Cross-linking effect
XLPE is the recognized abbreviation for cross-linked polyethylene. This and other cross-linked synthetic materials, of which EPR (ethylene propylene rubber) is a notable example, are being increasingly used as cable insulants for a wide range of voltages.
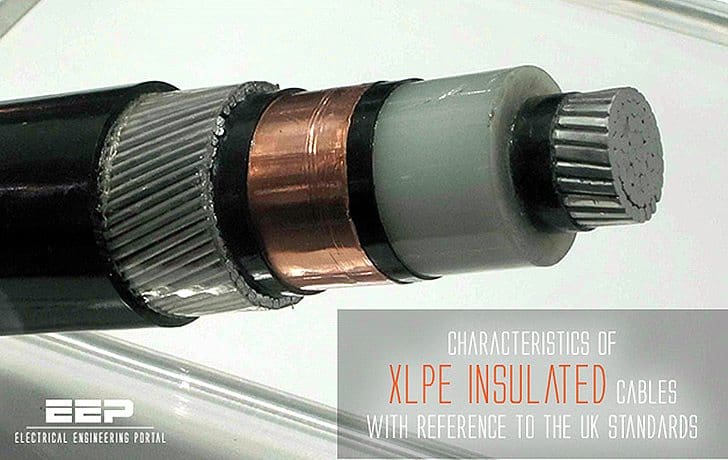
Polyethylene has good electrical properties and in particular a low dielectric loss factor, which gives it potential for use at much higher voltages than PVC. Polyethylene has been and still is used as a cable insulant, but, as a thermoplastic material, its applications are limited by thermal constraints.
The effect of the cross-linking is to inhibit the movement of molecules with respect to each other under the stimulation of heat and this gives the improved stability at elevated temperatures compared with the thermoplastic materials. This permits higher operating temperatures, both for normal loading and under short-circuit conditions, so that an XLPE cable has a higher current rating than its equivalent PVC counterpart.
The effects of ageing, accelerated by increased temperature, also have to be taken into account, but in this respect also XLPE has favourable characteristics.
BS 5467 specifies construction and requirements for XLPE and EPR-insulated wire-armoured cables for voltages up to 3.3kV. The construction is basically similar to that of PVC cables to BS 6346, except for the difference in insulant. Because of the increased toughness of XLPE the thicknesses of insulation are slightly reduced compared with PVC.

The standard also covers cables with HEPR (hard ethylene propylene rubber) insulation, but XLPE is the material most commonly used. From 3.8kV up to 33kV, XLPE and EPR insulated cables are covered by BS 6622 which specifies construction, dimensions and requirements.
To this end XLPE cables for 6.6 kV and above have semiconducting screens over the conductor and over each insulated core. The conductor screen is a thin layer extruded in the same operation as the insulation and cross-linked with it so that the two components are closely bonded. The screen over the core may be a similar extruded layer or a layer of semiconducting paint with a semiconducting tape applied over it.
Single-core and three-core designs are employed, and there is scope for constructional variation depending on the conditions of use, subject to the cores being surrounded individually or as a three-core assembly by a metallic layer, which may be an armour, sheath or copper wires or tapes.
A typical armoured construction which has been supplied in substantial quantities is shown in Figure 1 below.
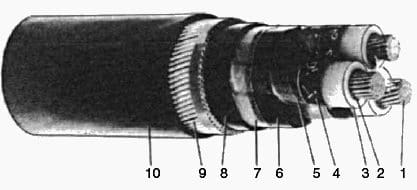
Where:
- Circular stranded conductor
- Semiconductor XLPE screen
- XLPE insulation
- Semiconducting tape screen
- Copper tape screen
- PVC filler
- Binder
- Extruded PVC sheath
- Galvanized steel wire armour 10. Extruded PVC oversheath
In the UK this type of cable, mainly in single-core form, is favoured for power station cabling, where lightness and convenience of terminating are major considerations. Three-core designs are also used for site supplies.

For underground distribution at 11kV, the XLPE cable does not compete economically with the paper-insulated aluminium-sheathed cable, but work is in progress on standardizing and assessing XLPE cable design, including trial installations, in preparation for any change in the situation. Overseas, where circumstances are different, XLPE cable is the type in major demand.
With manufacturing facilities increasingly orientated to this market, XLPE insulated cables constitute a large proportion of UK production.
Cold Shrink Cable Joint – XLPE Single Core High Voltage Cable
Reference: Newnes Electrical Pocket Book – E.A. Reeves DFH(Hons), CEng, MIEE Martin J. Heathcote BEng, CEng, FIEE










What is the minimum PVC bedding thickness for a three core 11kV LV cable?
When XLPF cable is used in place of old style oil filled for 138kV line are there significant changes in the radiation field? If so, are there any shielding suggestions?
Can XLPE Cables suffer insulation failure due to extreme hot temperature?
i want to know about best technology/ practices in U.G HIGH VOLTAGE (33KV) CABLE LAYING /PULLING
IN HDPE/PVC CONUIT DUCT BANKS including MANHOLE/VAULT DESIGN
I will like to have your material on characteristics of XLPE cables.
what equipment can used to cutoff the xlpe cable.. because i only want xlpe insulation in that cable to perform breakdown test.. tq
I’m Roxie from Hebei Fangyuan Instrument & Equipment Co.,Ltd,we produce cable test machine,XLPE cable insulation cutting machine,cable slicing and chipping machine,pls feel free to contat me.
Mob:0086-13931911354
Email:[email protected]
I am very much interested for manufacturing xlpe cables in my factory. Pl help me.
I can help you.Pls contact me.
Skype:roxiezhang
Email:[email protected]
Mobile:0086-13931911354
Please advice if the earth cable 150 sq.mm connected between the MDB to SMB can be spliced .
Thank for your prompt reply.
I am very interested in designing electrical substation