Course Description
This course is designed to allow you to simulate any power electronics device in MATLAB/Simulink, including rectifiers, DC-to-DC converters, and inverters. This course not only gives a review of the theory of how rectifiers, DC-to-DC converters, and inverters work but also gives several examples of how to simulate these devices using MATLAB/Simulink.
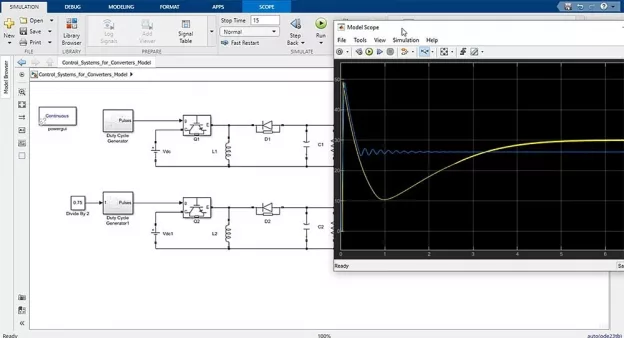
The MATLAB/Simulink models for the power electronics devices created during the lectures are available for download with each lecture.
The course is divided into the following sections:
1. Introduction to MATLAB/Simulink for Power Electronics
In the first section, we will begin by reviewing the theory behind the semiconductor devices that are used in power electronics, such as diodes, power BJTs, power MOSFETs, IGBTs, and Thyristors. We will then take a look at the libraries available in Simulink to represent these devices in our models. We will learn how to model voltage sources, current sources, and passive components (resistors, capacitors, and inductors), as well as how we can put them all together in a model using Simulink. We’ll also learn how to take measurements in the model to ensure proper simulation.
2. Rectifier Simulations in MATLAB/Simulink
The second section will start with reviewing the theory behind the operation and topologies of power electronics rectifiers. We will then see how we can simulate both single-phase and three-phase rectifiers using Simulink.
3. DC-to-DC Converter Simulations in MATLAB/Simulink
We will begin section 3 by reviewing the theory behind the operation and topologies of power electronics DC-to-DC converters. We will learn how to simulate buck, boost, and buck/boost converters.
4. Inverter Simulations in MATLAB/Simulink
The fourth section will start with reviewing the theory behind the operation and topologies of inverters. We will then see how we can simulate single-phase and three-phase inverters.
By learning how to simulate power electronics devices in MATLAB/Simulink, you will be able to further your career in electrical engineering and power electronics.
Course Summary
- How to simulate power electronics devices in MATLAB/Simulink
- Simulation of buck, boost, and buck/boost converters in MATLAB/Simulink
- How rectifiers, dc-to-dc converters, and inverters work
- How to design power electronics devices to meet certain design specifications
- How to implement a PID controller in MATLAB/Simulink
- Simulation of half-wave and full-wave rectifiers in MATLAB/Simulink
- Simulation of single-phase and three-phase inverters in MATLAB/Simulink
- How to determine the performance of power electronics devices
- MATLAB/Simulink models provided so you can follow along and use for your own designs
- Power Engineering and Electrical Engineering Simulations in MATLAB/Simulink
Who Is This Course For
- Engineering students
- Practicing engineers
- Anybody with an interest in learning about power electronics and/or MATLAB/Simulink
Requirements
- MATLAB/Simulink software, free trial available online
Downloadable course materials
After purchasing the course, students can download the following Simulink models:
- Boost Converter Model - Section 4 (zip)
- Buck-Boost Converter Model - Section 4 (zip)
- Buck Converter Model - Section 4 (zip)
- Control Systems for Converters Model - Section 4 (zip)
- Duty Cycle Model - Section 4 (zip)
- Inverter Pulses Single-Phase - Section 5 (zip)
- Inverter Pulses Three-Phase - Section 5 (zip)
- Sample Simulink Model - Section 2 (zip)
- Simulink Converters Model - Section 4 (zip)
- Single-Phase Full-Wave Rectifier Model - Section 3 (zip)
- Single-Phase Half-Wave Rectifier Model - Section 3 (zip)
- Single-Phase-Inverter-Model - Section 5 (zip)
- Three-Phase Full-Wave Rectifier Model - Section 3 (zip)
- Three-Phase Half-Wave Rectifier Model - Section 3 (zip)
- Three-Phase Inverter Model - S05 (zip)
- Universal Bridge Rectifier Model - S03 (zip)
Course Content
About Instructor