
What’s a Kilowatt?
When you use electricity to power a 1000-watt vacuum for 1 hour, you use 1,000 watt-hours (1,000 Wh) of electricity! One thousand watt-hours equals 1 kWh. Your utility bill usually shows what you are charged for the kilowatt-hours you use. The average residential rate is 11.88 cents/kWh.
For example, your heating system is not just a furnace – it’s a heat-delivery system that starts at the furnace and delivers heat throughout your home using a network of ducts.
Even a top-of-the-line, energy-efficient furnace will waste a lot of fuel if the ducts, walls, attic, windows, and doors are leaky or poorly insulated. Taking a whole-house approach to saving energy ensures that dollars you invest to save energy are spent wisely.
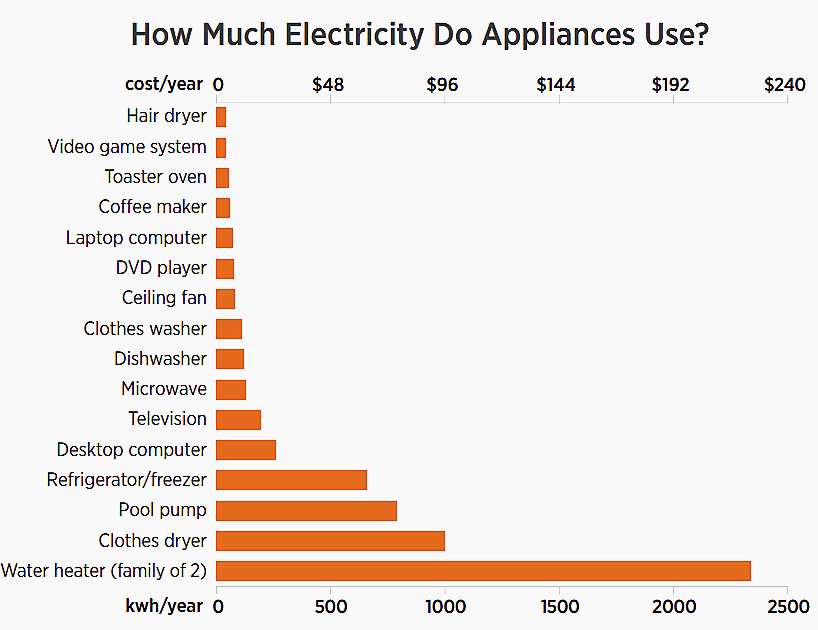
This chart shows how much energy a typical appliance uses per year and its corresponding cost based on national averages. For example, a refrigerator/freezer uses almost five times the electricity the average television uses.
Home energy assessment
A home energy assessment (sometimes referred to as an energy audit) will show what parts of your house use the most energy and suggest the best ways to cut energy costs. You can conduct a simple home energy assessment by doing it yourself (DIY) or, for a more detailed assessment, contact your local utility or an energy auditor.
Also, you can learn more about home energy audits and find free tools and calculators on energysaver.gov, the Residential Services Network at resnet.us, or the Building Performance Institute at bpi.org.
| Title: | Energy Saver Guide – The Real Tips on Saving Money and Energy at Home – U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 2.30 MB |
| Pages: | 44 |
| Download: | Right here | Video Courses | Membership | Download Updates |



The design is exquisite and the article is very informative. Thank you so much.
I guess this article is not at all applicable to us.