Abstract
Current transformers or CTs take up a lot of space in HV cubicles. Through knowledge of how they work makes it possible to:
- Reduce their dimensions and thus their cost,
- Use standard CTs in a larger number of configurations.
The purpose of this study is to learn more about CT operation in association with protection relays and to lay down a few rules for sizing them properly. After a brief theoretical review of CT operation and current protection devices, the behaviour of the CTprotection relay combination is studied in two particularly important cases
in HV:
- overcurrent relay supplied by a heavily saturated CT,
- protection relay connected to two CTs in parallel in duplex cubicles.
This study is completed by experimental results.
Theoretical Review
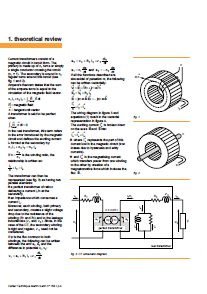
Current transformers consist of a magnetic circuit in toroid form. The primary is made up of n1 turns or simply a single conductor crossing the toroid (n1 = 1). The secondary is wound in n2 regular turns around this toroid (see fig. 1 and 2).
Ampere’s theorem states that the sum of the ampere-turns is equal to the circulation of the magnetic field vector.
AUTHOR: Schneider Electric expert | Michel ORLHAC
| Title: | Current transformers for HV protection |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 0.3MB |
| Pages: | 20 |
| Download: | Right here | Video Courses | Membership | Download Updates |


perfect