Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB)
Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) is a device used to directly detect currents leaking to earth from an installation and cut the power and mainly used in TT earthing systems.

There are two types of ELCBs:
- Voltage Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (voltage-ELCB)
- Current Earth Leakage Current Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (Current-ELCB).

An Voltage-ELCBs were first introduced about sixty years ago and Current-ELCB was first introduced about forty years ago. For many years, the voltage operated ELCB and the differential current operated ELCB were both referred to as ELCBs because it was a simpler name to remember. But the use of a common name for two different devices gave rise to considerable confusion in the electrical industry.
If the wrong type was used on an installation, the level of protection given could be substantially less than that intended.
To ignore this confusion, IEC decided to apply the term Residual Current Device (RCD) to differential current operated ELCBs. Residual current refers to any current over and above the load current.
Voltage Base ELCB
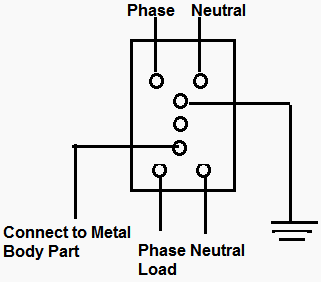
- Voltage-ELCB is a voltage operated circuit breaker. The device will function when the Current passes through the ELCB. Voltage-ELCB contains relay Coil which it being connected to the metallic load body at one end and it is connected to ground wire at the other end.
. - If the voltage of the Equipment body is rise (by touching phase to metal part or failure of insulation of equipment) which could cause the difference between earth and load body voltage, the danger of electric shock will occur. This voltage difference will produce an electric current from the load metallic body passes the relay loop and to earth. When voltage on the equipment metallic body rose to the danger level which exceed to 50Volt, the flowing current through relay loop could move the relay contact by disconnecting the supply current to avoid from any danger electric shock.
. - The ELCB detects fault currents from live to the earth (ground) wire within the installation it protects. If sufficient voltage appears across the ELCB’s sense coil, it will switch off the power, and remain off until manually reset. A voltage-sensing ELCB does not sense fault currents from live to any other earthed body.

- These ELCBs monitored the voltage on the earth wire, and disconnected the supply if the earth wire voltage was over 50 volts.
. - These devices are no longer used due to its drawbacks like if the fault is between live and a circuit earth, they will disconnect the supply. However, if the fault is between live and some other earth (such as a person or a metal water pipe), they will NOT disconnect, as the voltage on the circuit earth will not change. Even if the fault is between live and a circuit earth, parallel earth paths created via gas or water pipes can result in the ELCB being bypassed. Most of the fault current will flow via the gas or water pipes, since a single earth stake will inevitably have a much higher impedance than hundreds of meters of metal service pipes buried in the ground.
- The way to identify an ELCB is by looking for green or green and yellow earth wires entering the device. They rely on voltage returning to the trip via the earth wire during a fault and afford only limited protection to the installation and no personal protection at all. You should use plug in 30mA RCD’s for any appliances and extension leads that may be used outside as a minimum.
Advantages
- ELCBs have one advantage over RCDs: they are less sensitive to fault conditions, and therefore have fewer nuisance trips.
. - While voltage and current on the earth line is usually fault current from a live wire, this is not always the case, thus there are situations in which an ELCB can nuisance trip.
. - When an installation has two connections to earth, a nearby high current lightning strike will cause a voltage gradient in the soil, presenting the ELCB sense coil with enough voltage to cause it to trip.
. - If the installation’s earth rod is placed close to the earth rod of a neighboring building, a high earth leakage current in the other building can raise the local ground potential and cause a voltage difference across the two earths, again tripping the ELCB.
. - If there is an accumulated or burden of currents caused by items with lowered insulation resistance due to older equipment, or with heating elements, or rain conditions can cause the insulation resistance to lower due to moisture tracking. If there is a some mA which is equal to ELCB rating than ELCB may give nuisance Tripping.
. - If either of the earth wires become disconnected from the ELCB, it will no longer trip or the installation will often no longer be properly earthed.
. - Some ELCBs do not respond to rectified fault current. This issue is common for ELCBs and RCDs, but ELCBs are on average much older than RCB so an old ELCB is more likely to have some uncommon fault current waveform that it will not respond to.
. - Voltage-operated ELCB are the requirement for a second connection, and the possibility that any additional connection to earth on the protected system can disable the detector.
. - Nuisance tripping especially during thunderstorms.
Disadvantages
- They do not detect faults that don’t pass current through the CPC to the earth rod.
- They do not allow a single building system to be easily split into multiple sections with independent fault protection, because earthing systems are usually use common earth Rod.
- They may be tripped by external voltages from something connected to the earthing system such as metal pipes, a TN-S earth or a TN-C-S combined neutral and earth.
- As electrically leaky appliances such as some water heaters, washing machines and cookers may cause the ELCB to trip.
- ELCBs introduce additional resistance and an additional point of failure into the earthing system.
- Checking the health of the ELCB is simple and you can do it easily by pressing TEST Push Button Switch of ELCB. The test push-button will test whether the ELCB unit is working properly or not. Can we assume that If ELCB is Trip after Pressing TEST Switch of ELCB than your system is protected against earth protection? Then you are wrong.
. - The test facility provided on the home ELCB will only confirm the health of the ELCB unit, but that test does not confirm that the ELCB will trip when an electric shock hazard does occur. It is a really sad fact that all the while this misunderstanding has left many homes totally unprotected from the risk of electric shocks.
. - This brings us or alarming us to think over second basic requirement for earth protection. The second requirement for the proper operation of a home shock protection system is electrical grounding.
. - We can assume that the ELCB is the brain for the shock protection, and the grounding as the backbone. Therefore, without a functional grounding (Proper Earthing of Electrical System) there is totally no protection against electrical shocks in your house even if You have installed ELCB and its TEST switch show proper result. Looking after the ELCB alone is not enough. The electrical Earthing system must also be in good working order for the shock protection system to work. In addition to routine inspections that should be done by the qualified electrician, this grounding should preferably be inspected regularly at shorter intervals by the homeowner and need to pour Water in Earthing Pit at Regular interval of Time to minimize Earth Resistance.
Current-operated ELCB (RCB)
- Current-operated ELCBs are generally known as Residual-current devices (RCD). These also protect against earth leakage. Both circuit conductors (supply and return) are run through a sensing coil; any imbalance of the currents means the magnetic field does not perfectly cancel. The device detects the imbalance and trips the contact.
. - When the term ELCB is used it usually means a voltage-operated device. Similar devices that are current operated are called residual-current devices. However, some companies use the term ELCB to distinguish high sensitivity current operated 3 phase devices that trip in the milliamp range from traditional 3 phase ground fault devices that operate at much higher currents.

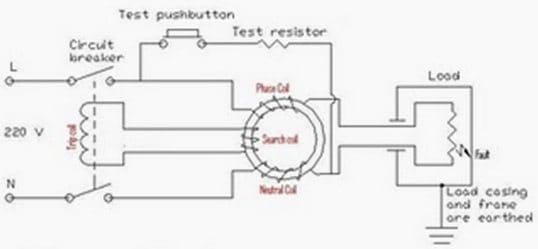
- Typical RCB circuit:

- The supply coil, the neutral coil and the search coil all wound on a common transformer core.
. - On a healthy circuit the same current passes through the phase coil, the load and return back through the neutral coil. Both the phase and the neutral coils are wound in such a way that they will produce an opposing magnetic flux. With the same current passing through both coils, their magnetic effect will cancel out under a healthy circuit condition.
. - In a situation when there is fault or a leakage to earth in the load circuit, or anywhere between the load circuit and the output connection of the RCB circuit, the current returning through the neutral coil has been reduced. Then the magnetic flux inside the transformer core is not balanced anymore. The total sum of the opposing magnetic flux is no longer zero. This net remaining flux is what we call a residual flux.
. - The periodically changing residual flux inside the transformer core crosses path with the winding of the search coil. This action produces an electromotive force (e.m.f.) across the search coil. An electromotive force is actually an alternating voltage. The induced voltage across the search coil produces a current inside the wiring of the trip circuit. It is this current that operates the trip coil of the circuit breaker. Since the trip current is driven by the residual magnetic flux (the resulting flux, the net effect between both fluxes) between the phase and the neutral coils, it is called the residual current devise.
.
- With a circuit breaker incorporated as part of the circuit, the assembled system is called residual current circuit breaker (RCCB) or residual current devise (RCD). The incoming current has to pass through the circuit breaker first before going to the phase coil. The return neutral path passes through the second circuit breaker pole. During tripping when a fault is detected, both the phase and neutral connection is isolated.
.- RCD sensitivity is expressed as the rated residual operating current, noted IΔn. Preferred values have been defined by the IEC, thus making it possible to divide RCDs into three groups according to their IΔn value.
- High sensitivity (HS): 6- 10- 30 mA (for direct-contact / life injury protection)
- Standard IEC 60755 (General requirements for residual current operated protective devices) defines three types of RCD depending on the characteristics of the fault current.
- Type AC: RCD for which tripping is ensured for residual sinusoidal alternating currents
Sensitivity of RCB:
- Medium sensitivity (MS): 100- 300- 500- 1000 mA (for fire protection)
- Low sensitivity (LS): 3- 10- 30 A (typically for protection of machine)
Types of RCB:
Type A: RCD for which tripping is ensured
- for residual sinusoidal alternating currents
- for residual pulsating direct currents
- For residual pulsating direct currents superimposed by a smooth direct current of 0.006 A, with or without phase-angle control, independent of the polarity.
Type B: RCD for which tripping is ensured
- as for type A
- for residual sinusoidal currents up to 1000 Hz
- for residual sinusoidal currents superposed by a pure direct current
- for pulsating direct currents superposed by a pure direct current
- for residual currents which may result from rectifying circuits
- three pulse star connection or six pulse bridge connection
- two pulse bridge connection line-to-line with or without phase-angle monitoring, independently of the polarity
- There are two groups of devices:
Break time of RCB:
1. G (general use) for instantaneous RCDs (i.e. without a time delay)
- Minimum break time: immediate
- Maximum break time: 200 ms for 1x IΔn, 150 ms for 2x IΔn, and 40 ms for 5x IΔn
2. S (selective) or T (time delayed) for RCDs with a short time delay (typically used in circuits containing surge suppressors)
- Minimum break time: 130 ms for 1x IΔn, 60 ms for 2x IΔn, and 50 ms for 5x IΔn
- Maximum break time: 500 ms for 1x IΔn, 200 ms for 2x IΔn, and 150 ms for 5x IΔn











we have a new rcd with 2 switch, for test monthly and leakage indication, but usually our rcd have a switch, just for test monthly, do you ever see this switch for leakage indication?
I HAVE DECORATIVE LED LIGHTING SUPPLIED THROUGH 220 V AC TO 22O V DC IN BUILD CIRCUIT AND TO BE FIXED ON METALIC GRIL .IF ANY FAULT ON DC SIDE(GROUNDING ).HOW THE FAULT IS CLEARED ? MY ELCB ON AC SIDE GETS TRIP IN THIS CASE? IS THERE ANY ALTERNATIVE PROTECTION FOR THIS?
PLEASE REPLY ME.
We can use ELCB 30mA for power supply to Gas chromatography systems ( Temperature UP and Down required in this instrument ) instrument required 10A,1500watt,220v power
It is important to stress the point that neither the ELCB or RCCB protect the circuit against overload/short circuit. That means, in any domestic wiring both MCB/MCCB ( for overload/short circuit protection) and ELCB/RCCB (for earth leakage protection) are to be used.
What I want to emphasize is ELCB/RCCB cannot be a substitute of MCB/MCCB as mains switch.
Is it good to have ELCBs in Industrial equipment like pump motors, reactor agitator’s motor, other unit equipment? or is it must to have protection device?
Please give your inputs.
At any time ELCB’s working depends external power supply and entire distribution system?
In my home place in Philippines, our Electric Cooperative is sending a drop voltage supply to each residential unit of 0-220V (Line to zero potential earth supply) two-wire system, live copper cable and cable earth guying,60hz and 1 phase.
My question is which type of breaker protection I will use or recommend having earth leakage protection and wiring sample if possible?
I switched off all mcbs in my home distribution board yet the RCD tripped without load. Please help.
What is Maximum load % use in ELCB?
i have a 3 phase control cabinet for a machine in an industrial factory. i have 3 hot legs and a ground
are there any way to hook Earth Leakage circuit breaker to protect this machine?
from the ground to each phase i have 105 volts and from phase to phase 200 volts fed from the secondary side of the transformer also it is a 60 amp circuit.
Can use ELCB for water pump?
I WANT to start manufacturing of ELCB.Can you help me.Write me your terms & condition for full technology transfer.
Hi, what should be the rating of earth leakage circuit beaker if one want to install in the home for current protection. And what will be the best criteria to select leakage circuit breaker , if your line voltage is 220V.
Regards/Kamran
Is single phase preventer required to connect in the motor feeder if ELR is already connected. ELR detects the phase imbalance even due to the single phasing. Please clarify?
hello
i want to measure leakage to ground can you help
thank you
Two high sensitivity ammeters ( multimeters or sensitive clip-on meters ) in Phase and neutral . their difference is the leakage current. Switching on one by one end device will show which is the faulty one also. But remember some machines like a submersible pump will have some leakage current though there is no danger.
Hi Sir,
I want to know the Difference between ELCB and GFCI.
GFCI works on RCD principle, both are same practically.
I have an industrial application where the equipment requires 400V. 3-Ph, 4W. So I’ll be using a 480-400V transformer, then I’ll need to run the secondary thru a Type B ELCB-current sensitive breaker to feed the machine. Am I correct by putting the breaker on the secondary side? Or should I put it on the transformer Primary? The load is 2700VA.
Better connect it on primary side as the transformer would also be protected against leakage or body shock.
Kindly Suggest a protection device against the leakage voltage in neutral
Many reasons may be behind it. Find out the reason and no need to connect any device for it. Probable reasons
1. Unbalanced load in phases
2. Broken or loose connection in neutral
3. Improper earthing of neutral point
4. Insulation failure of any one or more end
apparatus
Can you provide me the wiring diagram?FOR House wiring advatages ELCB HOW to Calculated rating for house wiring
Three phase 63Amps 4 pole30 mA ELCB can work if people touch at holder end with ground
sir,
i am working in pharma. we have a washing machine, 3phase suply. it connected to ELCB it was getting tripped when it starts.
i connected to 4 pole MCB. it is not getting tripped. the reason i can’t get nw. plz tell me the reason
Both serve different purposes. MCB and ELCB have different purposes. Leakage in your washing machine may be the problem. May be due to wet body your washing machine has a small leakage current which won’t cause any danger. Use a little more upgraded ELCB ( like 50 mA or 100 MA). Guess yours is 30mA now.
Are this system is useful for leak current while charging the laptop with ups supply .
Yes, only if the ups is properly grounded
sir, recently one of my worker tried to switch off the elcb suddenly elcb got blasted and his right arm totally burned , what is the exact reason behind this accident
could anyone elaborate on the concept of nuisance trips in TNC or TNC-S system , trying to understand exactly how an external fault from these systems can trigger a trip of the ELCB and also the issue of extraneous bonding say neighbours are connected to common water pipes which are all grounded at some point can ey also induce a trip
Eath fault implies a significant contact between phase and ground and it can cause heavy current and can cause damage; earth leakage is a high resistance contact with earth that the phase may have in cables; devices etc.; since the current is small it wont create any problem usually. However, its a sort of indication that there are insulation problems present in the cable/devices.
Earth leackage and Earth Fault relay
Nice tutorial. But I am having one question that how can we gurantee that the test switch works and makes rcd trip and this will protect us from electric shock? Because though test switch creates imbalance between currents but not via earth. And when we get electrocuted the current flows from our body to earth.
Your doubt is absolutely well informed one. No guarantee for safety on an actual shock.
What is diffrent betwin RCCB and RCD?
As i understood, MCB senses the earth leakage current to trip the MCB and it cannot sense earth to neutral shorting. My Earth leakage MCB is tripping just plugging in mixer,,,ie before switching ON. However other appliances works well in that plug point. What may be the reason.? please anybody…
Beautifully written.
My question is this – if you would have any hints.
A 24 Vdc power supply (negative grounded) works as a part of 240 Vac system empowering 2 robots. In one case Electrical Power Authority questioned this set up saying the 24 Vdc might be left floating (but not grounded). Is there any merit to this?. I always grounded the 24 Vdc to the same ground as the 240 Vac (or, for the sake, other ac voltage, – 480, 600 Vac etc.). Note also that the 24 Vdc might be a part of the safety system.
I would like to know the answer from other readers
You should not use the same earthing system. Both should be earthed seperately and maximum distance if possible.
nice article
Please let me know if an ELR with CBCT work on a 3ph,3wire system. Can an RCCB work on a circuit connected to 2 phases. No neutral in this system.
I stay in apartment consisting of 35 flats(3kws load each).The distributing panel has ELR relay for protection against leakage current.This relay has current and time settings switches.which can be put on or off as per requirement.Plse let me know the correct setting for this relay to avoid nuisance tripping.
Try from 25 mA in successive addition of mA. Whenever the system stables with wet eqpt ON, such as submersible pumps, washing machines etc. , leave it on that setting.
Sir,
(i) On what basis, the over – current and earth fault setting is set for a given load. If there is any formula . If so, please send the formula to my mail ID.
(ii) How to select the curve characteristics for the motor and transformer.
Looking for your positive reply.
dear sir i want to know how can i troubleshoot 3 phase fully automatic star delta starter.please reply..thanks in advance.
Kindly clarify the following . We have an elcb installed as the main switch in our home for current flow. When using a test lamp for finding whether the earthing is ok or not, i find the following.
1. Test lamp wires with bulb inserted in phase and neutral the lamp glows.
2. Test lamp wire with bulb inserted in phase and earth the elcb trips.
Does it mean my earthing of my home is ok or not?
Should the bulb glow in 2 case, if the earthing is okay. Please reply to my email. 09830231975
your ELCB works great
Your ELCB works good
sir,
I have a doubt about RCCB, some RCCB neutral indicate left and some have right side. Is there any difference between phase pole and neutral pole in a three phase RCCB.
Dear Sir, It was nice reading your article. However, my confusion still stands as how can a three phase ELCB be wired up in a common house electrical panel? Can you be kind to let me have a circuit showing the best possible location of 3 phase 4-wire system ELCB in the panel (house or office). With kind regards, Ansari
sir, i want to know while designing a 3-phase earth monitoring system how we can set reference voltage. you can reply me on my email.
sir, i want to know while designing a 3-phase circuit breaker how to choose the reference voltage to trip the phase if it exceeds the reference.
is there a device to control voltage incoming from neutral
Is it ok or not if the RCCB does not trip during the lightning strike? When I push the test button, the RCCB trips instantaneously. Does it show that the grounding connection is not in good condition?
RCCB is not designed to trip on lightning.
We mostly use 100ma ELCB for industrial / Commercial purpose and 30ma for domestic (Residential Wiring) to avoid nuisance Tripping .For further wiring Diagram may helpful to find solution.
Please can any body tell me why transformer is rated in “KVA” and Generating station is rated in ” Watt” ?you can answer me in email [email protected]
Can any body Please tell me how can i measure the Earth leakage current of the Lighting/Power Circuit?
Use a highly sensitive ( 3 decimal points ) to measure phase and neutral currents. Their difference is the leakage current.
I HAVE PUTTING ELCB (30MA) IN BETWEEN DOL STARTER,AND APPLICATION IS WATER AGITATOR ,5KW,BUT IT INSTANTLY TRIPPED IN ACTUAL WE CHECKED LAEAKAGE CURRENT ,IT IS .22MA SO I CAN NOT FOUND ANY REASON PLZ SUGGEST
Can you provide me the wiring diagram?
Wet equipment usually shows such. Try to install 50mA ( if OK , best ) or 100mA as the case.