
1. Introduction
A suspension insulator strain consists of a series of alternately insulators and metal parts, which bind each insulator to the next. This constitutes a series of connected capacitors, with each one’s capacitance being created by two successive metal connectors (clips) with the porcelain as a dielectric.
So let us consider a strain of four suspension insulators, as shown in the figure below, and let C be the same capacitance for each unit and kC the capacitance of each metal connector with earth.
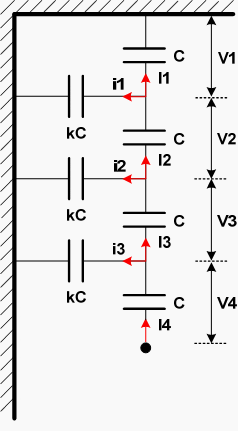
Then, if V1 is the potential difference between the two metal connectors (clips) of the first insulator, we have:
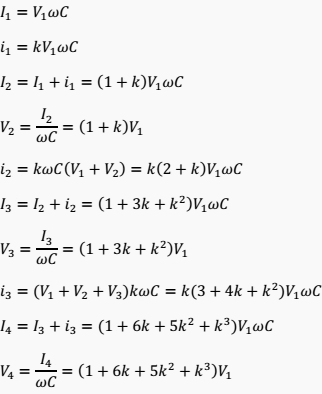
Even V1 + V2 + V3 + V4 = E (phase voltage of the line) → E = V1 (4 + 10k + 6k2 + k3)
So, if k = 0,1, we have:

2. Corona rings
The distribution of the potential along the insulators strain can be improved by using a smoothing ring (Corona ring) or a protective ring, which consists of a large metal ring surrounding the last insulator that is electricallyconnected to the line.
The corona ring inserts capacitances between the metal connectors (clips) of the insulators and the line. For these capacitances, special care can be taken in order to compensate the capacitances to earth.
3. Cases of insulators strains with or without Corona rings
Case 1
Determine the potential distribution in a strain of three insulators, if the capacitances of the links to earth and to the line are respectively 20% and 10% of the capacitance of the insulators. Also, determine the performance of the strain.


![]()
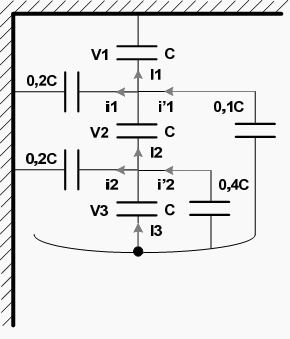
Case 2
An overhead 3-phase transmission line, which has phase voltage 30 kV, is hanging from a three insulators suspension strain. The capacitance between the links and the earth is 0,2 C, where C is the capacitance of an insulator.
- Determine the potential distribution along the insulators strain.
- If a protective (corona) ring inserts capacitances from the line, with the link of the middle and the lower insulator set at 0,4 C and the link of the medium and the higher insulator set at 0,1 C, find the new distribution.
2.1 Determine the potential distribution along the insulators strain


2.2 Protective (corona) ring inserts capacitances from the line

4. Generalized formula of voltage distribution in a suspension insulators strain
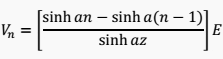
The above mathematical formula is the generalized formula we can use to find the voltage Vn of the (n-1) insulator.
E = phase voltage of the line.
The value of ‘a’ is given by the above formula:

4.1 Determine the voltage distribution in a six insulators strain (z=6) with k=0,1

4.2 Determine the voltage distribution of the first, the sixth and the twelfth insulator with z = 12 (12 – insulators strain) and k = 0,1
We have:

References:
- Vasilios N. Xanthos – Generation, Transmission, Distribution, Measurement and saving of Electrical Energy











Hi Sir very nice work and truly information given about of Voltage Distribution.
Thank you
http://electronicsrical.com/voltage-distribution-over-insulator-string-overhead-line-insulator/
please convey me the C value of :
What is the capacitance value of 11 kv disk insulator?
What is the capacitance value of single long rod insulators used at 145 kv and 245 kv line to line voltage?
nice explanation >>>