control of high voltage circuits, short-circuit analysis, substation protection, LV distribution design, solar energy systems, electrical designing & drafting, etc. If you are serious about electrical design, you can learn to design electrical systems in the most popular software like Matlab/Simulink, AutoCAD, ETAP, or Dialux.
Whether you are looking to improve your own job or trying to boost your electrical engineering career by expanding your knowledge on the field, the EEP has the most motivating learning paths for you.
More information you can find here.
Please note that courses are not ordered by importance or quality and that the list of the best ones doesn’t end here. There are also many other great courses and bundles worth checking. You can take a look at them all here – Course Catalogue.
- Ultimate Course To Electrical Design Drawing Using AutoCAD, Dialux And ETAP
- Earthing & Grounding in Power Systems – Calculations, Design & Measurements
- Low Voltage Distribution Design Course: AutoCAD, DIALux, Excel, Calculations
- Electrical Designing and Drafting Course
- Distribution Substation and Feeder Protection
- Design Tools – Low Voltage Power Calculations in Simaris Design
- MATLAB/Simulink Course: Power System Simulations
- PLC Programming Course – Fundamentals of PLC Ladder Programming Using Logixpro Simulator
- The Substation Fundamentals Course
- Power System Analysis – Load Flow and Short Circuits
1. Ultimate Course To Electrical Design Drawing Using AutoCAD, Dialux And ETAP
Course Content – 64 lectures in 8h 5m total length.


This course is essential for electrical power engineers who want to work in the distribution field; this will guide you from zero even if you don’t know anything. So what are we going to learn in this course?
- All necessary tools and commands required by electrical power engineers in AutoCAD.
- Different types of electrical drawings, various lighting schemes, and lighting situations.
- Requirements for a good lighting scheme, maintenance, and utilization factors.
- Lighting design steps (use of catalogs and photometric data in Dialux)
- How to do the manual calculation for lighting instead of Dialux.
- Interior design drawing by taking a factory floor and start creating rooms in Dialux.
- Wiring using AutoCAD and connect the luminaries with Wires and connect to the panel.
- Adding sockets, do the wiring for them, and connect them to the panel.
- Electrical panel schedule for our project.
- Circuit breakers and cables and how to select them for our project.
- Earthing system and how to design it.
- Calculation of the voltage drop and short circuit analysis using ETAP.
Who is this course for? – Electrical power engineers who want to learn about interior electrical design.
2. Earthing & Grounding in Power Systems (Design, Calculations, & Measurements)
Course Content – 27 lectures in 4h 36m total length.


This course will teach you how to calculate, design, and measure earthing and grounding systems. This course covers all of the earthing issues that you can deal with in real-life applications. You will also learn step potential, touch potential, mesh potential, transfer potential, etc., which are fundamental concepts for designing earthing systems.
General Overview Section – You will learn why we need earthing and grounding systems and the three fundamental grounding systems called TN, TT, and IT.
Measurement Section – You will learn how to measure and calculate soil resistivity with different methods like the variation of depth method, Wenner method, and Schlumberger–Palmer method. You will also learn how to measure earthing resistance with different methods: dead earth method, three-point method, fall of the potential method, and equilateral triangle method.
Design Section – You will learn different earthing topologies that you can use in your projects. A comprehensive example of the earthing system design is also included in the design section.
Calculation Section – You will learn each calculation method for different earthing system topologies like a single earthing rod, single earthing plate, earthing conductor mesh systems without earthing rods, earthing conductor mesh systems with earthing rods, etc.
Who is this course for? – Electrical engineers, technicians, electrical engineering students, anyone who wants to learn electrical power networks.
3. Low Voltage Distribution Design Course: AutoCAD, DIALux, Excel, Calculations
Course Content – 62 lectures in 10h 0m total length.
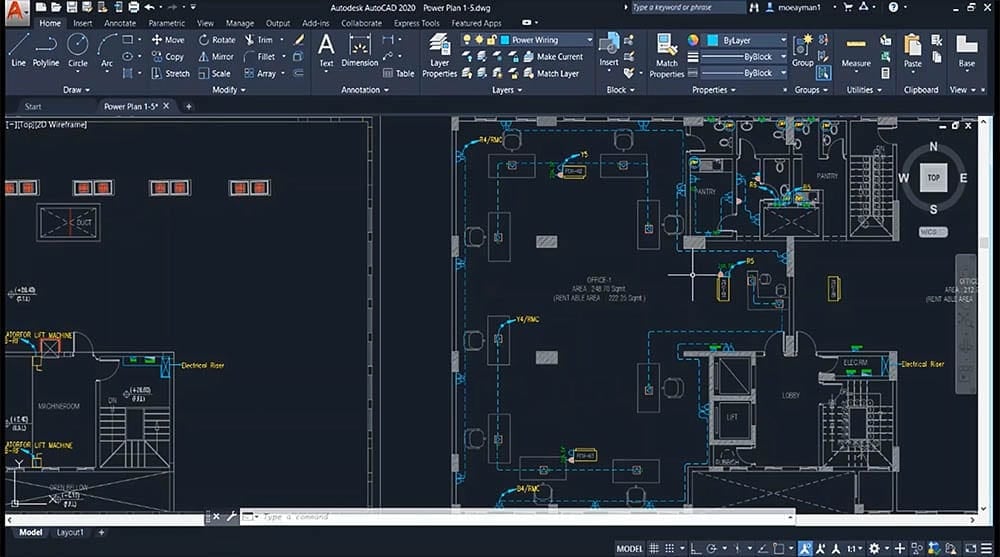

This course is dedicated to students who are looking to acquire electrical low-voltage power design experience from scratch. It covers low voltage distribution system design-related topics in a total duration of 10 hours.
Essentially, the course begins Section 1 by introducing the well-known drawing software “AutoCAD” by emphasizing its different toolbar options to prepare the student to be familiar with its use. Consequently, lighting design and lux calculations using DIALux software are fully explained in Section 2 to prepare for the lighting distribution system explained and designed as the following step in Section 3.
Thereafter, lighting & power systems distribution is covered in Sections 3 & 4, which in turn prepares the student to understand how to gather information and calculate the total connected loads by the lighting and power designed layouts to be reflected in the panel schedules and single line diagrams which will be explained in the 5th section of this course.
All these calculations will be explained separately in detail using simple steps that you will be able to apply manually and with the help of predefined Excel sheets for solving different formulas in Section 6.
The last section of this course covers the earthing and lightning system topics emphasizing their different types, components, and the appropriate methods to design these systems according to international standards.
Besides, the course is enhanced with a variety of helpful resources that are attached to it (XLSX, DOC, DWG, and PDF).
Who is this course for? – Electrical engineers, electrical draughtsmen, electrical designers, electrical fresh graduates and technicians.
4. Electrical Designing and Drafting Course (Bundle – 2 Courses)
Course Content – 136 lectures in 13h 51m total length.
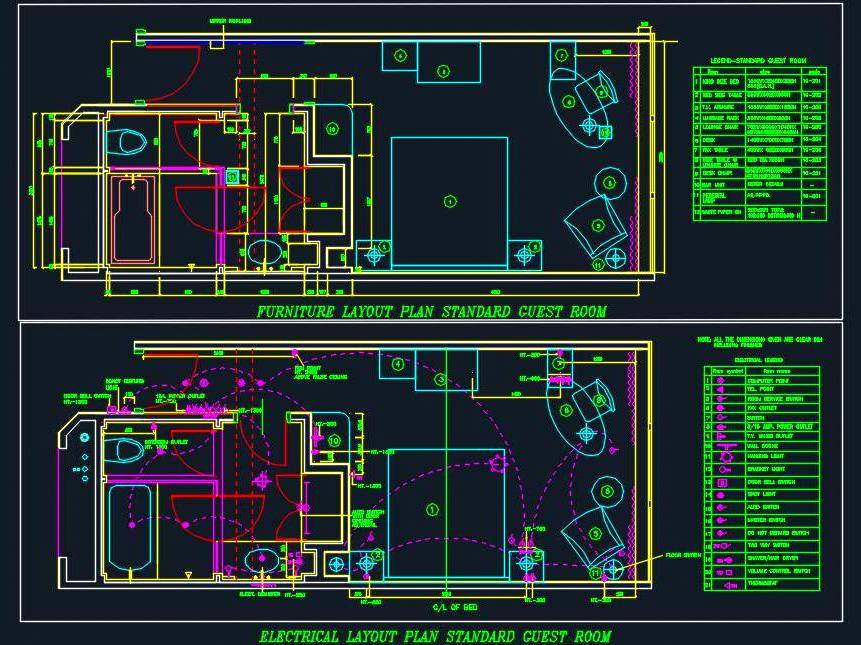

This course introduces the student to the process of designing residential and commercial projects. After completing this course, you will have high confidence in your practical work and start working on your design projects using AutoCAD. Or if you are fresher, you can start your career as a professional in this competitive world.
Students will learn various electrical calculations and have an access to the comprehensive chapter for learning AutoCAD from scratch to professional level (60 lessons + real project included in DWG). All calculations and explanations are as per the NEC and other international codes and standards.
- Basics of electrical: The basics of electrical engineering, basic formulae, types of load, operating voltage levels, etc.
- Basic formulae: Some most important formulae plus a short assignment for you.
- Codes, Standards & Lux Levels: Internationally acceptable codes & standards, lux level required for any area for lighting design.
- Illumination Design: Types of lighting lamps, types of the lighting system, Kelvin Color Temp., CRI.
- Basics of Air Conditioner: For small projects, you will learn the basics of A/C.
- Circuit Breakers: What is CB, types of CB, working & operation, calculation, etc.
- Capacitor Banks: The need for a capacitor bank, the benefits, and how to calculate the size of the capacitor bank.
- Electrical Designing: Calculation of lighting/raw power socket, fans, no. of lighting fixtures, sizing of A/C, load scheduling/balancing, distribution board, etc.
- Electrical Motors: Types of motor and their application, starting methods, starting current, etc.
- Electrical Transformer: Transformer parts, classification, cooling methods, winding insulation class, faults, size calculation, etc.
- Diesel Generator: DG parts of DG, ATS, transformer classification, DG faults, size calculation, etc.
- UPS: Introduction, types, size calculation, battery size calculation.
- Cables & Cable Sizing: Introduction, cable sizes, cable parts, insulation types, important points related to cable, size calculation, etc.
- Voltage Drop Calculation: Voltage Drop Calculation in a cable.
- Short-Circuit Calculation: Short circuit current capacity calculation for proposed cables, calculate the tripping time of CB.
- Cable Tray Size Calculation: The concept of cable tray, cable tray size calculation.
- Earthing: Earthing concept and calculation of earthing pit, strip, rod, etc.
AutoCAD (60 Lessons) – This section relates to the software part, where this AutoCAD chapter you will learn how to use AutoCAD in a professional manner, control keys, function keys, basic drawing commands, modifying commands, editing commands, dimension commands, block/layer, print commands, etc, plus practice.
Assignment At the end, you have given a Real-Time Project for ground + five floors. You have to do all the calculations for a complete electrical design for this building.
Who is this course for? – Electrical graduates, electrical designers, freshers, electrical operators, developers, site engineers, facility maintenance personel, and technicians.
5. Distribution Substation and Feeder Protection Course
Course Content – 5 chapters in 3h 51 min total length.


This course covers utility distribution stations and feeder protection including fuses, new intelligent electronic device (IED) relays, and old-school time overcurrent relays. Feeder relays and apparatus are examined including reclosers.
Power transformer protection is reviewed including current mismatch caused by differing CT ratios; delta-wye transformation & currents shifts; mismatch induced by load tap-changers; CT saturation and remanence, inrush phenomena, and harmonic content problems.
- Chapter 1 – Per Phase Analysis
- Chapter 2 – Substation Protection
- Chapter 3 – A Protection Coordination Problem
- Chapter 4 – Surge Protective Equipment
- Chapter 5 – Transformer Protection
- The Final Exam With 17 Questions
Who is this course for? – Engineers, technologists, technicians, supervisors and students.
6. Design Tools – Low Voltage Power Calculations in Simaris Design
Course Content – 12 lectures in 1h 25m total length
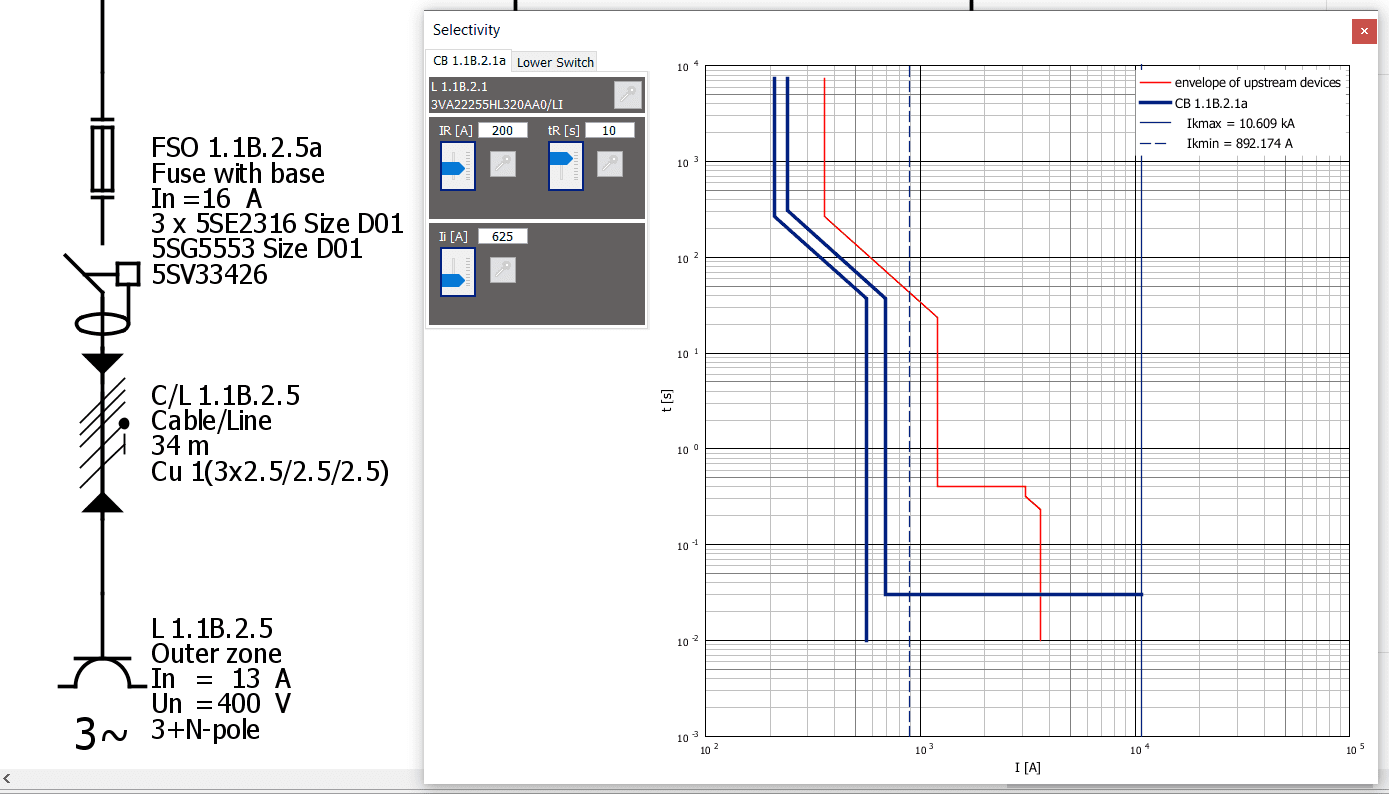

Planning an automation project and the electrical wiring on that project starts with power calculations. This is one of the first steps you should take when you start working on a new low voltage electrical system.
Simaris Design is, according to our experience, by far the best one out there to quickly set up a project, create single line diagrams, and output all the possible documents that one needs when performing power calculations (project documentation, different list in Excel, e.g. busbar, cable, device settings, selectivity documentation, etc., single line diagrams in PDF and DWG/DXF).
When creating single line diagrams in Simaris Design the devices you use are grouped into three categories:
1. System infeed – Transformer with primary and secondary side, transformer only with secondary side, coupling to use when you have also emergency power supply, like a diesel aggregate (generator), etc.
2. Distribution boards – With busbars, without busbar, sub-distribution boards, etc.
3. Final circuits – Electrical consumers ranging from general devices, motors (including DOL, soft starter, reverse-duty, and frequency converter), power outlets up to special dummy loads. You even have the possibility to insert a charging unit for electric cars. Talking about awesomeness :)
We definitely highly recommend this software to all of you who work in the electrical engineering field. We recommend you invest some time to get to know this program. It’s worth it.
Who is this course for? – students of electrical engineering, electricians, engineers, technicians, maintenance department in factories when planning new investments in production, construction site engineers to quickly plan and dimension their low voltage installation, engineering offices when designing new electrical and automation systems, and anyone who needs occasional dimensioning of their low voltage installations.
7. MATLAB/Simulink Course: Power System Simulations
Course Content – 18 lectures in 4h 32m total length.
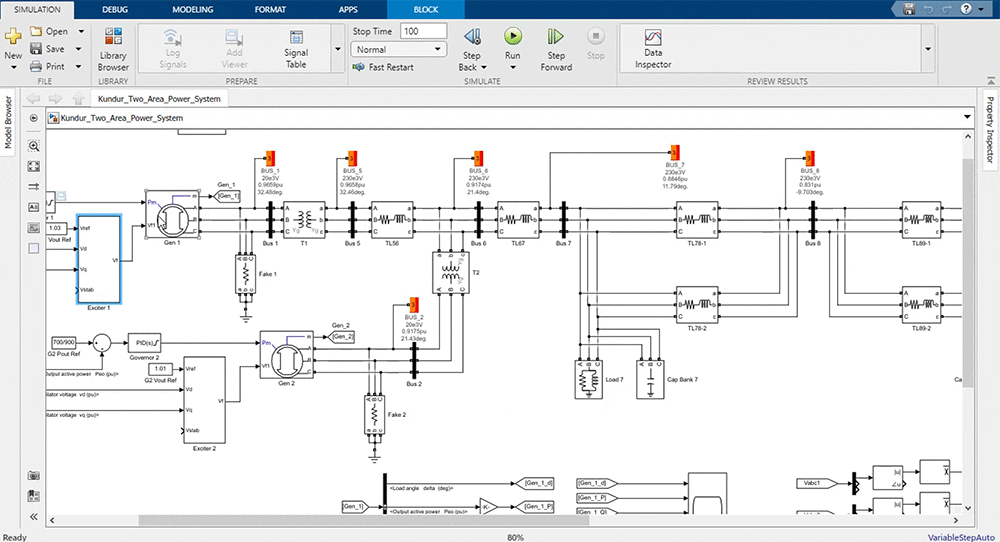

This course is designed to allow you to simulate power systems in MATLAB/Simulink. This course not only gives a review of the theory of how power systems operate but also gives several examples of how to run different types of power system studies using MATLAB/Simulink. The course is divided into the following sections:
1. Introduction to MATLAB/Simulink for Power Systems:
In the first section of the course, we will begin by reviewing the libraries available in Simulink to represent generators, transformers, transmission lines, and loads in our models. After that, we will take a look at how we can model these components in Simulink, as well as how we can put them together in a model and how we can take measurements in the model to ensure proper simulation.
2. Power System Studies in MATLAB/Simulink:
After we’ve made ourselves familiar with the MATLAB/Simulink environment building a small power system model, we will move on to build a large power system model which includes several generators, transformers, transmission lines, loads, and capacitor banks. We will also model the turbine control systems and excitation control systems for all generators to simulate the realistic dynamic behavior of power systems in real life.
In each section, we will go over several models to illustrate how we can design and simulate power systems in MATLAB/Simulink. The models are also available for download so that you can follow along, as well as use these models and modify them to create your own power system models.
Who is this course for? – Engineering students, practicing engineers, and anybody with an interest in learning about power systems and/or MATLAB/Simulink.
8. PLC Programming Course – Fundamentals of PLC Ladder Programming Using Logixpro Simulator
Course Content – 32 lectures in 6h 30m total length.


This course is designed for anyone who has zero knowledge about PLC and would like to learn the basics of PLC and ladder programming. In this course, we will use Logixpro Simulator in which we will write the coding and simulate inside the program so that we can see the effect of our ladder diagram.
In this course you will:
- Understand PLC hardware configuration,
- Understand the types of inputs and outputs in PLC,
- Understand the advantages of using PLC over classic control,
- Differentiate between PLC programming languages,
- Learn the definition of the PLC scan cycle,
- How to use markers in PLC,
- How to use counters and timers,
- Do tasks in silo, batch, I/O, and door simulators.
Who is this course for? – Anyone who would like to gain knowledge about ladder programming in PLC and engineers who wants to learn about Logixpro Simulator.
9. The Substation Fundamentals Course
Course Content – 29 lectures in 5h 01m total length


Course for power engineering students about substations and electric power systems (circuit breakers, grounding systems, ring main units, transmission lines, and more!).
This 5-hour course will discuss the following topics related to electrical power substations:
- Function, classification, and voltage of electrical substations.
- Main components like power transformers, conductors, insulators, switch gears, current transformer, capacitor voltage transformer, and voltage transformer.
- Different types of circuit breakers, relays, their classification according to time, construction, and function.
- Difference between circuit breaker and fuse and their applications.
- IP or ingress protection.
- Grounding system including the effect of current on the human body and components of the grounding system.
- Types of electric hazards and classification of earthing systems.
- Measuring the earthing resistance by Megger and the three-point method.
- Design of an earthing system using ETAP program.
- Ring main unit and its importance in electrical power system.
- Types of switches used in electrical power systems and substations.
- Overhead transmission lines, underground cables, and the difference between them.
- Busbars in power system, its importance, its different schemes and how to select them.
- Lightning arrester and wave trap used in substations.
- Air and gas-insulated substations.
- Overview of the design of an electrical substation and single line diagram of 66/11 kV substation.
Who is this course for? – Electrical power engineers who want to learn about electrical engineering power systems and substations.
10. Power System Analysis Course: Load Flow and Short Circuits
Course Content – 19 lectures in 3h 27m total length.
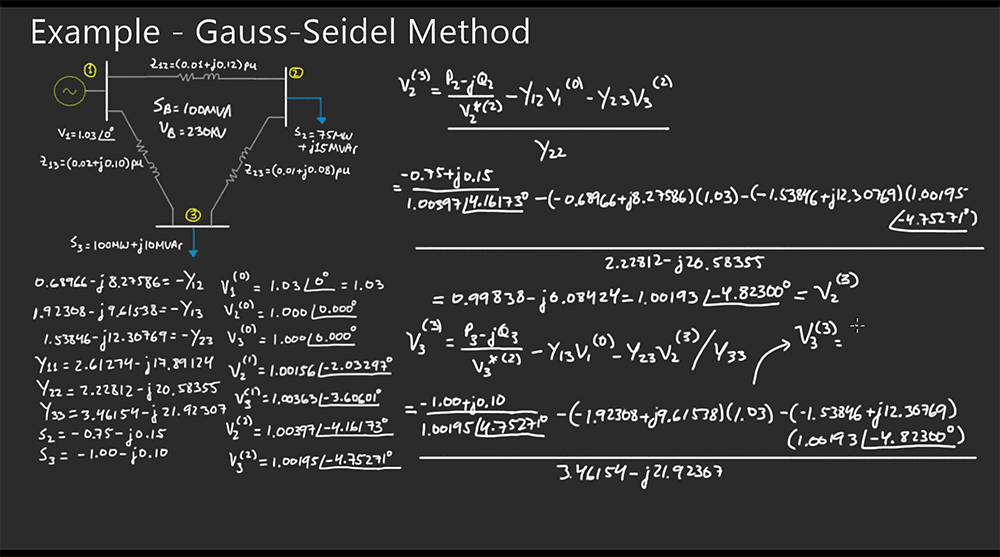

This course is dedicated to one of the main areas of electrical engineering: power system analysis. Power system analysis is the core of power engineering and its understanding is therefore essential for a career in this field. In this course, you will learn about power flow (load flow) analysis and short circuit analysis and their use in power systems.
The course is divided into the following sections:
1. Power Flow (Load Flow) Analysis:
In section 1, we will introduce the concept of power flow. Also referred to as load flow, power flow is the analysis of how apparent, real, and reactive power flows between parts of a power system, from generation to loads. Two different methods will be covered, which are the most widely used methods in power system analysis: the Gauss-Seidel method and the Newton-Raphson method.
Several examples will be solved to help explain how these methods are used for power flow analysis.
2. Short Circuit Analysis of Balanced Faults:
In section 2, we will introduce short circuits. Also referred to as faults, short circuits are undesired occurrences in power systems when conductors are shorted between each other, to ground, or a combination of these.
3. Short Circuit Analysis of Unbalanced Faults:
In section 3, we will continue discussing short circuits (faults) but will discuss the more complex analysis of unbalanced faults (e.g., single-line-to-ground, line-to-line, and line-to-line-to-ground faults). To do this, we will introduce the technique of symmetrical components, which allows us to analyze unbalanced power systems more easily.
In each section, several examples are solved to illustrate how to analyze real-world power systems.
By learning about power flow analysis and short circuit analysis and how they are used in power systems, you will be able to continue your study of power system analysis for a career in power engineering and electrical engineering.
Who is this course for? – Electrical designers, power engineers, and anybody with an interest in learning about power systems and power engineering.











Explain in 11 kv line one phase line cut and fallen on ground out going side of the line at the stage feeder breaker not tripped due to line out going side fall on ground
really very good explain
A great work and very interested and educating
Wonderful and very useful guide
Good note
Thanx for inviting me to the House of learned friends.
Am hungry for all the courses But honestly, I don’t know where to start.
Kindly Advise.