
What is ANSI code for Antipumping relay?
ANSI codes 94 or even 52 can be used.
How relays are classified based on functional categories?
Relays can be divided into six functional categories shown below:
Protective relays
Detect defective lines, defective apparatus, or other dangerous or intolerable conditions. These relays generally trip one or more circuit breaker, but may also be used to sound an alarm.
Monitoring relays
Verify conditions on the power system or in the protection system. These relays include fault detectors, alarm units, channel monitoring relays, synchronism verification, and network phasing. Power system conditions that do not involve opening circuit breakers during faults can be monitored by verification relays.
Reclosing relays
Establish a closing sequence for a circuit breaker following tripping by protective relays. Regulating relays are activated when an operating parameter deviates from predetermined limits. Regulating relays function through supplementary equipment to restore the quantity to the prescribed limits.
Auxiliary relays
Operate in response to the opening or closing of the operating circuit to supplement another relay or device. These include timers, contact-multiplier relays, sealing units, isolating relays, lockout relays, closing relays, and trip relays.
Synchronizing (or synchronism check) relays
Assure that proper conditions exist for interconnecting two sections of a power system.
Many modern relays contain several varieties of these functions. In addition to these functional categories, relays may be classified by input, operating principle or structure, and performance characteristic.
The following are some of the classifications and definitions described in ANSI/IEEE Standard C37.90 (also ANSI/IEEE C37.100 “Definitions for Power Switchgear”):
Current
Voltage
Power
Pressure
Frequency
Temperature
Flow
Vibration
Operating Principle or Structures
Current balance
Percentage
Multirestraint
Product
Solid state
Static
Microprocessor
Electromechanical
Thermal
Differential
Distance
Directional over current
Inverse time
Definite time
Under voltage
Over voltage
Ground or phase
High or low speed
Pilot
Phase comparison
Directional comparison
Current differential
Solid-state (and static) relays are further categorized under one of the following designations:
Analog
Analog relays are those in which the measured quantities are converted into lower voltage but similar signals, which are then combined or compared directly to reference values in level detectors to produce the desired output (e.g., SA-1 SOQ, SI-T, LCB, circuit shield relays).
Digital
Digital relays are those in which the measured ac quantities are manipulated in analog form and subsequently converted into square-wave (binary) voltages. Logic circuits or microprocessors compare the phase relationships of the square waves to make a trip decision.
Numerical
Numerical relays are those in which the measured ac quantities are sequentially sampled and converted into numeric data form. A microprocessor performs mathematical and/or logical operations on the data to make trip decisions.
How do we classify an Antipumping relay?
It is classified as an auxiliary relay.
Why Antipumping relay is used?
Anti pumping relaying is done primarily to indicate the spring failure of TNC switch and a person need to attend the problem. The function of this relay is to cut off the supply to 52C (CB closing coil) in case of TNC switch spring failure and prevent CB hunting effect (i.e. continuous closing, opening operation).
Anti pumping is also called trip free mechanism of any circuit breaker. Suppose the breaker has been instructed to close by manual instruction by pressing the TNC (trip neutral close push button) switch. The operating mechanism will start operating for closing operation.
Meanwhile a fault has taken place and relay closes the trip circuit of breaker. The trip free mechanism/ Anti pumping feature permits the circuit breaker to be tripped by protective relay even if it is under process of closing. Thus auxiliary relay (or sometimes the inbuilt feature of circuit breaker) which prevent alternate tripping and closing of the circuit breaker if closing push button is held close during fault is called the trip free mechanism or anti pumping mechanism.
What will happen if Antipumping relay circuit is not present?
If the circuit breaker is closed using TNC switch, and at the same instant let spring of TNC switch has failed and it did not came to its neutral state, and primary protection relay had been operated at this instant and opened the CB, since supply is being extended to 52C (CB closing coil) because of TNC spring failure, then CB will close again, since fault is still persisting the following cycle occurs.
CB trip, because of protection. Operation -> CB close, because of TNC switch spring failure-> CB trip, because of protection. Operation-> CB close, because of TNC switch spring failure-> CB trip, because of protection. Operation -> CB close, because of TNC switch spring.
The above cycle is termed as circuit breaker hunting. Circuit breaker hunting will cause damage to breaker and it can be avoided by using 52 (Circuit breaker Antipumping relay).The function of this relay is to cut off the supply to 52C (CB closing coil) coil in case of TNC switch spring failure and prevent CB hunting effect (i.e. continuous closing, opening operation).
Let us analyse the behavior of circuit in case anti pumping is present and in case it is not present, one by one:
CASE 1: Closing Coil Circuit Without 52 Relay
The path for CB close with out 52 relay is shown in Figure 1. In this case if spring of TNC switch fails, then supply will be get extended to 52C (CB closing coil) coil as shown in Figure 2.
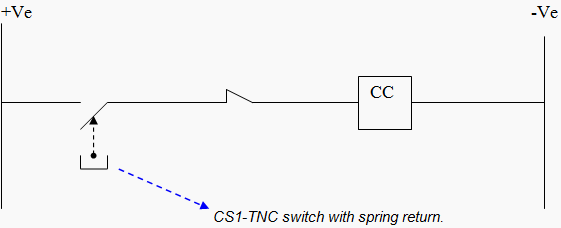
If the TNC switch spring has failed then supply will be extended as shown below.
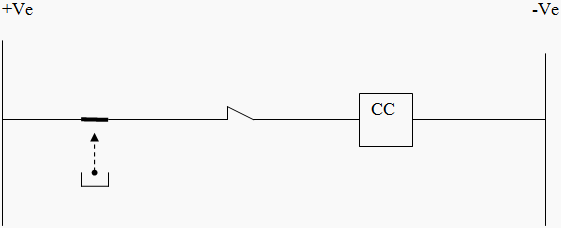
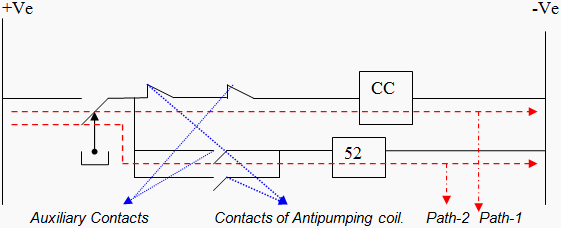
CASE 2: Closing Coil Circuit With 52 Relay
Closing coil circuit with 52 present is as shown in Figure 3. Path 1 in Figure 3 shows how 52C (CB closing coil) will be energized when we press TNC switch CS1.if CS1 comes to its original state once we release it then 52 will not come in picture. if CS1 does not comes to its original state then 52 will be energized as shown in path 2.then 52-NC contact present in path 1 will be got opened up and prevents extension of supply.
We have the concept that initially for the energization of 52 80% to 90% of 110V is required. But once after energization 60-70% of 110V is sufficient to maintain its energization state. This logic is achieved by introducing a resistance in 52 energization maintenance path. This path is shown in Figure 4.
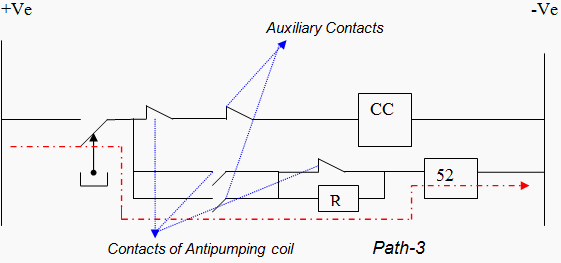
Once 52 is energized it will give an alarm and a maintenance person in the substation need to attend that problem. This is how 52 is useful in avoiding CB hunting effect.
What is ANSI code for Master trip lockout relay?
ANSI code 86 is used.
What is function & Utility of lockout relay?
When a ‘‘drive-to-lockout’’ input is energized, the reclosing relay will go into lockout from any point in the sequence. The relay will stay in lockout until the input is removed and the breaker is closed manually or by supervisory control. Upon removal, the recloser will go through its reset sequence and return to ‘‘ready’ state.
All the different trip signals from fault detection devices are wired to the lockout relay, which is the master trip relay for the circuit breaker. It is usually a manually reset relay with an indicating flag or lamp. In case of DG a similar philosophy of tripping is used in the engine control panel in which all the mechanical failure signals are received at the engine lockout relay (86-T, T for turbine). This lockout relay also trips the generator circuit breaker.
When either the 86-G or the 86-T relay sends its signal to the circuit-breaker trip coil, time is taken before the circuit breaker begins to move and finally reach its fully open state. The generator switchgear is recommended to have two separate lockout relays. One will receive all the electrical protection relay trip signals, and denoted as 86–1. The other will receive a master trip signal (or several trip signals) from the turbine unit control panel, and denoted as 86–2.
It operates whenever any of the protection relay operates and would prevent any circuit breaker operation until the lock out relay is manually rest.
Can we manage without anti pumping since operation of lock out relay would prevent any further operations of CB even continuous opening-closing?
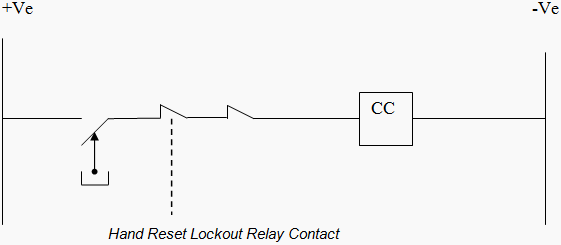
Let us assume that we have closed the circuit breaker using the TNC switch CS1.At this instant TNC switch spring failed and fault is there which is sensed by primary protection relay and sends tripping command to circuit breaker. This would energize the trip coil of breaker; this will result in operation of lock out relay.
The lock out relay will go into lock out state as shown in Figure 6 below:
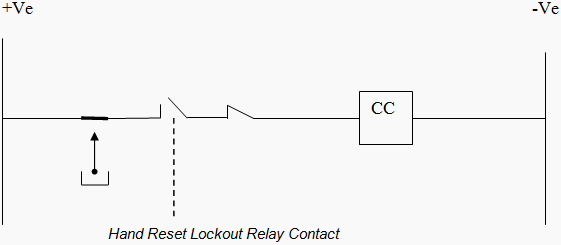
Now let a person had attended that fault and resetted 86 lockout contacts. After resetting its status will be NC and a closed command will be extended to closing coil without any human interface which is a mal function.
The function of anti pumping relay is to cut off the supply to closing coil in case of TNC switch spring failure and prevent CB hunting effect (i.e. continuous closing, opening operation) and a person needs to attend the problem. Where as 86 lock out relay contact in closing circuit is meant to ensure that a person had attended the fault occurred and we are closing the circuit after clearing the circuit.
It is extra mechanical protection meant for safety of equipments considering the cost and sophistication involved; it is always advisable to go for extra human interface.
REFERENCES:
1. ANSI/IEEE C37.100 ‘‘Definitions for Power Switchgear”.
2. Relay And Circuit-Breaker Application Authors: E. L. Harder and J. C. Cunningham.
3. Protection Application Handbook: ABB, Transmission Systems and Substations.
4. http://www.electrotechnik.net/2009/06/what-is-anti-pumping-relay.html











Thanks sir your notes on anti pumping device ,
Sir i want gain knowlege of protection system,
How i achive this plz help me.
I am electrical engg having 4 years of site experiance.
Dear Sir,
Kindly send to me quotation as soon as possible it will be closing date 07-11-2017. I will be waiting for kind response.
RELAY,ANTI-PUMPING:
CONTACT RATING:
125 VDC;
CONTACT ARRANGEMENT:
1NO1NC;
CONTACT:
SILVER PLATED;
ACTION:
1P2T;
COIL VOLTAGE:
125 VDC;
TERMINAL:
(3) SCREW TERMINAL;
MOUNT:
SURFACE;
ENCLOSURE:
GENERAL PURPOSE;
STANDARD/SPECIFICATION:
IEC 6094;
ADDITIONAL DATA:
FIG NO: 7, REF NO: 11 AND MANUAL NO: GE
K-39634.
TYPE: CLOSING CUTOFF AND ANTI-PUMP
GENERAL ELECTRIC/DIELEKTROL/LENTRONICS:
P/N#0103A1438P051
Qty-01
Thanks & best regards;
——————————-
Abdul Rahman Khaliq
Tel #. +966 12 605 6565 Ext.109
Fax #. +966 12 605 6767
Mob #. +966 58 367 7743
sales2@almdarij.com
Al Mdarij International Marketing Co.(MIMCO)
Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
MIMCO provide Repair & Maintenance service for all industrial electronic and electrical equipment.
please consid
But Asif Eqbal, what about auxiliary NC contact present in series with CC. Will it in close position or open position? when a moment breaker trips.
Really good information thank you Asif sir.. In all other portal they only tell about function in just two or three words without any pratical example…but here the explanation present with example so easy to understand.
Does anti pumping carried out only during spring failure. Means it only activate when tnc spring get fail otherwise not.
How does closing command be in process after cb contacts get closed.
Great information very thanks to the admin and the people who are sharing such a great information to us
Thanks a lot
Information is quite useful . Thank You.
Good works
Nice one. Thanks asif.
hi,
I would like learn the detaile and basic engineeering of High voltage equipment.
Can you sugest me best possible way.
Im electrical engineer and having 8 year of experience on site and factory for ehev substation.
In Figure No.3, I didn’t understand-
(1) how the 52 relay coil energized which is having NO contact of Auxiliary (of what???) and
(2) if it is being energized due to CS1 failure/permanent NC due to spring failure then while pressing the TNC for closing, why 52 will not get energized?
Regards,
T.D.
Dear Mr T.D, Your first question is auxiliary contact of what in fig-3? Well it is auxiliary contact of breakers main contact. Your second question is about its operation in anti pumping circuit. If you go through the internal schematic drawing of any ABB or equivalent reputed make CB than you will find that main contact always have mechanically latched switches whose contacts are used in anti pumping circuitry. They are mechanically latched and moment breaker trips that is main contact separate than auxiliary contacts in anti pumping circuit closes to energize anti pumping relay and consequently NC contact of anti pumping opens in closing circuit. I hope this answers the query raised.
Regards