
ANSI/IEEE C62.41
Three different surge protective classes or zones have been defined by ANSI/IEEE C62.41, Recommended Practice on Surge Voltages in Low Voltage Power Circuits.
These classes are illustrated in the pictorial diagram Fig. 12-1.
Category C (outdoors)
Category C (outdoors) is the region outside the home or building that includes external conductors, and it extends inside to the load center main circuit breaker or service entrance disconnect breaker.
It is expected that surges originating outside the building could enter it by way of the service drop from the pole to the building through the watthour meter busbars to the circuit breakers, as well as from other overhead and underground conductors.
Examples of these include lightning strikes on or near power lines and surges set up by the switching or failure of power company generators or other equipment. Both of these sources cause energy surges to be coupled into the building by induction. Consequently, the best surge protection is afforded by surge protective devices (SPDs), sized to withstand high-magnitude surges, that are installed ahead of service entrance disconnect circuit breakers.
Category B (indoors)
Category B (indoors) is a zone within a residence or building that extends at least 30 ft (10 m) from the service entrance disconnect breaker along feeders or branch circuits to electrical receptacles or outlets.
As stated previously, the most probable sources of surges within this zone are the on/off switching of electric motors or motordriven appliances. Other sources are high-voltage or high-frequency medical and scientific apparatus located close to the structure being protected.
Consequently, all SPDs installed in the B zone should be sized to withstand the largest-magnitude surges expected from all of these sources.
Category A (indoors)
Category A (indoors) is the zone farthest from the disconnect breaker.
It is defined as the zone within the building where the branch circuits extend to all outlets that are more than 30 ft (10 m) from Category B outlets, and more than 60 ft (20 m) from the service entrance disconnect breaker located in the Category C zone.
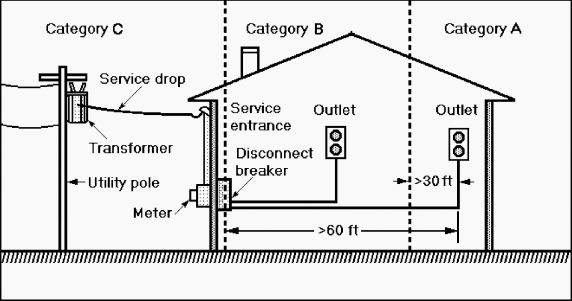
Category C: Outside and service entrances (line side)
- Service drops from pole to building
- Conducted between meter and disconnect breaker
- Overhead lines to nearby buildings
Category B: Feeders and short branch circuits (line side)
- Distribution panel equipment
- Short branch circuits and feeder lines
Category A: Branch circuits and outlets distant from Categories B and C
- Outlets > 30 ft (10 m) from Category B boundary
- Outlets > 60 ft (20 m) from Category C boundary
Exposure levels
ANSI/IEEE C62.41 defines the three exposure levels that characterize the rate of surge occurrence versus voltage level at an unprotected site as follows:
Low
Geographic locations where lightning activity is known to be low, and little load switching is anticipated.
Medium
Geographic locations where medium to high lightning activity is expected, significant load switching is anticipated, or both.
High
Geographic locations where surges greater than those defined as low or medium are expected.
Reference: Handbook of electrical design details // Second edition – Neil Sclater; John E. Traister
(Purchase ebook)











Keen to have more storey on power quality equipment’s & speciality transformers
MOV selection calculation for over voltage protection in house.